Characteristics of Noninstitutionalized DI and SSI Program Participants, 2010 Update
Research and Statistics Note No. 2014-02 (released February 2014)
Michelle Stegman Bailey and Jeffrey Hemmeter are economists with the Office of Program Development, Office of Research, Demonstration, and Employment Support, Office of Retirement and Disability Policy, Social Security Administration.
Acknowledgments: The authors thank David Weaver, Susan Wilschke, Susan Kalasunas, Paul Davies, Michael Stephens, Jim Twist, and Joyce Nicholas for their valuable suggestions and comments, and Thuy Ho and Jim Fahlfeder for their assistance with the data.
The findings and conclusions presented in this note are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Social Security Administration.
Introduction
| DI | Disability Insurance |
| SIPP | Survey of Income and Program Participation |
| SNAP | Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program |
| SSA | Social Security Administration |
| SSI | Supplemental Security Income |
The Social Security Administration (SSA) produces several statistical publications based on the data used to administer the Disability Insurance (DI) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI) programs. Although these data are extensive, they do not capture many of the economic and demographic characteristics of program participants. To better understand those beneficiary populations, SSA matches information from its administrative records with data collected by the Census Bureau in the Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP). DeCesaro and Hemmeter (2008) contains tables describing the characteristics of DI and SSI program participants based on 2002 data. This note updates those tables with data for 2010.
Data
The SIPP is a household survey of the noninstitutionalized resident population of the United States. The survey broadly measures the economic situations of households, paying particular attention to the role of government transfer and service programs. Within a given SIPP wave, each participating household is tracked for several years and is interviewed every 4 months.1 In addition to the core questions about income and program participation, each interview includes questions from a rotating module on a topic such as marital history or education.
Although the previous iteration of this analysis included a special sample of known DI beneficiaries and SSI recipients, such a sample was not interviewed in the 2008 SIPP, which provided the data for this note. Thus, the estimates presented here are based on smaller samples of DI beneficiaries and SSI recipients included in the public-use SIPP data file. Additionally, the definitions of some of the characteristics differ from those used in the previous work. Those changes were necessary to avoid disclosing information about individual sample members.
To improve the quality of the data, SIPP results are matched to Social Security administrative records based on the respondent's validated Social Security number. For individuals with valid numbers, we use the administrative records to determine whether they received DI benefits or SSI payments and, if so, the amounts received. For individuals who did not provide a valid Social Security number, we use self-reported values from the SIPP. We identify individuals as DI beneficiaries and SSI recipients if they received a payment in December 2010.2 Consistent with the prior edition of this study, we define SSI receipt only in terms of federal payments; that is, we do not include state SSI supplements (even those that are federally administered) in our definition. In tabulations of SSI recipients' Medicaid coverage, we recode the SIPP Medicaid variable to reflect the automatic Medicaid coverage of SSI recipients in certain states under Section 1634 of the Social Security Act.
We weight the SIPP results using December 2010 Social Security administrative data adjusted for institutional status.3 We use data for September, October, November, and December 2010 to measure income and poverty. Those months span waves 7 and 8 of the 2008 SIPP. All demographic characteristics other than income and SSI and DI benefit amounts are based on SIPP data for December 2010.
Discussion of the Estimates
This section highlights selected estimates from the tables and charts.
DI Beneficiaries
DI beneficiaries in this sample comprise disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children. Because 89 percent of the beneficiaries in this sample were disabled workers, the tables present information separately for that subgroup, although we do not discuss those results in the text. For convenience and consistency with other publications, we refer to all these groups as DI beneficiaries regardless of whether their benefits are paid from the Disability Insurance or the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund and as long as their eligibility is based on disability.4
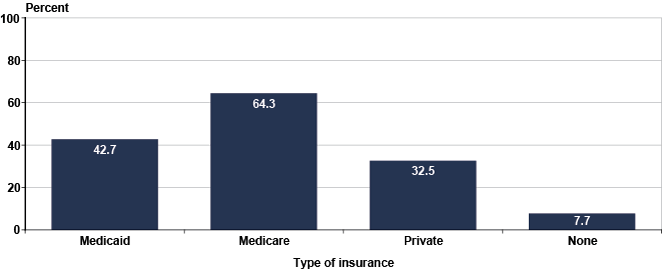
Although DI beneficiaries are eligible for Medicare, coverage does not begin until 24 months after the first month of benefit receipt. In December 2010, 64 percent of DI beneficiaries reported Medicare coverage (alone or in combination with other coverage), 43 percent reported Medicaid coverage, and 33 percent had private health insurance (Chart 1). Nearly one-quarter of beneficiaries held joint Medicare and Medicaid coverage and a similar proportion had only Medicare coverage (Table 1). About 8 percent of DI beneficiaries in the sample reported having no health insurance.
DI beneficiaries, by type of health insurance coverage, December 2010 (in percent)
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All disabled beneficiaries | Disabled workers | All disabled beneficiaries | Disabled workers | |
| All beneficiaries | 8,993,173 | 8,031,344 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 4,613,671 | 4,155,490 | 51.3 | 51.7 |
| Women | 4,379,502 | 3,875,854 | 48.7 | 48.3 |
| Race | ||||
| White | 6,732,147 | 5,951,064 | 74.9 | 74.1 |
| Black | 1,801,612 | 1,658,014 | 20.0 | 20.6 |
| Other | 459,414 | 422,266 | 5.1 | 5.3 |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Hispanic | 961,876 | 888,398 | 10.7 | 11.1 |
| Non-Hispanic | 8,031,297 | 7,142,946 | 89.3 | 88.9 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 3,472,334 | 3,432,746 | 38.6 | 42.7 |
| Widowed | 705,296 | 501,970 | 7.8 | 6.3 |
| Divorced or separated | 2,291,473 | 2,240,468 | 25.5 | 27.9 |
| Never married | 2,524,070 | 1,856,160 | 28.1 | 23.1 |
| Years of education | ||||
| 0–11 | 1,519,369 | 1,254,822 | 16.9 | 15.6 |
| 12 | 3,449,413 | 2,914,750 | 38.4 | 36.3 |
| 13–15 | 2,511,658 | 2,411,218 | 27.9 | 30.0 |
| 16 or more | 1,512,733 | 1,450,554 | 16.8 | 18.1 |
| Health insurance | ||||
| Medicaid only | 1,267,596 | 1,080,531 | 14.1 | 13.5 |
| Medicare only | 2,002,125 | 1,828,470 | 22.3 | 22.8 |
| Private only | 1,040,313 | 994,086 | 11.6 | 12.4 |
| Medicaid and Medicare | 2,120,409 | 1,737,020 | 23.6 | 21.6 |
| Medicaid and private | 223,931 | 214,141 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
| Medicare and private | 1,426,962 | 1,329,801 | 15.9 | 16.6 |
| Medicaid, Medicare, and private | 222,292 | 190,264 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
| None | 689,545 | 657,031 | 7.7 | 8.2 |
| Source of income a | ||||
| Public assistance | ||||
| SSI | 1,770,455 | 1,469,973 | 19.7 | 18.3 |
| Other b | 2,911,810 | 2,534,996 | 32.4 | 31.6 |
| Earnings | 979,632 | 813,472 | 10.9 | 10.1 |
| Property income | 2,767,635 | 2,576,508 | 30.8 | 32.1 |
| Other income | 2,603,976 | 2,424,101 | 29.0 | 30.2 |
| Veteran status | ||||
| Veteran | 1,034,102 | 1,012,043 | 11.5 | 12.6 |
| Nonveteran | 7,959,071 | 7,019,301 | 88.5 | 87.4 |
| Total 4-month personal income c ($) | ||||
| Less than 1,500 | 64,276 | 51,120 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 1,500–1,999 | 112,071 | 89,209 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| 2,000–2,499 | 159,042 | 126,605 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| 2,500–2,999 | 1,268,725 | 1,088,653 | 14.1 | 13.6 |
| 3,000–3,499 | 964,634 | 832,578 | 10.7 | 10.4 |
| 3,500–3,999 | 912,619 | 780,486 | 10.1 | 9.7 |
| 4,000–4,499 | 881,662 | 744,647 | 9.8 | 9.3 |
| 4,500–4,999 | 601,835 | 547,683 | 6.7 | 6.8 |
| 5,000 or more | 4,028,309 | 3,770,364 | 44.8 | 46.9 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
||||
| a. Individuals may be counted in more than one category. | ||||
| b. Includes state SSI supplementation, Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, General Assistance, food assistance (including food stamps and the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), clothing assistance, short-term assistance, transportation assistance, and other welfare. | ||||
| c. September–December 2010. | ||||
Many of those who reported Medicaid coverage were likely to be among the 20 percent of disabled beneficiaries who also received SSI payments. Other forms of income included earnings (received by 11 percent of DI beneficiaries), property income from all assets (received by 31 percent), and other public assistance (received by 32 percent).
The majority of DI beneficiaries had 4-month personal income below $5,000 (Table 1). DI benefits were an important income source, constituting 75–100 percent of personal income for more than one-half of DI beneficiaries (Table 2).
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | Percentage distribution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Under 50% of income | 50–74% of income | 75–99% of income | 100% of income | |||
| All disabled beneficiaries | |||||||
| Total | 8,993,173 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 20.7 | 27.8 | 31.0 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 4,613,671 | 51.3 | 100.0 | 20.8 | 19.9 | 26.2 | 33.1 |
| Women | 4,379,502 | 48.7 | 100.0 | 20.2 | 21.5 | 29.6 | 28.7 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 1,354,823 | 15.1 | 100.0 | 30.0 | 24.5 | 23.9 | 21.6 |
| 40–49 | 1,622,598 | 18.0 | 100.0 | 16.5 | 17.9 | 26.4 | 39.2 |
| 50–59 | 3,335,921 | 37.1 | 100.0 | 17.2 | 18.6 | 28.5 | 35.7 |
| 60 or older | 2,679,831 | 29.8 | 100.0 | 22.2 | 23.1 | 29.9 | 24.9 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 6,732,147 | 74.9 | 100.0 | 19.0 | 20.1 | 28.3 | 32.7 |
| Black | 1,801,612 | 20.0 | 100.0 | 24.9 | 23.4 | 24.8 | 26.9 |
| Other | 459,414 | 5.1 | 100.0 | 25.7 | 19.4 | 33.3 | 21.7 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 961,876 | 10.7 | 100.0 | 20.9 | 14.1 | 27.9 | 37.1 |
| Non-Hispanic | 8,031,297 | 89.3 | 100.0 | 20.4 | 21.5 | 27.8 | 30.2 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 3,472,334 | 38.6 | 100.0 | 19.2 | 18.6 | 28.5 | 33.7 |
| Widowed | 705,296 | 7.8 | 100.0 | 15.6 | 36.0 | 24.5 | 23.9 |
| Divorced or separated | 2,291,473 | 25.5 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 28.1 | 30.9 |
| Never married | 2,524,070 | 28.1 | 100.0 | 23.6 | 19.5 | 27.6 | 29.2 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 1,519,369 | 16.9 | 100.0 | 19.5 | 17.1 | 29.1 | 34.3 |
| 12 | 3,449,413 | 38.4 | 100.0 | 19.7 | 21.9 | 28.7 | 29.8 |
| 13–15 | 2,511,658 | 27.9 | 100.0 | 20.1 | 20.2 | 27.1 | 32.7 |
| 16 or more | 1,512,733 | 16.8 | 100.0 | 24.1 | 22.4 | 26.0 | 27.5 |
| Living arrangement | |||||||
| Lives alone | 2,433,990 | 27.1 | 100.0 | 19.2 | 20.3 | 30.8 | 29.6 |
| Lives with relatives | 5,989,639 | 66.6 | 100.0 | 21.6 | 20.2 | 26.6 | 31.6 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 569,543 | 6.3 | 100.0 | 14.3 | 27.9 | 28.0 | 29.8 |
| Disabled workers | |||||||
| Total | 8,031,344 | 89.3 | 100.0 | 20.6 | 20.2 | 28.1 | 31.2 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 4,155,490 | 46.2 | 100.0 | 20.7 | 19.6 | 26.4 | 33.3 |
| Women | 3,875,854 | 43.1 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 20.8 | 29.8 | 28.8 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 966,097 | 10.7 | 100.0 | 31.0 | 24.8 | 24.5 | 19.7 |
| 40–49 | 1,515,879 | 16.9 | 100.0 | 17.1 | 17.8 | 26.4 | 38.7 |
| 50–59 | 3,094,287 | 34.4 | 100.0 | 16.6 | 18.4 | 28.5 | 36.5 |
| 60 or older | 2,455,081 | 27.3 | 100.0 | 23.7 | 22.1 | 29.9 | 24.3 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 5,951,064 | 66.2 | 100.0 | 18.9 | 19.5 | 28.5 | 33.1 |
| Black | 1,658,014 | 18.4 | 100.0 | 25.7 | 23.0 | 24.6 | 26.8 |
| Other | 422,266 | 4.7 | 100.0 | 23.6 | 19.0 | 35.9 | 21.5 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 888,398 | 9.9 | 100.0 | 20.1 | 12.6 | 28.6 | 38.7 |
| Non-Hispanic | 7,142,946 | 79.4 | 100.0 | 20.6 | 21.1 | 28.0 | 30.2 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 3,432,746 | 38.2 | 100.0 | 19.1 | 18.6 | 28.6 | 33.7 |
| Widowed | 501,970 | 5.6 | 100.0 | 17.7 | 33.0 | 24.6 | 24.6 |
| Divorced or separated | 2,240,468 | 24.9 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 20.3 | 28.3 | 31.0 |
| Never married | 1,856,160 | 20.6 | 100.0 | 24.2 | 19.6 | 27.6 | 28.6 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 1,254,822 | 14.0 | 100.0 | 20.0 | 16.1 | 29.2 | 34.7 |
| 12 | 2,914,750 | 32.4 | 100.0 | 19.6 | 21.5 | 29.2 | 29.7 |
| 13–15 | 2,411,218 | 26.8 | 100.0 | 20.4 | 20.2 | 26.8 | 32.6 |
| 16 or more | 1,450,554 | 16.1 | 100.0 | 23.4 | 21.1 | 26.8 | 28.7 |
| Living arrangement | |||||||
| Lives alone | 2,170,268 | 24.1 | 100.0 | 19.7 | 19.9 | 30.9 | 29.6 |
| Lives with relatives | 5,421,511 | 60.3 | 100.0 | 21.5 | 19.6 | 27.1 | 31.8 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 439,566 | 4.9 | 100.0 | 13.4 | 29.7 | 26.2 | 30.7 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
Personal income is for September–December 2010.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
|||||||
Two out of three DI beneficiaries reported a family size of one or two individuals, and one-third of DI beneficiaries reported that two or more individuals in the household received any Social Security disability, old-age, or survivor benefits (Table 3). About one-half of DI beneficiaries had 4-month family income below $10,000. Nearly 60 percent owned their own home and very few relied on energy assistance (8 percent) or housing assistance (2 percent). However, nearly 32 percent of DI beneficiary households relied on food assistance through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP, formerly known as the Food Stamp program).
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All disabled beneficiaries | Disabled workers | All disabled beneficiaries | Disabled workers | |
| All beneficiaries | 8,993,173 | 8,031,344 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Household type | ||||
| Family | ||||
| Married couple | 3,916,336 | 3,710,600 | 43.5 | 46.2 |
| Male householder | 521,339 | 450,181 | 5.8 | 5.6 |
| Female householder | 1,452,533 | 1,178,582 | 16.2 | 14.7 |
| Nonfamily | ||||
| Male householder | 1,484,598 | 1,327,084 | 16.5 | 16.5 |
| Female householder | 1,535,784 | 1,321,529 | 17.1 | 16.5 |
| Group quarters | 82,581 | 43,368 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| Ownership of residence a | ||||
| Owned | 5,326,043 | 4,851,666 | 59.2 | 60.4 |
| Not owned | ||||
| Public housing | 987,867 | 844,240 | 11.0 | 10.5 |
| Other | 2,679,263 | 2,335,438 | 29.8 | 29.1 |
| Household receipt of assistance b | ||||
| Energy | 686,566 | 589,022 | 7.6 | 7.3 |
| Housing | 215,951 | 191,963 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Food (SNAP) | 2,869,935 | 2,520,941 | 31.9 | 31.4 |
| Household size | ||||
| 1 | 2,433,990 | 2,170,268 | 27.1 | 27.0 |
| 2 | 3,157,919 | 2,883,796 | 35.1 | 35.9 |
| 3–4 | 2,639,041 | 2,300,104 | 29.3 | 28.6 |
| 5 or more | 762,222 | 677,177 | 8.5 | 8.4 |
| Family size | ||||
| 1 | 3,224,642 | 2,799,596 | 35.9 | 34.9 |
| 2 | 2,714,032 | 2,509,403 | 30.2 | 31.2 |
| 3–4 | 2,432,191 | 2,154,457 | 27.0 | 26.8 |
| 5 or more | 622,308 | 567,889 | 6.9 | 7.1 |
| Children younger than age 18 in family | ||||
| None | 7,258,075 | 6,416,081 | 80.7 | 79.9 |
| 1 | 908,614 | 840,395 | 10.1 | 10.5 |
| 2 | 542,357 | 513,679 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| 3–4 | 259,037 | 236,099 | 2.9 | 2.9 |
| 5 or more | 25,089 | 25,089 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Social Security c beneficiaries in household | ||||
| 1 | 5,893,060 | 5,368,511 | 65.5 | 66.8 |
| 2 | 2,191,239 | 1,911,282 | 24.4 | 23.8 |
| 3 or more | 908,874 | 751,551 | 10.1 | 9.4 |
| Total 4-month household income d ($) | ||||
| Less than 2,500 | 73,865 | 60,247 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 2,500–4,999 | 1,756,029 | 1,549,562 | 19.5 | 19.3 |
| 5,000–7,499 | 1,226,634 | 1,096,352 | 13.6 | 13.7 |
| 7,500–9,999 | 1,023,618 | 925,286 | 11.4 | 11.5 |
| 10,000–14,999 | 1,605,413 | 1,393,084 | 17.9 | 17.3 |
| 15,000–19,999 | 1,206,228 | 1,060,589 | 13.4 | 13.2 |
| 20,000 or more | 2,101,385 | 1,946,222 | 23.4 | 24.2 |
| Total 4-month family income d ($) | ||||
| Less than 2,500 | 101,204 | 73,267 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| 2,500–4,999 | 2,173,574 | 1,854,130 | 24.2 | 23.1 |
| 5,000–7,499 | 1,369,261 | 1,225,648 | 15.2 | 15.3 |
| 7,500–9,999 | 926,061 | 855,080 | 10.3 | 10.6 |
| 10,000–14,999 | 1,399,550 | 1,256,642 | 15.6 | 15.6 |
| 15,000–19,999 | 1,100,551 | 968,802 | 12.2 | 12.1 |
| 20,000 or more | 1,922,972 | 1,797,776 | 21.4 | 22.4 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption. A "household" includes related family members and any unrelated persons, such as lodgers, foster children, wards, or employees, who share the housing unit. A household may comprise a person living alone in a housing unit or a group of unrelated persons sharing a housing unit as partners.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
||||
| a. Refers to ownership by any member of the household, not necessarily the beneficiary. | ||||
| b. Individuals may be counted in more than one category. | ||||
| c. Includes disability, old-age, and survivors benefits. | ||||
| d. September–December 2010. | ||||
As Table 4 shows, the two largest sources of family income for DI beneficiaries were their Social Security benefits (58 percent) and earnings (23 percent). Among the marital-status groups, the contribution of earnings toward family income was highest for married DI beneficiaries; those who were divorced or separated relied more heavily on their DI benefits. For beneficiaries with fewer than 12 years of education, benefits accounted for 63 percent and earnings accounted for 18 percent of family income. For those with at least 16 years of education, benefits accounted for 52 percent and earnings accounted for 26 percent of family income.
| Characteristic | Total | Social Security a | Public assistance | Earnings | Property income | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSI | Other | ||||||
| All disabled beneficiaries | |||||||
| Total | 100.0 | 57.7 | 4.9 | 1.7 | 22.7 | 0.7 | 12.3 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 100.0 | 58.9 | 4.1 | 1.8 | 21.8 | 0.7 | 12.7 |
| Women | 100.0 | 56.4 | 5.7 | 1.7 | 23.7 | 0.8 | 11.7 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 100.0 | 50.4 | 8.7 | 3.2 | 27.3 | 0.5 | 9.9 |
| 40–49 | 100.0 | 58.1 | 5.7 | 1.6 | 24.9 | 0.3 | 9.4 |
| 50–59 | 100.0 | 59.1 | 3.4 | 1.6 | 23.0 | 0.7 | 12.2 |
| 60 or older | 100.0 | 59.4 | 4.4 | 1.3 | 18.6 | 1.2 | 15.1 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 100.0 | 57.8 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 23.5 | 0.9 | 12.5 |
| Black | 100.0 | 56.7 | 9.0 | 2.6 | 20.1 | 0.2 | 11.4 |
| Other | 100.0 | 59.6 | 4.4 | 1.8 | 20.5 | 0.7 | 13.0 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 100.0 | 52.7 | 7.4 | 1.4 | 30.1 | 0.1 | 8.3 |
| Non-Hispanic | 100.0 | 58.3 | 4.6 | 1.8 | 21.8 | 0.8 | 12.7 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 100.0 | 44.9 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 36.3 | 1.2 | 14.0 |
| Widowed | 100.0 | 64.3 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 16.5 | 0.6 | 13.4 |
| Divorced or separated | 100.0 | 69.5 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 9.4 | 0.4 | 12.2 |
| Never married | 100.0 | 62.8 | 7.4 | 2.2 | 17.7 | 0.5 | 9.4 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 100.0 | 63.0 | 10.0 | 2.5 | 17.9 | 0.4 | 6.2 |
| 12 | 100.0 | 57.6 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 24.2 | 0.4 | 11.6 |
| 13–15 | 100.0 | 58.2 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 21.6 | 0.8 | 13.4 |
| 16 or more | 100.0 | 51.9 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 25.7 | 1.7 | 17.8 |
| Living arrangement | |||||||
| Lives alone | 100.0 | 77.4 | 6.0 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 10.7 |
| Lives with relatives | 100.0 | 47.8 | 4.1 | 1.7 | 31.8 | 1.0 | 13.6 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 100.0 | 77.6 | 8.7 | 2.4 | 6.4 | 0.4 | 4.5 |
| Disabled workers | |||||||
| Total | 100.0 | 57.2 | 4.6 | 1.7 | 23.1 | 0.8 | 12.6 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 100.0 | 58.8 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 21.7 | 0.7 | 13.4 |
| Women | 100.0 | 55.4 | 5.6 | 1.7 | 24.7 | 0.8 | 11.8 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 100.0 | 48.1 | 7.8 | 3.4 | 29.6 | 0.5 | 10.6 |
| 40–49 | 100.0 | 57.8 | 5.7 | 1.6 | 24.9 | 0.3 | 9.7 |
| 50–59 | 100.0 | 59.1 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 23.5 | 0.7 | 12.0 |
| 60 or older | 100.0 | 58.1 | 4.6 | 1.4 | 19.0 | 1.3 | 15.6 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 100.0 | 57.2 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 24.2 | 0.9 | 12.8 |
| Black | 100.0 | 56.5 | 9.0 | 2.7 | 20.0 | 0.2 | 11.6 |
| Other | 100.0 | 59.7 | 4.1 | 1.7 | 20.3 | 0.7 | 13.5 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 100.0 | 53.5 | 6.7 | 1.4 | 29.5 | 0.1 | 8.8 |
| Non-Hispanic | 100.0 | 57.7 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 22.4 | 0.8 | 13.0 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 100.0 | 44.9 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 36.3 | 1.2 | 14.0 |
| Widowed | 100.0 | 64.2 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 16.4 | 0.4 | 13.7 |
| Divorced or separated | 100.0 | 69.9 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 9.2 | 0.4 | 12.0 |
| Never married | 100.0 | 62.7 | 6.8 | 2.3 | 17.4 | 0.5 | 10.3 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 100.0 | 62.6 | 10.0 | 2.5 | 18.4 | 0.3 | 6.2 |
| 12 | 100.0 | 56.5 | 3.9 | 1.7 | 25.4 | 0.5 | 12.0 |
| 13–15 | 100.0 | 58.0 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 21.5 | 0.8 | 13.7 |
| 16 or more | 100.0 | 52.6 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 25.4 | 1.7 | 17.5 |
| Living arrangement | |||||||
| Lives alone | 100.0 | 77.1 | 6.0 | 1.7 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 11.1 |
| Lives with relatives | 100.0 | 47.5 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 32.3 | 1.0 | 13.7 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 100.0 | 78.0 | 7.4 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 5.8 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
|
|||||||
| a. Includes disability, old-age, and survivor benefits. | |||||||
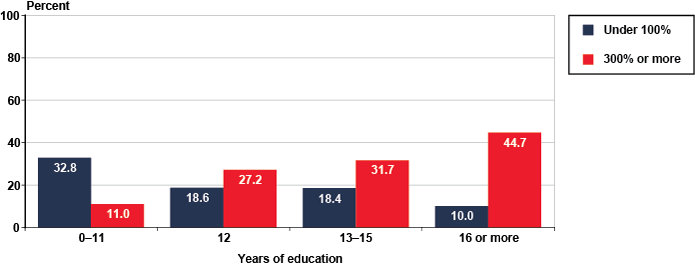
Although 29 percent of DI beneficiaries had family income of at least 300 percent of the poverty threshold, nearly 20 percent were in poverty (Table 5). Female DI beneficiaries and beneficiaries who were not married were among those most likely to have family income below the poverty threshold. The proportions of DI beneficiaries above 300 percent of the poverty threshold differed widely by educational attainment. Only 11 percent of those with fewer than 12 years of education were above 300 percent of the threshold, compared with 45 percent of those with 16 years or more of education (Chart 2).
| Characteristic | Total | Family income relative to poverty threshold | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 100% | 100–124% | 125–149% | 150–199% | 200–299% | 300% or more | ||
| All disabled beneficiaries | |||||||
| Total | 8,993,173 | 19.5 | 9.9 | 8.0 | 15.9 | 18.0 | 28.7 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 4,613,671 | 15.9 | 10.3 | 7.8 | 17.3 | 18.1 | 30.6 |
| Women | 4,379,502 | 23.4 | 9.5 | 8.2 | 14.4 | 17.9 | 26.6 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 1,354,823 | 23.2 | 7.5 | 9.4 | 18.1 | 16.8 | 25.0 |
| 40–49 | 1,622,598 | 21.1 | 12.2 | 6.5 | 13.4 | 20.0 | 26.8 |
| 50–59 | 3,335,921 | 17.5 | 10.4 | 9.1 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 29.2 |
| 60 or older | 2,679,831 | 19.1 | 9.2 | 6.7 | 15.0 | 19.0 | 31.0 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 6,732,147 | 17.4 | 10.0 | 7.7 | 15.2 | 18.8 | 30.9 |
| Black | 1,801,612 | 27.9 | 8.9 | 9.0 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 21.2 |
| Other | 459,414 | 17.8 | 13.1 | 8.4 | 21.8 | 13.9 | 25.0 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 961,876 | 23.0 | 7.9 | 6.3 | 20.7 | 19.3 | 22.8 |
| Non-Hispanic | 8,031,297 | 19.1 | 10.2 | 8.2 | 15.3 | 17.9 | 29.4 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 3,472,334 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 16.1 | 21.0 | 45.5 |
| Widowed | 705,296 | 24.3 | 11.8 | 11.9 | 11.7 | 23.2 | 17.1 |
| Divorced or separated | 2,291,473 | 32.8 | 12.3 | 10.0 | 15.9 | 16.1 | 12.8 |
| Never married | 2,524,070 | 24.5 | 13.3 | 8.2 | 16.7 | 14.3 | 23.1 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 1,519,369 | 32.8 | 15.9 | 10.2 | 18.3 | 11.7 | 11.0 |
| 12 | 3,449,413 | 18.6 | 9.1 | 8.0 | 16.5 | 20.7 | 27.2 |
| 13–15 | 2,511,658 | 18.4 | 9.1 | 7.1 | 15.3 | 18.4 | 31.7 |
| 16 or more | 1,512,733 | 10.0 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 13.1 | 18.0 | 44.7 |
| Disabled workers | |||||||
| Total | 8,031,344 | 18.4 | 9.9 | 7.7 | 16.0 | 18.3 | 29.6 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 4,155,490 | 15.1 | 10.0 | 7.7 | 17.3 | 18.4 | 31.6 |
| Women | 3,875,854 | 21.9 | 9.8 | 7.8 | 14.7 | 18.2 | 27.5 |
| Age | |||||||
| Under 40 | 966,097 | 22.2 | 8.2 | 9.2 | 18.0 | 16.9 | 25.5 |
| 40–49 | 1,515,879 | 22.1 | 12.0 | 6.5 | 13.0 | 19.8 | 26.6 |
| 50–59 | 3,094,287 | 17.0 | 9.6 | 9.3 | 17.1 | 17.4 | 29.7 |
| 60 or older | 2,455,081 | 16.5 | 9.7 | 6.0 | 15.7 | 19.1 | 33.0 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 5,951,064 | 16.0 | 9.8 | 7.4 | 15.3 | 19.3 | 32.1 |
| Black | 1,658,014 | 26.8 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 17.4 | 16.1 | 21.8 |
| Other | 422,266 | 19.1 | 13.7 | 9.1 | 20.4 | 12.6 | 25.2 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 888,398 | 23.7 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 19.7 | 18.4 | 23.6 |
| Non-Hispanic | 7,142,946 | 17.7 | 10.1 | 7.9 | 15.6 | 18.3 | 30.4 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 3,432,746 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 16.0 | 21.2 | 45.6 |
| Widowed | 501,970 | 17.0 | 14.6 | 10.5 | 13.9 | 26.3 | 17.8 |
| Divorced or separated | 2,240,468 | 33.4 | 12.3 | 10.2 | 15.9 | 15.5 | 12.8 |
| Never married | 1,856,160 | 23.5 | 13.7 | 8.2 | 16.7 | 14.2 | 23.6 |
| Years of education | |||||||
| 0–11 | 1,254,822 | 31.6 | 16.9 | 11.3 | 17.7 | 11.4 | 11.1 |
| 12 | 2,914,750 | 16.8 | 8.5 | 7.6 | 17.3 | 21.8 | 28.0 |
| 13–15 | 2,411,218 | 18.4 | 9.4 | 6.3 | 15.6 | 18.3 | 32.1 |
| 16 or more | 1,450,554 | 10.3 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 12.6 | 17.5 | 44.8 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
Family income is for September–December 2010.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
|||||||
DI beneficiaries with family incomes at selected percentages of the poverty threshold, by years of education, December 2010 (in percent)
| Years of education | Family income relative to poverty threshold | |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 100% | 300% or more | |
| 0–11 | 32.8 | 11.0 |
| 12 | 18.6 | 27.2 |
| 13–15 | 18.4 | 31.7 |
| 16 or more | 10.0 | 44.7 |
As part of the social safety net, DI benefits help keep some individuals out of poverty. If DI benefits were removed from their income, one-half of disabled beneficiaries would have been in poverty in 2010 based on their family income level (Table 6). With DI benefits included in family income, only 20 percent of beneficiaries had income below the poverty threshold. Beneficiaries' economic behavior would likely change if they did not receive disability benefits; thus, hypothetical estimates that simply exclude DI benefits do not fully capture the economic situation beneficiaries would experience in the absence of the program. Rather, these estimates represent how the program contributes to the reduction in poverty under existing patterns of behavior. Receiving DI benefits reduced the aggregate poverty gap, or the aggregate difference between family income and the poverty threshold for those below the threshold, by 87 percent (Table 7).
| Family income minus DI benefits as a percentage of poverty threshold | Total | Actual family income as a percentage of poverty threshold | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percent | Total | Under 100% | 100–150% | 150% or more | |
| All disabled beneficiaries | 8,993,173 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 19.5 | 17.9 | 62.6 |
| Under 100% | 4,540,240 | 50.5 | 100.0 | 38.6 | 34.0 | 27.3 |
| 100–150% | 1,034,894 | 11.5 | 100.0 | . . . | 6.2 | 93.8 |
| 150% or more | 3,418,039 | 38.0 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| Disabled workers | 8,031,344 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 18.4 | 17.6 | 64.0 |
| Under 100% | 3,997,802 | 49.8 | 100.0 | 37.0 | 34.1 | 28.9 |
| 100–150% | 915,120 | 11.4 | 100.0 | . . . | 5.9 | 94.1 |
| 150% or more | 3,118,422 | 38.8 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
. . . = not applicable.
|
||||||
| Characteristic | Aggregate poverty gap (thousands of dollars) | Reduction in poverty gap (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| If DI benefits were excluded | With DI benefits | ||
| Total | 13,787,968 | 1,754,290 | 87.3 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 7,076,164 | 748,254 | 89.4 |
| Female | 6,711,804 | 1,006,036 | 85.0 |
| Age | |||
| Under 40 | 1,932,316 | 414,840 | 78.5 |
| 40–49 | 2,516,821 | 369,936 | 85.3 |
| 50–59 | 5,451,543 | 574,884 | 89.5 |
| 60 or older | 3,887,288 | 394,629 | 89.8 |
| Race | |||
| White | 10,086,296 | 1,168,938 | 88.4 |
| Black | 2,970,752 | 515,134 | 82.7 |
| Other | 730,920 | 70,218 | 90.4 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic | 1,413,066 | 245,870 | 82.6 |
| Non-Hispanic | 12,374,901 | 1,508,420 | 87.8 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||
| NOTES: "DI beneficiaries" includes disabled workers, disabled widow(er)s, and disabled adult children, but excludes nondisabled individuals receiving DI benefits as dependents of disabled workers.
"Poverty gap" refers to the difference between family income and the poverty threshold for a family in poverty. Aggregate poverty gap is the sum of individual poverty gaps for all families with DI beneficiaries.
A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
Family income data and poverty thresholds are for September–December 2010.
|
|||
SSI Recipients
SSI recipients in this sample include aged, blind, and disabled individuals. Our SSI tables show results for three subgroups: children (younger than age 18), working-age adults (18–64), and the aged (65 or older).5 The maximum monthly SSI payment amount, called the federal benefit rate, can be reduced for individuals with countable earnings and unearned income. In 2010, the federal benefit rate was $674 for an individual and $1,011 for a couple in which both members were eligible.
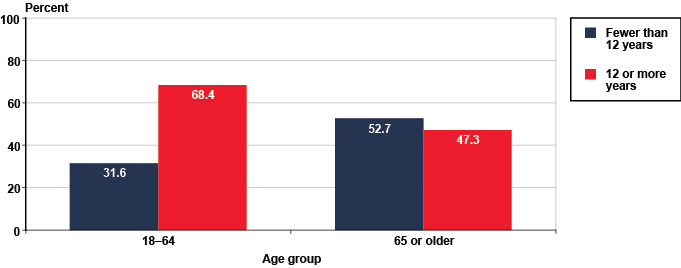
Working-age SSI recipients were more likely to have higher levels of education than aged recipients in December 2010. Among working-age recipients, 68 percent had at least 12 years of education, compared with 47 percent of aged recipients (Chart 3). About 37 percent of aged recipients had fewer than 9 years of education, compared with 12 percent of working-age recipients (Table 8). We note that a substantial proportion of aged SSI recipients reported Social Security benefits in the SIPP (72 percent); however, according to SSA records, only 56 percent of SSI recipients aged 65 or older had Social Security benefits (SSA 2012, Table 7.D2).
SSI recipients, by educational attainment and age group, December 2010 (in percent)
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Under 18 | 18–64 | 65 or older | Total | Under 18 | 18–64 | 65 or older | |
| All recipients | 7,497,490 | 1,193,848 | 4,367,934 | 1,935,708 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 3,246,059 | 789,201 | 1,857,618 | 599,240 | 43.3 | 66.1 | 42.5 | 31.0 |
| Female | 4,251,430 | 404,647 | 2,510,315 | 1,336,468 | 56.7 | 33.9 | 57.5 | 69.0 |
| Race | ||||||||
| White | 4,382,409 | 611,252 | 2,696,922 | 1,074,235 | 58.5 | 51.2 | 61.7 | 55.5 |
| Black | 2,284,788 | 472,286 | 1,292,364 | 520,139 | 30.5 | 39.6 | 29.6 | 26.9 |
| Other | 830,292 | 110,310 | 378,648 | 341,335 | 11.1 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 17.6 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||||
| Hispanic | 1,538,306 | 284,124 | 717,034 | 537,148 | 20.5 | 23.8 | 16.4 | 27.7 |
| Non-Hispanic | 5,959,184 | 909,724 | 3,650,900 | 1,398,560 | 79.5 | 76.2 | 83.6 | 72.3 |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married | 1,295,186 | . . . | 802,368 | 492,819 | 17.3 | . . . | 18.4 | 25.5 |
| Widowed | 674,295 | . . . | 121,842 | 552,452 | 9.0 | . . . | 2.8 | 28.5 |
| Divorced or separated | 1,689,446 | . . . | 1,092,029 | 597,417 | 22.5 | . . . | 25.0 | 30.9 |
| Never married | 3,838,563 | 1,193,848 | 2,351,695 | 293,020 | 51.2 | 100.0 | 53.8 | 15.1 |
| Years of education a | ||||||||
| 0–8 | 1,234,240 | . . . | 514,541 | 719,700 | 16.5 | . . . | 11.8 | 37.2 |
| 9–11 | 1,165,887 | . . . | 866,353 | 299,535 | 15.6 | . . . | 19.8 | 15.5 |
| 12 | 2,408,456 | . . . | 1,852,198 | 556,258 | 32.1 | . . . | 42.4 | 28.7 |
| 13–15 | 995,359 | . . . | 802,789 | 192,570 | 13.3 | . . . | 18.4 | 9.9 |
| 16 or more | 499,699 | . . . | 332,054 | 167,645 | 6.7 | . . . | 7.6 | 8.7 |
| Health insurance b | ||||||||
| Medicaid | 7,111,729 | 1,132,184 | 4,155,033 | 1,824,512 | 94.9 | 94.8 | 95.1 | 94.3 |
| Medicaid only | 3,836,070 | 998,838 | 2,787,849 | 49,382 | 51.2 | 83.7 | 63.8 | 2.6 |
| Medicare | 3,025,004 | . . . | 1,139,658 | 1,885,346 | 40.3 | . . . | 26.1 | 97.4 |
| Medicaid and Medicare only | 2,687,546 | . . . | 1,023,125 | 1,664,421 | 35.8 | . . . | 23.4 | 86.0 |
| Private | 656,951 | 147,436 | 386,393 | 123,122 | 8.8 | 12.3 | 8.8 | 6.4 |
| None | 167,555 | 47,573 | 119,982 | 0 | 2.2 | 4.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 |
| Source of income b | ||||||||
| Social Security c | 2,901,367 | 104,688 | 1,407,967 | 1,388,712 | 38.7 | 8.8 | 32.2 | 71.7 |
| Public assistance other than SSI d | 4,051,129 | 32,261 | 2,861,015 | 1,157,853 | 54.0 | 2.7 | 65.5 | 59.8 |
| Earnings | 480,650 | . . . | 426,306 | 54,345 | 6.4 | . . . | 9.8 | 2.8 |
| Property income | 986,580 | . . . | 715,101 | 271,479 | 13.2 | . . . | 16.4 | 14.0 |
| Other income | 680,722 | . . . | 517,709 | 163,013 | 9.1 | . . . | 11.9 | 8.4 |
| Veteran status a | ||||||||
| Veteran | 132,375 | . . . | 93,726 | 38,649 | 1.8 | . . . | 2.1 | 2.0 |
| Nonveteran | 6,171,267 | . . . | 4,274,208 | 1,897,059 | 82.3 | . . . | 97.9 | 98.0 |
| Total 4-month personal income e ($) | ||||||||
| Less than 2,000 | 700,118 | 241,416 | 344,627 | 114,074 | 9.3 | 20.2 | 7.9 | 5.9 |
| 2,000–2,499 | 514,928 | 150,429 | 232,175 | 132,324 | 6.9 | 12.6 | 5.3 | 6.8 |
| 2,500–2,999 | 3,159,526 | 726,975 | 1,551,991 | 880,560 | 42.1 | 60.9 | 35.5 | 45.5 |
| 3,000 or more | 3,122,919 | 75,028 | 2,239,140 | 808,750 | 41.7 | 6.3 | 51.3 | 41.8 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||||
| NOTES: Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
. . . = not applicable.
|
||||||||
| a. Adult population only. | ||||||||
| b. Individuals may be counted in more than one category. | ||||||||
| c. Includes disability, old-age, and survivor benefits. | ||||||||
| d. Includes state SSI supplementation, Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, General Assistance, food assistance (including food stamps and the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), clothing assistance, short-term assistance, transportation assistance, and other welfare. | ||||||||
| e. September–December 2010. | ||||||||
Unlike Medicare coverage under DI, which begins only after 24 months in the program, Medicaid coverage begins immediately for SSI recipients in most states. In December 2010, 95 percent of all SSI recipients had Medicaid coverage and 40 percent had Medicare coverage. A majority (64 percent) of working-age SSI recipients was covered by Medicaid only, while 23 percent reported having joint Medicare and Medicaid coverage but no private insurance. The percentage of aged SSI recipients with Medicare coverage is undoubtedly high, although perhaps not quite the 97 percent reported in the SIPP.6 Private health insurance covered almost 9 percent of SSI recipients. All aged SSI recipients had at least one type of health insurance; however, 4 percent of children and 3 percent of working-age recipients had no coverage.
Table 8 also shows that 54 percent of recipients reported receiving public assistance other than SSI (such as General Assistance), and 6 percent reported earnings. Nearly 39 percent of SSI recipients reported receiving Social Security benefits and 9 percent reported other sources of income.
A majority of SSI adult recipients did not own their own home, and most received SNAP food assistance (Table 9). SSI recipients were typically unique in their households with regard to type of recipient. For example, 78 percent of child recipients resided in households where they were the sole SSI child recipient. Similarly, for working-age SSI recipients, 76 percent resided in households where there was only one working-age recipient.
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Under 18 | 18–64 | 65 or older | Total | Under 18 | 18–64 | 65 or older | |
| All recipients | 7,497,490 | 1,193,848 | 4,367,934 | 1,935,708 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Household type a | ||||||||
| Family | ||||||||
| Married couple | 1,818,347 | . . . | 1,248,580 | 569,767 | 28.8 | . . . | 28.6 | 29.4 |
| Male householder | 386,973 | . . . | 283,644 | 103,329 | 6.1 | . . . | 6.5 | 5.3 |
| Female householder | 1,724,357 | . . . | 1,376,503 | 347,854 | 27.4 | . . . | 31.5 | 18.0 |
| Nonfamily or group quarters | 2,373,965 | . . . | 1,459,206 | 914,758 | 37.7 | . . . | 33.4 | 47.3 |
| Ownership of residence b | ||||||||
| Owned | 2,577,932 | 358,762 | 1,439,837 | 779,333 | 34.4 | 30.1 | 33.0 | 40.3 |
| Not owned | ||||||||
| Public housing | 1,738,110 | 205,676 | 1,001,939 | 530,495 | 23.2 | 17.2 | 22.9 | 27.4 |
| Other | 3,181,448 | 629,410 | 1,926,158 | 625,880 | 42.4 | 52.7 | 44.1 | 32.3 |
| Household receipt of assistance c | ||||||||
| Energy | 947,151 | 183,339 | 561,358 | 202,454 | 12.6 | 15.4 | 12.9 | 10.5 |
| Housing | 370,305 | 77,503 | 219,972 | 72,831 | 4.9 | 6.5 | 5.0 | 3.8 |
| Food (SNAP) | 4,631,961 | 712,601 | 2,835,501 | 1,083,859 | 61.8 | 59.7 | 64.9 | 56.0 |
| Household size | ||||||||
| 1 | 1,832,665 | . . . | 998,093 | 834,572 | 24.4 | . . . | 22.9 | 43.1 |
| 2 | 1,841,895 | 121,396 | 1,179,662 | 540,837 | 24.6 | 10.2 | 27.0 | 27.9 |
| 3–4 | 2,321,434 | 558,997 | 1,409,515 | 352,922 | 31.0 | 46.8 | 32.3 | 18.2 |
| 5 or more | 1,501,496 | 513,454 | 780,664 | 207,377 | 20.0 | 43.0 | 17.9 | 10.7 |
| Family size | ||||||||
| 1–2 | 4,094,297 | 146,082 | 2,510,508 | 1,437,706 | 54.6 | 12.2 | 57.5 | 74.3 |
| 3–4 | 2,145,348 | 566,412 | 1,255,671 | 323,264 | 28.6 | 47.4 | 28.7 | 16.7 |
| 5 or more | 1,257,845 | 481,353 | 601,754 | 174,738 | 16.8 | 40.3 | 13.8 | 9.0 |
| Children in family | ||||||||
| None | 4,833,116 | . . . | 3,142,251 | 1,690,864 | 64.5 | . | 71.9 | 87.4 |
| 1 | 908,935 | 308,752 | 469,360 | 130,822 | 12.1 | 25.9 | 10.7 | 6.8 |
| 2 | 940,760 | 393,882 | 485,326 | 61,552 | 12.5 | 33.0 | 11.1 | 3.2 |
| 3 or more | 814,679 | 491,214 | 270,996 | 52,470 | 10.9 | 41.1 | 6.2 | 2.7 |
| Child SSI recipients in household | ||||||||
| None | 4,103,253 | . . . | 4,103,253 | . . . | 54.7 | . . . | 93.9 | . . . |
| 1 | 1,133,659 | 925,020 | 208,639 | . . . | 15.1 | 77.5 | 4.8 | . . . |
| 2 or more | 324,870 | 268,828 | 56,042 | . . . | 4.3 | 22.5 | 1.3 | . . . |
| Suppressed | 1,935,708 | . . . | . . . | 1,935,708 | 25.8 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| Adult SSI recipients in household | ||||||||
| None | 930,224 | 930,224 | . . . | . . . | 12.4 | 77.9 | . . . | . . . |
| 1 | 4,969,724 | 204,936 | 3,308,142 | 1,456,645 | 66.3 | 17.2 | 75.7 | 75.3 |
| 2 or more | 1,597,541 | 58,687 | 1,059,792 | 479,063 | 21.3 | 4.9 | 24.3 | 24.7 |
| Total 4-month household income d ($) | ||||||||
| Less than 5,000 | 2,579,932 | 170,855 | 1,411,874 | 997,203 | 34.4 | 14.3 | 32.3 | 51.5 |
| 5,000–7,499 | 1,353,736 | 226,168 | 860,000 | 267,568 | 18.1 | 18.9 | 19.7 | 13.8 |
| 7,500–9,999 | 780,717 | 175,786 | 487,583 | 117,348 | 10.4 | 14.7 | 11.2 | 6.1 |
| 10,000–14,999 | 939,943 | 227,218 | 528,213 | 184,513 | 12.5 | 19.0 | 12.1 | 9.5 |
| 15,000–19,999 | 676,808 | 165,138 | 359,387 | 152,283 | 9.0 | 13.8 | 8.2 | 7.9 |
| 20,000 or more | 1,166,353 | 228,682 | 720,879 | 216,793 | 15.6 | 19.2 | 16.5 | 11.2 |
| Total 4-month family income d ($) | ||||||||
| Less than 5,000 | 3,109,838 | 206,267 | 1,826,829 | 1,076,742 | 41.5 | 17.3 | 41.8 | 55.6 |
| 5,000–7,499 | 1,404,896 | 242,715 | 875,097 | 287,085 | 18.7 | 20.3 | 20.0 | 14.8 |
| 7,500–9,999 | 693,297 | 195,468 | 388,757 | 109,072 | 9.2 | 16.4 | 8.9 | 5.6 |
| 10,000–14,999 | 779,525 | 206,808 | 432,861 | 139,856 | 10.4 | 17.3 | 9.9 | 7.2 |
| 15,000–19,999 | 573,461 | 140,579 | 286,523 | 146,359 | 7.6 | 11.8 | 6.6 | 7.6 |
| 20,000 or more | 936,473 | 202,010 | 557,867 | 176,595 | 12.5 | 16.9 | 12.8 | 9.1 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||||
| NOTE: A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption. A "household" includes related family members and any unrelated persons, such as lodgers, foster children, wards, or employees, who share the housing unit. A household may comprise a person living alone in a housing unit or a group of unrelated persons sharing a housing unit as partners.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
||||||||
| a. Adult recipients only. | ||||||||
| b. Refers to ownership by any member of the household, not necessarily the recipient. | ||||||||
| c. Individuals may be counted in more than one category. | ||||||||
| d. September–December 2010. | ||||||||
The majority of SSI recipients (58 percent) had 4-month total personal income below $3,000 and most of those individuals had income between $2,500 and $2,999 (Table 8). We note that SSI payments for a recipient who qualified for the federal benefit rate of $674 in 2010 would amount to $2,696 over a 4-month period, which would fall within that range. Although family income was generally higher than personal income for SSI recipients, total family income across 4 months was still less than $7,500 ($1,875/month) for 60 percent of SSI recipients (Table 9). SSI payments accounted for 100 percent of personal income for 34 percent of working-age SSI recipients and for 19 percent of SSI recipients aged 65 or older (Table 10).
| Characteristic | Number | Percent | Percentage distribution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Under 25% of income | 25–49% of income | 50–74% of income | 75–99% of income | 100% of income | |||
| All recipients | 6,303,642 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 24.3 | 16.1 | 18.2 | 12.1 | 29.3 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 2,456,858 | 39.0 | 100.0 | 27.3 | 14.2 | 18.0 | 11.8 | 28.7 |
| Female | 3,846,784 | 61.0 | 100.0 | 22.3 | 17.3 | 18.4 | 12.2 | 29.8 |
| Age group | ||||||||
| 18–64 | 4,367,934 | 69.3 | 100.0 | 19.5 | 13.3 | 19.5 | 14.0 | 33.7 |
| 65 or older | 1,935,708 | 30.7 | 100.0 | 35.1 | 22.3 | 15.4 | 7.7 | 19.4 |
| Race | ||||||||
| White | 3,771,157 | 59.8 | 100.0 | 26.5 | 16.7 | 17.0 | 12.9 | 26.9 |
| Black | 1,812,502 | 28.8 | 100.0 | 21.2 | 17.2 | 20.4 | 9.2 | 32.0 |
| Other | 719,982 | 11.4 | 100.0 | 20.1 | 10.3 | 19.5 | 14.8 | 35.4 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||||
| Hispanic | 1,254,182 | 19.9 | 100.0 | 24.7 | 15.9 | 20.8 | 10.3 | 28.3 |
| Non-Hispanic | 5,049,460 | 80.1 | 100.0 | 24.2 | 16.1 | 17.6 | 12.5 | 29.6 |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married | 1,295,186 | 20.5 | 100.0 | 22.4 | 16.2 | 14.9 | 11.9 | 34.7 |
| Widowed | 674,295 | 10.7 | 100.0 | 37.1 | 26.8 | 8.9 | 6.1 | 21.1 |
| Divorced or separated | 1,689,446 | 26.8 | 100.0 | 29.2 | 15.8 | 19.4 | 11.7 | 24.0 |
| Never married | 2,644,715 | 42.0 | 100.0 | 18.7 | 13.5 | 21.5 | 13.9 | 32.2 |
| Years of education | ||||||||
| 0–8 | 1,234,240 | 19.6 | 100.0 | 27.3 | 18.6 | 14.6 | 10.9 | 28.6 |
| 9–11 | 1,165,887 | 18.5 | 100.0 | 16.5 | 13.9 | 25.8 | 8.8 | 35.0 |
| 12 | 2,408,456 | 38.2 | 100.0 | 26.8 | 14.6 | 18.1 | 12.4 | 28.2 |
| 13–15 | 995,359 | 15.8 | 100.0 | 22.8 | 21.2 | 15.7 | 15.0 | 25.4 |
| 16 or more | 499,699 | 7.9 | 100.0 | 25.8 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 15.2 | 31.5 |
| Living arrangement | ||||||||
| Lives alone | 1,832,665 | 29.1 | 100.0 | 33.4 | 14.7 | 16.6 | 10.7 | 24.5 |
| Lives with relatives | 3,961,819 | 62.8 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 16.5 | 18.3 | 13.0 | 31.6 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 509,158 | 8.1 | 100.0 | 20.6 | 17.5 | 23.3 | 9.3 | 29.3 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||||
| NOTES: Personal income data and poverty thresholds are for September–December 2010.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
||||||||
Family income for SSI recipients primarily comprised SSI payments, Social Security benefits, and earnings (Table 11). SSI payments accounted for 44 percent of family income, earnings accounted for 23 percent, and Social Security benefits accounted for 22 percent. The share of family income contributed by earnings was higher for families with child SSI recipients than for those with working-age recipients (38 percent versus 20 percent). The majority of family income for SSI recipients aged 65 or older was provided by the combination of Social Security benefits (37 percent) and SSI payments (36 percent).
| Characteristic | Total | Social Security a | Public assistance | Earnings | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSI | Other | |||||
| All recipients | 100.0 | 22.0 | 43.9 | 5.3 | 22.5 | 6.3 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 100.0 | 20.4 | 42.6 | 5.2 | 25.4 | 6.4 |
| Female | 100.0 | 23.2 | 45.0 | 5.4 | 20.4 | 6.0 |
| Age group | ||||||
| Under 18 | 100.0 | 8.0 | 42.6 | 4.0 | 37.6 | 7.8 |
| 18–64 | 100.0 | 19.1 | 47.7 | 6.4 | 19.9 | 6.9 |
| 65 or older | 100.0 | 37.2 | 36.3 | 3.8 | 19.3 | 3.4 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 100.0 | 23.3 | 41.1 | 4.9 | 24.1 | 6.6 |
| Black | 100.0 | 21.5 | 49.2 | 5.8 | 18.2 | 5.3 |
| Other | 100.0 | 16.5 | 44.2 | 6.3 | 26.5 | 6.5 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Hispanic | 100.0 | 20.4 | 41.1 | 4.2 | 28.8 | 5.5 |
| Non-Hispanic | 100.0 | 22.4 | 44.6 | 5.6 | 20.9 | 6.5 |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Married | 100.0 | 21.6 | 42.9 | 5.5 | 24.4 | 5.6 |
| Widowed | 100.0 | 35.8 | 32.0 | 3.6 | 22.8 | 5.8 |
| Divorced or separated | 100.0 | 30.8 | 48.8 | 6.2 | 9.6 | 4.6 |
| Never married | 100.0 | 15.8 | 44.2 | 5.1 | 27.6 | 7.3 |
| Years of education | ||||||
| 0–8 | 100.0 | 29.9 | 40.6 | 5.7 | 19.5 | 4.3 |
| 9–11 | 100.0 | 21.7 | 50.6 | 6.1 | 14.6 | 7.0 |
| 12 | 100.0 | 23.6 | 40.5 | 5.2 | 24.4 | 6.3 |
| 13–15 | 100.0 | 26.4 | 48.6 | 5.7 | 14.4 | 4.9 |
| 16 or more | 100.0 | 20.2 | 46.8 | 5.2 | 19.6 | 8.2 |
| Unknown | 100.0 | 8.0 | 42.6 | 4.0 | 37.6 | 7.8 |
| Living arrangement | ||||||
| Lives alone | 100.0 | 35.8 | 53.3 | 5.5 | 2.1 | 3.3 |
| Lives with relatives | 100.0 | 16.9 | 38.5 | 5.2 | 31.7 | 7.7 |
| Lives only with nonrelatives | 100.0 | 23.7 | 63.6 | 5.8 | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||
| NOTE: A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption. | ||||||
| a. Includes disability, old-age, and survivor benefits. | ||||||
A substantial minority (43 percent) of SSI recipients had family income below the poverty level in December 2010 (Table 12). Among those most likely to fall under the poverty threshold were aged SSI recipients, those who were widowed, those who were divorced or separated, and recipients with 13–15 years of education. Although families with a child SSI recipient were somewhat less likely than families with an adult recipient to be in poverty, almost one-third were below the poverty line.
| Characteristic | Total | Family income relative to poverty threshold | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 100% | 100–124% | 125–149% | 150–199% | 200–299% | 300% or more | ||
| All recipients | 7,497,490 | 42.9 | 13.6 | 8.1 | 14.0 | 11.1 | 10.3 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 3,246,059 | 36.8 | 15.1 | 8.5 | 15.1 | 11.3 | 13.2 |
| Female | 4,251,430 | 47.6 | 12.5 | 7.8 | 13.1 | 11.0 | 8.0 |
| Age group | |||||||
| Under 18 | 1,193,848 | 31.6 | 16.2 | 9.7 | 16.9 | 14.6 | 10.9 |
| 18–64 | 4,367,934 | 43.4 | 12.7 | 8.7 | 14.0 | 9.8 | 11.3 |
| 65 or older | 1,935,708 | 48.7 | 14.2 | 5.6 | 12.1 | 12.0 | 7.4 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 4,382,409 | 40.9 | 13.1 | 8.7 | 13.1 | 11.7 | 12.5 |
| Black | 2,284,788 | 50.0 | 14.8 | 6.3 | 13.1 | 10.0 | 5.7 |
| Other | 830,292 | 33.8 | 13.3 | 9.9 | 20.9 | 11.3 | 10.8 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Hispanic | 1,538,306 | 40.5 | 11.8 | 7.7 | 18.5 | 13.2 | 8.3 |
| Non-Hispanic | 5,959,184 | 43.5 | 14.1 | 8.2 | 12.8 | 10.6 | 10.7 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 1,295,186 | 32.1 | 22.2 | 11.9 | 16.9 | 9.9 | 7.0 |
| Widowed | 674,295 | 49.6 | 10.5 | 3.9 | 6.5 | 20.2 | 9.3 |
| Divorced or separated | 1,689,446 | 62.4 | 10.5 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 4.7 |
| Never married | 3,838,563 | 36.8 | 12.7 | 7.8 | 16.5 | 12.2 | 14.0 |
| Years of education a | |||||||
| 0–8 | 1,234,240 | 48.3 | 15.6 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 10.6 | 8.4 |
| 9–11 | 1,165,887 | 49.8 | 14.7 | 8.2 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 3.8 |
| 12 | 2,408,456 | 37.8 | 12.8 | 6.8 | 17.4 | 11.3 | 14.0 |
| 13–15 | 995,359 | 55.4 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 11.4 | 6.8 | 9.1 |
| 16 or more | 499,699 | 40.2 | 11.0 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 12.2 | 12.9 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||||||
| NOTES: A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
Family income is for September–December 2010.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
|||||||
| a. Adult recipients only. | |||||||
SSI payments helped some families move above the poverty line, but most families remained within 150 percent of the poverty threshold. Without counting SSI payments in family income, the poverty rate would be 65 percent, compared with the actual rate (43 percent) when SSI payments are included (Table 13). The percentage of child SSI recipients with family income below the poverty line falls from 58 percent to 32 percent when SSI is counted. Thus, of children whose family income without SSI would be below the poverty line, about 46 percent are not in poverty when SSI payments are included in family income. The impact of SSI payments on family income of aged recipients is somewhat smaller, helping 28 percent move above the poverty threshold. SSI payments reduced the aggregate poverty gap by 71 percent (Table 14). The reduction was slightly larger for aged SSI recipients and slightly smaller for child recipients. As with the estimated impacts of DI benefits on poverty, these estimates do not capture any changes in the economic behavior of SSI recipients that could result from the presence or absence of SSI payments.
| Family income minus SSI payments as a percentage of poverty threshold | Total | Actual family income as a percentage of poverty threshold | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percent | Total | Under 100% | 100–150% | 150% or more | |
| All recipients | 7,497,490 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 42.9 | 21.7 | 35.4 |
| Under 100% | 4,894,873 | 65.3 | 100.0 | 65.7 | 27.3 | 6.9 |
| 100–150% | 900,151 | 11.8 | 100.0 | . . . | 32.3 | 67.7 |
| 150% or more | 1,702,466 | 23.0 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| Under age 18 | 1,193,848 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 31.6 | 25.9 | 42.5 |
| Under 100% | 692,696 | 58.0 | 100.0 | 54.5 | 36.3 | 9.3 |
| 100–150% | 187,481 | 15.7 | 100.0 | . . . | 31.1 | 68.9 |
| 150% or more | 313,670 | 26.3 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| Aged 18–64 | 4,367,934 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 43.4 | 21.4 | 35.1 |
| Under 100% | 2,899,741 | 66.4 | 100.0 | 65.4 | 26.6 | 8.0 |
| 100–150% | 498,345 | 11.4 | 100.0 | . . . | 33.1 | 66.9 |
| 150% or more | 969,848 | 22.2 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| Aged 65 or older | 1,935,708 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 48.7 | 19.8 | 31.5 |
| Under 100% | 1,302,436 | 67.3 | 100.0 | 72.4 | 24.3 | 3.4 |
| 100–150% | 214,325 | 11.1 | 100.0 | . . . | 31.6 | 68.4 |
| 150% or more | 418,947 | 21.6 | 100.0 | . . . | . . . | 100.0 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | ||||||
| NOTES: A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
. . . = not applicable.
|
||||||
| Characteristic | Aggregate poverty gap (thousands of dollars) | Reduction in poverty gap (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| If SSI payments were excluded | With SSI payments | ||
| Total | 15,390,849 | 4,423,993 | 71.3 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 6,600,996 | 1,916,465 | 71.0 |
| Female | 8,789,854 | 2,507,528 | 71.5 |
| Age group | |||
| Under 18 | 3,176,588 | 1,136,064 | 64.2 |
| 18–64 | 9,408,465 | 2,585,928 | 72.5 |
| 65 or older | 2,805,797 | 702,000 | 75.0 |
| Race | |||
| White | 8,019,139 | 2,207,033 | 72.5 |
| Black | 5,791,516 | 1,870,553 | 67.7 |
| Other | 1,580,194 | 346,407 | 78.1 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic | 3,088,345 | 863,756 | 72.0 |
| Non-Hispanic | 12,302,504 | 3,560,237 | 71.1 |
| SOURCE: Social Security administrative records matched to 2008 SIPP wave 7 and 8 results for December 2010. | |||
| NOTES: A "family" is two or more persons residing together who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption.
"Poverty gap" refers to the difference between family income and the poverty threshold for a family in poverty. Aggregate poverty gap is the sum of individual poverty gaps for all families with SSI recipients.
Family income data and poverty thresholds are for September–December 2010.
Totals do not necessarily equal the sum of rounded components.
|
|||
Notes
1 Beginning in 2014, the Census Bureau will conduct SIPP interviews yearly rather than every 4 months. SSA is funding a supplemental interview that the Census Bureau will field about halfway through the first year of the redesigned survey.
2 As in the prior edition of this study, SSI payment amounts are identified as actual payments received (rather than payments due), and DI benefits are identified as the monthly amount due before Medicare premium deductions.
3 We use a range of 1.1–24.2 percent in our estimates of the percentages of DI beneficiaries and SSI recipients residing in an institution, depending on DI and SSI program participation. These are based on internal estimates and are the same percentages used in the prior edition of this study. Although the weights used for this analysis may be antiquated, they are the best currently available.
4 Nondisabled dependents of disabled workers may also receive auxiliary DI benefits, but we exclude those individuals from this analysis. Therefore, the tables (and the accompanying discussion) cover only individuals who are entitled to DI benefits based on their own disability. In December 2010, nondisabled dependents accounted for less than 17 percent of DI beneficiaries (SSA 2011, Table 1).
5 SSI recipients who are both disabled and aged 65 or older are counted in the aged category.
6 Many respondents who reported Medicare coverage likely fell within the 72 percent of aged SSI recipients in our sample who had any Social Security income, many of whom would thus be eligible for Medicare. A few others may have received Medicare coverage through Railroad Retirement or other programs. However, we suspect that the self-reported 97 percent Medicare coverage rate is partially due to confusion between Medicare and Medicaid among SSI recipients.
References
DeCesaro, Anne, and Jeffrey Hemmeter. 2008. “Characteristics of Noninstitutionalized DI and SSI Program Participants.” Research and Statistics Note No. 2008-02. http://www.socialsecurity.gov/policy/docs/rsnotes/rsn2008-02.html.
[SSA] Social Security Administration. 2011. Annual Statistical Report on the Social Security Disability Insurance Program, 2010. Washington, DC: SSA. http://www.socialsecurity.gov/policy/docs/statcomps/di_asr/2010/index.html.
———. 2012. Annual Statistical Supplement to the Social Security Bulletin, 2011. Washington, DC: SSA. http://www.socialsecurity.gov/policy/docs/statcomps/supplement/2011/index.html.