Introduction
We are pleased to provide the revised Best Practices for Claimants' Representatives. We hope that all claimants’ representatives will use these best practices as an aid when advocating or appearing before the Social Security Administration.
The Social Security Administration operates one of the largest administrative adjudicatory systems in the world. The claimants who appear before us may feel overwhelmed by the legal and administrative requirements associated with pursuing a Social Security claim. Therefore, it is important for those most closely associated with this effort to work together in a collegial and professional manner to make this process as productive and efficient as possible. With those goals in mind, we share these best practices so that we can successfully fulfill our joint mission to provide the best possible service to the public.

Christopher Dillon
Deputy Chief Administrative Law Judge
Social Security Administration
Office of Hearings Operations
Jeffrey P. Kirkwood
Executive Director
Social Security Administration
Office of Analytics, Review, and Oversight
Office of Appellate Operations
November 2024
1.01 Be familiar with and follow the rules of conduct and standards of responsibility for representatives.
All claimants' representatives should be familiar with, and follow, the rules set forth at 20 CFR 404.1740 and 416.1540. These rules identify both the affirmative duties of a representative and the prohibited actions. See also Hearings, Appeals, and Litigation Law (HALLEX) Manual I-1-1-40.
1.02 Obtain as much information as possible from our website.
This practice is a general rule for all dealings with the Social Security Administration (SSA). At the hearing level, the majority of claimants are represented, and we encourage our employees to cooperate as much as possible with requests for information or assistance from representatives. Every personal request for information from hearing office personnel, however, diverts an employee from performing other hearing-related tasks. The time saved when representatives obtain information from the website can mean thousands of saved hours that can be devoted to handling other hearing related tasks. Additional information is available on SSA’s website for representatives.
1.03 Submit all necessary forms timely and properly.
This practice should include forms SSA-1696 (Claimant's Appointment of a Representative) and SSA-827 (Authorization to Disclose Information to SSA), as well as any fee agreement. If applicable, obtain and submit withdrawals and waivers from prior representatives to avoid possible delay in payment.
1.04 Establish and maintain a good working relationship with hearing office staff and management.
Participate in periodic group meetings with the Hearing Office Chief Administrative Law Judge and Hearing Office Director in the offices in which you practice, and any group meetings scheduled by the Regional Chief Administrative Law Judge in regions in which you practice. Open dialogue allows both representatives and the agency to exchange suggestions for improving service in the local area.
1.05 Provide timely notification to the hearing office of any change of address or phone number for either yourself or the claimant.
This practice ensures that claimants and representatives receive timely notifications and limits the potential for a non-appearance at a scheduled hearing.
1.06 When withdrawing representation, provide sufficient written notice to the claimant as well as to the hearing office.
If you decide to withdraw as a representative, please notify the hearing office and claimant as far in advance of the hearing date as possible. See 20 CFR 404.1740 and 416.1540. If you withdraw after a hearing is scheduled you may be in violation of the rules of conduct and standards of responsibility unless you can show that withdrawal is necessary due to extraordinary circumstances.
1.07 Ensure a fee agreement or a fee petition is consistent with Social Security law and policy.
We presume representatives will charge a fee for their services. See Social Security Act §§ 206(a) and (b), 1631(d)(2); 20 CFR 404.1700 et seq. and 416.1500 et seq.; and HALLEX I-1-2. If you intend to waive either your fee or the direct payment of your fees, you must submit appropriate documentation. See 20 CFR 404.1720 and 416.1520.
1.08 If the claimant decides to withdraw their request for hearing, provide timely and sufficient written notice of the withdrawal request to the hearing office.
Notifying the hearing office in a timely fashion, and preferably as far in advance of the hearing date as possible, increases the likelihood that another hearing can be scheduled during that time. This notification helps expedite the scheduling of hearings for other claimants, including those you represent.
Prior to an Administrative Law Judge Hearing
Under 20 CFR 404.935 and 416.1435, all claimants have a duty to inform us about or submit additional written evidence or a summary of the evidence no later than five business days before the date of the scheduled hearing. Therefore, we encourage all representatives to review the file and submit evidence as early in the hearing process as possible. Primary representatives who have registered for the Appointed Representative Services (ARS) system and who request eFolder access can view and download documents in Sections A, B, D, E, and F of the case documents and exhibit list tabs of their clients’ certified electronic folders (CEF) and can access any digital hearing recordings. Principal appointed representatives requesting direct fee payment must access and obtain copies of the claimant’s CEF through ARS, and as of November 4, 2020, must submit evidence electronically through ERE, ARS, or iAppeals. Secondary representatives associated with the principal representative using the same Employer Identification Number must arrange to obtain copies of the CEF from the principal representative. Hearing office and Appeals Council staff will no longer provide compact disc copies of the claimant’s CEF, except in limited circumstances. See HALLEX I-5-1-22.
Submitting Evidence
2.01 Submit or inform us about all known evidence relating to whether the claimant is disabled.
A claimant and representative must inform us about or submit all known evidence that relates to whether the claimant is disabled, subject to two narrow exceptions for privileged communications (oral and written communications that fall under the attorney work-product doctrine). However, neither the attorney-client privilege nor the attorney work-product doctrine allow withholding of factual information, medical opinions, or other medical evidence that we may consider in determining whether or not a claimant is entitled to benefits. See 20 CFR 404.1513(b) and 416.913(b). Failure to comply with the rules of conduct may lead to sanctions against a representative.
A representative may ask the hearing office for assistance in obtaining existing medical evidence from a medical source after they have made a good faith effort to obtain that evidence, or when the representative is unable to obtain the evidence for reasons beyond their control. See HALLEX I-2-5-14. These requests for assistance should be submitted no later than 30 days before the hearing to allow time for the hearing office to request and receive the evidence in time. Failure to do so could result in case processing delays.
2.02 Do not submit duplicative or illegible evidence.
Agency regulations require claimants and representatives to submit all evidence that relates to the claimant’s disability claim received from any source in its entirety, unless the same evidence was previously submitted to the Agency. See 20 CFR 404.1512(a) and 416.912(a).
Agency regulations also require the claimant’s representative to help the claimant obtain the information or evidence that we require the claimant to submit under our regulations. See 20 CFR 404.1740(b) and 416.1540(b). Submitting duplicative or illegible evidence significantly delays preparation of cases for hearing. Hearing office staff often spend several hours on any given case sorting out duplicate evidence. The sooner a case is prepared and exhibited, the sooner the hearing office can schedule the case. If a document is not readable because it is illegible or a poor copy, provide a typed and legible version or a clearer copy, when possible. Representatives can use ARS to ensure that evidence is not duplicative before submitting it.
2.03 Submit evidence as far in advance of the hearing as possible, using ARS.
Representatives should provide sufficient time for hearing office staff to associate the evidence with the file. Please submit evidence via ARS more than 15 business days before the hearing, as this practice allows hearing office personnel to exhibit the evidence and ensures that the claimant’s copy of the file includes a copy of all the evidence that has been received. It also gives the ALJ time to review all the evidence and helps to ensure that all relevant evidence is timely provided to experts scheduled to appear at a hearing. As noted above, the regulations provide that evidence must be submitted no later than five business days before the hearing, absent a showing of good cause for not adhering to this timeframe.
2.04 Do not submit voluminous records as one document.
Up to 200 pages at one time can be faxed into the electronic folder using the fax number and barcode supplied with the Acknowledgment of Hearing notice. However, we recommend smaller submissions, when possible, and submitting evidence via ARS rather than faxing. Instead of submitting new evidence into the record as one large exhibit, divide the evidence into separate exhibits containing the records from a single medical source, preferably less than 30 pages, for ease of processing and identification. This practice assists hearing office staff in reviewing the evidence for duplicates and exhibiting the records.

2.05 Before submitting evidence, check to ensure the evidence submitted belongs to the claimant.
This simple precaution significantly reduces the time hearing offices spend contacting representatives and re-associating evidence with the appropriate file, and avoids any potential loss of Personally Identifiable Information.
2.06 Submit evidence via ERE, ARS, or iAppeals when required/possible.
Appointed representatives are required to use ERE, ARS, or iAppeals, as available, to submit evidence electronically in claims for disability insurance benefits under title II of the Act and claims for SSI payments based on disability under title XVI of the Act, for which: (1) the representative requests direct fee payment, (2) the claim or case has an electronic folder, and (3) the claim is pending at OHO or the Appeals Council.
Although we do not require it, we also strongly encourage representatives who are not requesting direct payment to submit evidence electronically. Registered representatives with a recognized notice of appointment in a case should continue to use the “Upload New File” function in ARS to upload documents to the claimant’s electronic folder. This process does not require a barcode. Alternatively, representatives can also submit documents with a barcode using the “Send Individual Response” function in ARS and Electronic Records Express (ERE).
If you are not required to submit evidence electronically or are not registered for ARS, and you must submit evidence via fax, separate different sources by placing a barcode as the first document for each source and submit in chronological order. If submitting evidence by fax, be sure you are using the office’s efax number. The efax generates an electronic copy of the document and routes it to the designated email box associated with a specific hearing office. The efax number is toll-free, with area code “833” assigned to the servicing hearing office.
Submitting evidence separately by source is the most effective way to assist the hearing office in completing a timely and accurate review of the record. This allows the hearing office to associate new evidence with any previous medical or opinion evidence from the same source, and helps the hearing office to review the claimant’s case faster. Organizing records by date of medical service, oldest to newest, likewise assists the hearing office in quickly and accurately reviewing the claimant’s course of treatment with a particular source. This practice also assists hearing office staff with reviewing the evidence for duplicates and in exhibiting the records.
Ensure that the barcode is the first item faxed in order to ensure proper identification of all records. If you do not have a barcode for a particular case, please ask the hearing office to provide you with one. Barcodes may be photocopied and used more than once, but only for the same claimant.
2.07 Submit a cover letter with the evidence identifying what is being submitted and the dates of the evidence.
Submitting evidence with a cover letter and the dates of the evidence will assist hearing office staff in identifying duplicates and exhibiting the records. Clearly label newly submitted evidence with the source’s name, dates covered, and number of pages. For example: Attachment A – records from Mercy General Hospital, Topeka, KS, for the period 1/2017 through 6/2018, 16 pages; Attachment B – records from treating physician John Smith, M.D., Topeka, KS, for the period 12/2019 through 1/2020, 5 pages.
2.08 Do not submit medical evidence with non-medical evidence documents, such as appointment of representative forms or fee agreements.
As these documents are exhibited in different sections of the record, it requires more time to separate documents if they are submitted together.
2.09 Submit requests for a subpoena only after you have exhausted good faith, reasonable efforts to obtain the evidence and ensure that the request meets all of the requirements.
Our regulations require all subpoena requests to be submitted no later than 10 business days prior to the date of the scheduled hearing, unless you demonstrate good cause for a late request. See 20 CFR 404.950(d) and 416.1450(d) and HALLEX I-2-5-78 for requirements for subpoena requests. Please note that a subpoena will only be issued if you have met all of those requirements, including compliance with the timeframe for submitting a request, and after you have made good faith, reasonable efforts to obtain the evidence without a subpoena.
Pre-hearing Brief
2.10 Address employment (substantial gainful activity, unsuccessful work attempts, sheltered work environments, etc.) and earnings issues in a pre-hearing brief or at the hearing.
Be sure to distinguish short or long-term disability, vacation, or bonus pay, which may appear as earnings after alleged onset.
2.11 Address workers’ compensation issues in a pre-hearing brief or at the hearing.
If there has been a settlement, provide appropriate proof.
2.12 Submit timely and concise pre-hearing briefs whenever possible.
This practice assists an ALJ in preparing for the hearing and focusing on the issues or arguments you wish to raise. Pre-hearing briefs are most effective when they identify specific evidence supporting a finding of disability. Any pre-hearing written statements are required to be submitted no later than 5 business days before the date set for the hearing, absent a showing of good cause, per 20 CFR 404.949 and 416.1449.
Submitting On-The-Record (OTR) Decision Requests
2.13 Clearly label an OTR decision request "OTR Decision Request" and submit as early as possible (but only when a request is appropriate).
OTR decision requests are not appropriate in every case, and you should only request an OTR decision when the evidence in the record unequivocally supports a favorable outcome.
2.14 Identify evidence that supports the OTR Decision.
OTR decision requests should include a concise summary at the beginning of the brief outlining the argument, followed by a more detailed explanation specifically directing the reviewer's attention to evidence supporting a favorable decision.
2.15 Make sure the evidence supports the alleged onset date.
Onset issues are one of the most frequent reasons an OTR decision request cannot be granted.
2.16 When contacted, work with attorney advisors to expedite decisions.
Attorney advisors may review and screen cases for an OTR decision, and some senior attorney advisors have the authority to issue a fully favorable OTR decision when it is warranted. If you are contacted by an attorney advisor regarding substantial gainful activity or onset issues in a particular case, discuss the matter with the attorney advisor to see if the issue can be resolved without a hearing.
2.17 Submit updated evidence with an OTR decision request.
With updated evidence, we may be able to issue a fully favorable decision without a hearing, which saves time and resources for both the claimant and the hearing office.
Submitting Dire Need and Terminal Illness Requests, or
Information Regarding Incarcerated Individuals
2.18 Notify the hearing office when the claimant has a terminal condition, is homeless, or in dire need. Include appropriate documentation supporting these allegations.
If the allegation is supported, notifying a hearing office of these circumstances can expedite the processing of a case. You must provide sufficient documentation to support the request. The criteria for critical case processing are located in HALLEX I-2-1-40.
2.19 If the claimant is incarcerated, know our procedures and keep the hearing office informed.
It is very important that the hearing office be apprised of the status of an incarcerated claimant and the anticipated duration of the incarceration.
Scheduling, logistical and other issues arise when a claimant is incarcerated. These may include the manner of appearance available at the correctional facility and scheduling a consultative examination. As stated in HALLEX I-2-0-15, if the claimant is incarcerated and an appearance by agency video and online video is not available, we will schedule the claimant’s appearance by audio, unless we find that there are facts in the particular case that provide a good reason to schedule the claimant’s appearance in person if allowed by the place of confinement, or by agency video, online video, or in person upon the claimant’s release.
Scheduling Hearings
2.20 Provide scheduling availability.
Hearings require the participation of numerous individuals. In addition to the ALJ, the claimant, the hearing reporter, and the representative, others participating may include one or more expert witnesses, other witnesses, and an interpreter. When requested, please provide your scheduling availability to ease the scheduling process for all involved.
2.21 Do not request postponements unless essential.
Be flexible when providing dates and times for hearings, and timely request postponements in writing whenever possible. When you have already agreed to the time of a scheduled hearing, avoid requesting a postponement for a conflict that arises later.
2.22 Consider appearing at the hearing by agency video, online video, or audio (telephone)
We encourage you to consider appearing at hearings by agency video, or remotely by online video or by audio using a telephone. We will conduct these hearings the same way as we conduct in-person hearings. We require agreement in writing prior to scheduling an online video hearing.
When a hearing is held by online video, the claimant and their representative can attend their online video hearing from any private place with a secure internet connection using their camera enabled phone, tablet, or computer. The claimant will see the ALJ and their representative if they are not in the same location. Other participants such as vocational experts, medical experts and interpreters will join by phone.
When a hearing is held by audio/telephone, the claimant and their representative must be available to answer their telephone at the number included in the notice of hearing. A member of our hearing office staff will call a few minutes before the scheduled hearing time.
For audio hearings using a telephone and online video hearings, the representative and the claimant must be in a private, quiet place for the hearing to protect privacy and avoid distractions.
When a hearing is held by agency video, the claimant and their representative may appear at a field office or hearing office, as directed by the agency.
More information regarding our hearing options can be found here: Ways to Attend Your Social Security Hearing Before a Judge.
2.23 When representing a child, have an adult available to care for the child during the entirety of the hearing.
Remind claimants that the child needs to be present for the hearing unless directed otherwise by the ALJ. However, a child claimant may not be able, or required, to remain present in the hearing room for the entire hearing. An adult must be present to care for the child outside of the hearing room. SSA staff will not provide care for the child.
2.24 Notify the hearing office in advance if any special accommodation or assistance is needed.
The agency will provide an interpreter free of charge if a claimant has difficulty understanding or communicating in English. However, interpreters for some languages are more difficult to obtain. Please ensure that the request is submitted as far in advance as possible. Additionally, under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, other accommodations may be possible to ensure that claimants are able to fully participate in their hearings. Make such requests as far in advance of the hearing as possible. For more information, see HALLEX I-2-0-8.
After an Administrative Law Judge Hearing

3.01 If you are permitted to submit post-hearing evidence by an ALJ, you must do so within the time period allotted by the ALJ. Please submit the evidence as soon as possible and include a written brief or letter identifying how the evidence supports a favorable decision.
This practice will assist the ALJ in reviewing the records and appropriately focus attention on the information supporting your arguments, resulting in the issuance of a timely decision. If you are unable to submit evidence within the time period allotted by the ALJ, timely advise the hearing office of the circumstances, including whether you are requesting additional time, or if you need our assistance in obtaining the evidence (see information in 2.03). If you did not inform the hearing office about the evidence or you submitted it less than 5 business days prior to the date set for the hearing, and you did not address the issue at the hearing, include a statement with the evidence providing an explanation regarding the reasons for your actions. This increases the likelihood that the ALJ will accept the evidence under the good cause provisions of 20 CFR 404.935(b) and 416.1435(b).
3.02 Submit fee petitions within 60 days of a decision or as soon as possible after your services have been terminated or withdrawn.
Submitting fee documents within this period will have a significant impact on the time a representative waits for payment. This practice reduces the number of follow-ups necessary to determine if a fee petition will be submitted, allowing the ALJ to act on the fee authorization at an earlier date. It reduces the likelihood that funds withheld for direct payment will be released to the claimant, and reduces the wait time if administrative review of an authorized fee is requested.
Please note: To submit a fee petition electronically after a decision is issued, you must request a barcode and upload the fee petition by using “Send Individual Response” within ERE or ARS.
Actions Before the Appeals Council
Requests for Review
4.01 How to ask for Appeals Council review.
You must ask for an Appeals Council (AC) review within 60-days of receiving your hearing decision. We provide three ways to request an AC review as described below. Please use only one of these methods. Use of multiple methods is unnecessary and may result in delay.
-
iAppeal Online Appeals Application
The AC Request for Review link below will take you to our Getting Ready Webpage that provides helpful information before you start your online appeal. This is the preferred method for filing an appeal.
-
Download Request for Hearing Review/Order
Prior to completing the appeal form, you should look over our instructions at Request for Review of Hearing Decision/Order. You can then fill-in the HA-520, Request for Review of Hearing Decision/Order Form; print/save the file and return it to us. You should send it directly to:
Social Security Administration
Office of Appellate Operations
6401 Security Blvd.
Baltimore, MD 21235-6401Instructions: Request for Review of Hearing Decision/Order
Download Fillable Form: HA-520 Contact Us
You can also file an appeal by contacting your local Social Security office, local hearing office, or by calling our toll-free telephone number (1-800-772-1213) (TTY 1-800-325-0778) and filling out a request for review form.
4.02 Preferred method and note for submitting a request for review.
The preferred method to file an appeal of an Administrative Law Judge decision or dismissal is through the secure online process (iAppeals i520), available at https://www.ssa.gov/benefits/disability/appeal.html.
If you must submit an appeal via paper, this Appointed Representative Guide to Requesting Appeals Council Review chart describes the three methods to submit it to the Appeals Council.
Using any other method, including submission by Electronic Records Express or by fax with a barcode, is discouraged as they can cause significant delays in processing because AC staff does not receive an alert that a request was filed.
4.03 Candor and truthfulness is necessary in any submission to the AC, including the request for review.
Please note that submissions to the AC, including the request for review, additional arguments, and any additional evidence, are governed by 18 USC §§ 1001 and 1621. These statutes, as well as our regulations, require representatives to be forthright in their dealings with us and prohibit a representative from knowingly making false or misleading oral or written statements, assertions, or representations to us about a material fact or law (20 CFR 404.1740 and 416.1540).
Requesting Critical/Terminal Illness (TERI) Case Status
4.04 If a claimant’s case is critical, let us know when you file the request for review.
If you believe a claimant’s case qualifies for expedited processing under our critical case procedures at HALLEX I-3-1-5, clearly state this in the request for review. Point to or provide evidence to support your request. You can follow up on the request by calling the Claimant and Public Assistance Branch (CPAB) at (877) 670-2722.
4.05 If you later learn that a claimant’s situation is critical, contact us immediately.
If a claimant’s medical or financial situation becomes critical after you have already filed the request for review, fax a brief statement and supporting documents to CPAB staff at (833) 763-0405. You can also contact the CPAB staff by phone at (877) 670-2722. A specialist on the CPAB staff will evaluate the claimant’s situation under HALLEX I-3-1-5 and take appropriate action.
Procedural Requests
4.06 If you are requesting a copy of the record, submit a clear request.
If you wish to receive a copy of the exhibits or hearing recording in a case, please clearly state this request at the beginning of your correspondence to facilitate support staff screening and action on your request. The AC will generally not send copies of a hearing recording or claim(s) file material if you are registered for online access to the electronic folder. Upon request, the AC will grant you a 25-day extension of time (EOT) and will include two AC level barcodes that you can use to submit additional evidence or arguments.
4.07 Be specific in requesting an EOT.
Requests for an EOT should explain how much additional time you need and why the AC should grant the request. For an initial EOT request, the AC generally provides 25 days from the date of the notice granting the EOT. For second requests, or requests for more than 40 days, the AC will consider the particular set of circumstances in each case and whether there is good cause for requesting a second EOT or a longer than usual timeframe to submit additional evidence or arguments. If the AC grants an EOT, we will provide you with barcodes to submit additional evidence or arguments.
4.08 If you want barcodes, request an EOT.
You may receive barcodes with the AC acknowledgment of your request for review; however, the best way to ensure that you get AC level barcodes is to request an EOT when you submit the request for review.
Representative Access to Electronic Folders
4.09 Take advantage of your ability to access a claimant’s electronic folder.
Appointed representatives who have registered with SSA for ARS and who request eFolder access are able to view and download documents in Sections A, B, D, E, and F of the Case Documents and Exhibit List tabs of their clients’ certified electronic folders (CEF). As long as the case is pending before the AC, representatives can also download any digital hearing recordings in the CEF to their personal computers.
4.10 Make the AC aware of any changes in representation.
If a claimant has appointed more than one representative, only the principal representative (as indicated on the Form SSA-1696 with the most recent date) will have access to the CEF. If a claimant’s principal representative changes, it is very important that you notify the AC right away so we can update our records.
4.11 Other issues to note about access to the CEF:
If our records indicate that you have access to the CEF, we will not send you copies of a claimant’s hearing recording or exhibited evidence on compact discs (CD). We will grant you an extension of time and notify you in our letter that our records indicate you have access to the CEF.
If a claimant has more than one claim pending at the same time (e.g., a claimant has a claim pending at the hearing level and at the AC), representatives will not have access to the CEF of either claim. A CD will be burned for these specific cases.
A representative has access to a claimant’s CEF for 90 days after the AC completes action in a case. During the 90 days, only the representative recorded in our case control system at the time the case was closed has access to the CEF. If the claimant obtains a new representative to file a civil action, the new representative will not have access to the claimant’s CEF.
Evidence Submissions
4.12 Submit any additional evidence or comments at the same time as the request for review.
For internal review and association purposes, it is very helpful if you submit the request for review and all evidence at the same time.
4.13 If you have additional evidence, explain how it is related to the period at issue.
In regard to new evidence, the AC applies 20 CFR 404.970 and 416.1470. The AC will only consider additional evidence that is new, material, and related to the period on or before the date of the hearing decision, and there is a reasonable probability that the additional evidence would change the outcome of the decision. Additionally, the AC will only consider additional evidence if you show good cause for not informing us about or submitting the evidence at least 5 business days before the date of the scheduled hearing.
4.14 Avoid submitting duplicative evidence.
The AC has access to the entire record at prior levels of adjudication, including the hearing level. Please do not resubmit information that is already available to the AC.
4.15 Submit evidence to the AC via ERE, ARS, or iAppeals if you are required to do so or whenever possible even if you are not.
You may be required to submit evidence directly to the electronic folder via ARS, iAppeals, or the Electronic Records Express website. See 2.06, above. Even if you are not required to submit evidence electronically, you are encouraged to do so. You can also submit evidence by paper fax directly to the AC. Please see this Appointed Representative Guide to Requesting Appeals Council Review chart for a detailed explanation of each method. Please note, as discussed in section 4.02 above, you should never submit a request for review via the Electronic Records Express website.
4.16 When submitting evidence, organizing it chronologically and by source greatly aids case processing.
The AC reviews all evidence presented at prior levels of adjudication as well as evidence submitted while a claim is pending with the AC. Submitting evidence separately by source is the most effective way to assist the AC in completing a timely and accurate review of the record. Instead of submitting all new evidence into the record as one large exhibit, divide the evidence into separate exhibits containing the records from a single medical source. This allows the AC to associate new evidence with any previous medical or opinion evidence from the same source and helps the AC to review the claimant’s case faster. Organizing records by date of medical service, oldest to newest, assists the AC in quickly and accurately reviewing the claimant’s course of treatment with a particular source.
Clearly label newly-submitted evidence with the source’s name, dates covered, and number of pages. For example: Attachment A – records from Mercy General Hospital, Topeka, KS, for the period 1/2012 through 6/2013, 16 pages; Attachment B – records from treating physician John Smith, M.D., Topeka, KS, for the period 12/2011 through 1/2013, 5 pages.
Contentions
4.17 Contentions should be specific.
The AC appreciates receiving concise, focused arguments. We recommend using 2,000 words or less if possible.
4.18 Contentions need not include a recitation of the jurisdictional history or evidence generally, unless related to a specific point of contention.
As the record is already before the AC and the AC reviews the entire record in each claim, a summary of the evidence is not necessary. There is also no need to send us a copy of the administrative law judge’s decision or a copy of the hearing recording.
4.19 Cite to the record.
Citing specific exhibits and pertinent page numbers in support of a specific point of contention helps us review the record more efficiently.
Status Inquiries
4.20 Do not make automatic, multiple requests for the status of a request for review.
You can verify that the AC has received the request for review through the online status report available in ARS, by contacting your local Social Security office or hearing office, or by calling our Congressional and Public Affairs Branch staff at (877) 670-2722 or SSA’s National 800 Number staff at (800) 772-1213.
4.21 Requirements to view the online AC status reports.
On August 26, 2013, SSA expanded ARS to include an online status report for cases pending at the AC. To have access to the AC status report, representatives must register with SSA for ARS. Additionally, the case must be pending before the AC with a record in our case control system, and the representative attempting to access the report must be shown as the claimant’s representative in our case control system.
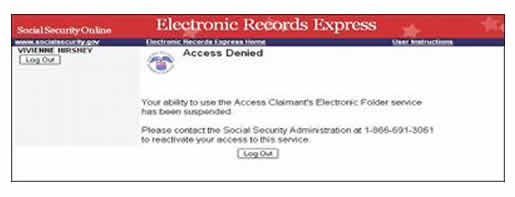
If you are denied access and the error message says, “Your ability to use the Access Claimant’s Electronic Folder service has been suspended” (see screenshot below), please call the telephone number provided in the message to reinstate your access. If you have already called to reinstate access and the problem persists, send your REP ID, contact information, the error message, and the claimant’s full name and last 4 digits of the SSN to OHO.HQ.ARS@ssa.gov and request assistance.
4.22 Representatives have three options for viewing their AC status report:
- Search for individual cases by SSN. (Cases must be active or closed within the last 90 days.)
- View a list of up to 100 of the oldest cases for all AC offices. (Cases must be active or closed within the last 90 days.)
- Download all cases for all AC offices in a spreadsheet file. (Cases must be active or closed within the last 90 days.)
4.23 The view-only AC status report will display the following information:
- Claimant Name (Last, First)
- Last 4 Digits of SSN
- Case Status/Status Date
- Appeals Office with Jurisdiction
- Transfer Information
- Electronic Case (Yes or No)
- Request Date
- Expedited (Yes or No)
4.24 The downloaded AC status report will display the following information:
- Claimant Name (Last, First)
- Last 4 Digits of SSN
- Case Status/Status Date
- Claim Type
- Appeals Office with Jurisdiction
- Transfer Information
- Electronic Case (Yes or No)
- Request Date
- Expedited (Yes or No)
- Fee Agreement (Yes or No)
- Fee Petition (Yes or No)
- Title II and Title XVI (T2 & T16, respectively) Decision Type
NOTE: The Fee Agreement field displayed in the downloaded AC Status Report will always contain a NO unless the AC issues a favorable decision.
4.25 What it means if the T2 or T16 Decision field shows “Other.”
The AC status report may show cases with dispositions displayed as “Other.” These are not requests for review.
The workload types below will display the T2 & T16 disposition code “Other” when one of the following types of cases is closed.

NOTE: A disposition code of “Other” does not delay or prevent an appeal from being filed. If you would like to file an appeal, please timely file the appeal according to the instructions in the Notice of Decision.
4.26 Further descriptions of the “Case Status” field:
- New case – New request entered in control system pending further screening
- Case workup – Screening or case preparation actions (e.g., responses to claimant or rep initiated requests for extensions, file material, timeliness of filing etc.)
- Pending analyst assignment – Preparation actions completed; in assignment queue
- Assigned to analyst – Assigned to analyst for workup and referral to adjudicator
- Assigned to adjudicator – With AC for disposition
- Document preparation – AC notice prepared for release
4.27 Other issues to note about the AC online status report:
- Only the representative recorded in the AC’s case control system will have access to the detailed information in the status report. If a claimant’s principal representative changes, it is very important that you notify the AC right away so we can update our records. (The AC recognizes as the representative of record the person designated as the principal representative on the Form SSA-1696 with the most recent date.)
- The AC online status report only provides information for active cases or cases closed within the last 90 days. Only the representative recorded in our case control system at the time the case was closed has access to the online status report.
- Federal court cases are excluded from the AC status report.