P.L. 78–410, Approved July 1, 1944 (58 Stat. 682)
Public Health Service Act
* * * * * * *
Sec. 306. [42 U.S.C. 242k]
* * * * * * *
(e) For the purpose of producing comparable and uniform health information and statistics, there is established the Cooperative Health Statistics System. The Secretary, acting through the Center, shall—
(1) coordinate the activities of Federal agencies involved in the design and implementation of the System;
* * * * * * *
GRANTS FOR COMPREHENSIVE HEALTH PLANNING AND PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICES
Grants to States for Comprehensive State Health Planning
Sec. 314. [42 U.S.C. 246] (a) (1) Authorization.—In order to assist the States in comprehensive and continuing planning for their current and future health needs, the Secretary is authorized during the period beginning July 1, 1966, and ending June 30, 1973, to make grants to States which have submitted, and had approved by the Secretary, State plans for comprehensive State health planning. For the purposes of carrying out this subsection, there are hereby authorized to be appropriated $2,500,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1967, $7,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1968, $10,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1969, $15,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1970, $15,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1971, $17,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1972, $20,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1973, and $10,000,000 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1974.
(2) State plans for comprehensive state health planning.—In order to be approved for purposes of this subsection, a State plan for comprehensive State health planning must—
(A) designate, or provide for the establishment of, a single State agency, which may be an interdepartmental agency, as the sole agency for administering or supervising the administration of the State’s health planning functions under the plan;
(B) provide for the establishment of a State health planning council, which shall include representatives of Federal, State, and local agencies (including as an ex officio member, if there is located in such State one or more hospitals or other health care facilities of the Department of Veterans Affairs the individual whom the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall have designated to serve on such council as the representative of the hospitals or other health care facilities of such Department which are located in such State) and nongovernmental organizations and groups concerned with health (including representation of the regional medical program or programs included in whole or in part within the State), and of consumers of health services, to advise such State agency in carrying out its functions under the plan, and a majority of the membership of such council shall consist of representatives of consumers of health services;
(C) set forth policies and procedures for the expenditure of funds under the plan, which, in the judgment of the Secretary, are designed to provide for comprehensive State planning for health services (both public and private and including home health care), including the facilities and persons required for the provision of such services, to meet the health needs of the people of the State and including environmental considerations as they relate to public health;
(D) provide for encouraging cooperative efforts among governmental or nongovernmental agencies, organizations and groups concerned with health services, facilities, or manpower, and for cooperative efforts between such agencies, organizations, and groups and similar agencies, organizations, and groups in the fields of education, welfare, and rehabilitation;
(E) contain or be supported by assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the funds paid under this subsection will be used to supplement and, to the extent practicable, to increase the level of funds that would otherwise be made available by the State for the purpose of comprehensive health planning and not to supplant such non-Federal funds;
(F) [235] provide such methods of administration (including methods relating to the establishment and maintenance of personnel standards on a merit basis, except that the Secretary shall exercise no authority with respect to the selection, tenure of office, and compensation of any individual employed in accordance with such methods) as are found by the Secretary to be necessary for the proper and efficient operation of the plan;
(G) provide that the State agency will make such reports, in such form and containing such information, as the Secretary may from time to time reasonably require, and will keep such records and afford such access thereto as the Secretary finds necessary to assure the correctness and verification of such reports;
(H) provide that the State agency will from time to time, but not less often than annually, review its State plan approved under this subsection and submit to the Secretary appropriate modifications thereof;
(I) effective July 1, 1968, (i) provide for assisting each health care facility in the State to develop a program for capital expenditures for replacement, modernization, and expansion which is consistent with an overall State plan developed in accordance with criteria established by the Secretary after consultation with the State which will meet the needs of the State for health care facilities, equipment, and services without duplication and otherwise in the most efficient and economical manner, and (ii) provide that the State agency furnishing such assistance will periodically review the program (developed pursuant to clause (i)) of each health care facility in the State and recommend appropriate modification thereof;
(J) provide for such fiscal control and fund accounting procedures as may be necessary to assure proper disbursement of and accounting for funds paid to the State under this subsection; and
(K) contain such additional information and assurances as the Secretary may find necessary to carry out the purposes of this subsection.
(3)(A) State allotments.—From the sums appropriated for such purpose for each fiscal year, the several States shall be entitled to allotments determined, in accordance with regulations, on the basis of the population and the per capita income of the respective States; except that no such allotment to any State for any fiscal year shall be less than 1 per centum of the sum appropriated for such fiscal year pursuant to paragraph (1). Any such allotment to a State for a fiscal year shall remain available for obligation by the State, in accordance with the provisions of this subsection and the State’s plan approved thereunder, until the close of the succeeding fiscal year.
(B) The amount of any allotment to a State under subparagraph (A) for any fiscal year which the Secretary determines will not be required by the State, during the period for which it is available, for the purposes for which allotted shall be available for reallotment by the Secretary from time to time, on such date or dates as he may fix, to other States with respect to which such a determination has not been made, in proportion to the original allotments to such States under subparagraph (A) for such fiscal year, but with such proportionate amount for any of such other States being reduced to the extent it exceeds the sum the Secretary estimates such State needs and will be able to use during such period; and the total of such reductions shall be similarly reallotted among the States whose proportionate amounts were not so reduced. Any amount so reallotted to a State from funds appropriated pursuant to this subsection for a fiscal year shall be deemed part of its allotment under subparagraph (A) for such fiscal year.
(4) Payments to states.—From each State’s allotment for a fiscal year under this subsection, the State shall from time to time be paid the Federal share of the expenditures incurred during that year or the succeeding year pursuant to its State plan approved under this subsection. Such payments shall be made on the basis of estimates by the Secretary of the sums the State will need in order to perform the planning under its approved State plan under this subsection, but with such adjustments as may be necessary to take account of previously made underpayments or overpayments. The “Federal share” for any State for purposes of this subsection shall be all, or such part as the Secretary may determine, of the cost of such planning, except that in the case of the allotments for the fiscal year ending June 30, 1970, it shall not exceed 75 per centum of such cost.
* * * * * * *
Sec. 317. [42 U.S.C. 247b]
* * * * * * *
(j) Authorization of Appropriations.—
(1) Except for grants for immunization programs the authorization of appropriations for which are established in paragraph (2), for grants under subsections (a) and (k)(1) of this section for preventive health service programs to immunize without charge children, adolescents, and adults against vaccine-preventable diseases, there are authorized such sums as may be necessary for each of the fiscal years 1998 through 2005. Not more than 10 percent of the total amount appropriated under the preceding sentence for any fiscal year shall be available for grants under subsection (k)(1) of this section for such fiscal year.
(2) For grants under subsection (a) of this section for preventive health service programs for the provision without charge of immunizations with vaccines approved for use, and recommended for routine use, after October 1, 1997, there are authorized to be appropriated such sums as may be necessary.
* * * * * * *
SCREENINGS, REFERRALS, AND EDUCATION REGARDING LEAD POISONING
Sec. 317A. [42 U.S.C. 247b-1]
(a) Authority for Grants.—
(1) In general.—Subject to paragraph (2), the Secretary, acting through the Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, may make grants to States and political subdivisions of States for the initiation and expansion of community programs designed—
(A) to provide, for infants and children—
(i) screening for elevated blood lead levels;
(ii) referral for treatment of such levels; and
(iii) referral for environmental intervention associated with such levels; and
(B) to provide education about childhood lead poisoning.
(2) Authority regarding certain entities.—With respect to a geographic area with a need for activities authorized in paragraph (1), in any case in which neither the State nor the political subdivision in which such area is located has applied for a grant under paragraph (1), the Secretary may make a grant under such paragraph to any grantee under section 329, 330, 340, or 340A for carrying out such activities in the area.
(3) Provision of all services and activities through each grantee.—In making grants under paragraph (1), the Secretary shall ensure that each of the activities described in such paragraph is provided through each grantee under such paragraph. The Secretary may authorize such a grantee to provide the services and activities directly, or through arrangements with other providers.
(b) Status as Medicaid Provider.—
(1) In general.—Subject to paragraph (2), the Secretary may not make a grant under subsection (a) unless, in the case of any service described in such subsection that is made available pursuant to the State plan approved under title XIX of the Social Security Act for the State involved—
(A) the applicant for the grant will provide the service directly, and the applicant has entered into a participation agreement under the State plan and is qualified to receive payments under such plan; or
(B) the applicant will enter into an agreement with a provider under which the provider will provide the service, and the provider has entered into such a participation agreement and is qualified to receive such payments.
(2) Waiver regarding certain secondary agreements.—
(A) In the case of a provider making an agreement pursuant to paragraph (1)(B) regarding the provision of services, the requirement established in such paragraph regarding a participation agreement shall be waived by the Secretary if the provider does not, in providing health care services, impose a charge or accept reimbursement available from any third-party payor, including reimbursement under any insurance policy or under any Federal or State health benefits plan.
(B) A determination by the Secretary of whether a provider referred to in subparagraph (A) meets the criteria for a waiver under such subparagraph shall be made without regard to whether the provider accepts voluntary donations regarding the provision of services to the public.
(c) Priority in Making Grants.—In making grants under subsection (a), the Secretary shall give priority to applications for programs that will serve areas with a high incidence of elevated blood lead levels in infants and children.
(d) Grant Application.—No grant may be made under subsection (a), unless an application therefor has been submitted to, and approved by, the Secretary. Such an application shall be in such form and shall be submitted in such manner as the Secretary shall prescribe and shall include each of the following:
(1) A complete description of the program which is to be provided by or through the applicant.
(2) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the program to be provided under the grant applied for will include educational programs designed to—
(A) communicate to parents, educators, and local health officials the significance and prevalence of lead poisoning in infants and children (including the sources of lead exposure, the importance of screening young children for lead, and the preventive steps that parents can take in reducing the risk of lead poisoning) which the program is designed to detect and prevent; and
(B) communicate to health professionals and paraprofessionals updated knowledge concerning lead poisoning and research (including the health consequences, if any, of low-level lead burden; the prevalence of lead poisoning among all socioeconomic groupings; the benefits of expanded lead screening; and the therapeutic and other interventions available to prevent and combat lead poisoning in affected children and families).
(3) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the applicant will report on a quarterly basis the number of infants and children screened for elevated blood lead levels, the number of infants and children who were found to have elevated blood lead levels, the number and type of medical referrals made for such infants and children, the outcome of such referrals, and other information to measure program effectiveness.
(4) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the applicant will make such reports respecting the program involved as the Secretary may require.
(5) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the applicant will coordinate the activities carried out pursuant to subsection (a) with related activities and services carried out in the State by grantees under title V or XIX of the Social Security Act.
(6) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that Federal funds made available under such a grant for any period will be so used as to supplement and, to the extent practical, increase the level of State, local, and other non-Federal funds that would, in the absence of such Federal funds, be made available for the program for which the grant is to be made and will in no event supplant such State, local, and other non-Federal funds.
(7) Assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the applicant will ensure complete and consistent reporting of all blood lead test results from laboratories and health care providers to State and local health departments in accordance with guidelines of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for standardized reporting as described in subsection (m) of this section.
(8) Such other information as the Secretary may prescribe.
* * * * * * *
HEALTH CENTERS
Sec. 330. [42 U.S.C. 254b]
(a) Health Center Defined.—
(1) In general.—For purposes of this section, the term “health center” means an entity that serves a population that is medically underserved, or a special medically underserved population comprised of migratory and seasonal agricultural workers, the homeless, and residents of public housing, by providing, either through the staff an supporting resources of the center or through contracts or cooperative arrangements—
(A) required primary health services (as defined in subsection (b)(1) of this section); and
(B) as may be appropriate for particular centers, additional health services (as defined in subsection (b)(2) of this section) necessary for the adequate support of the primary health services required under subparagraph (A);
for all residents of the area served by the center (hereafter referred to in this section as the “catchment area”).
(2) Limitation.—The requirement in paragraph (1) to provide services for all residents within a catchment area shall not apply in the case of a health center receiving a grant only under subsection (g), (h), or (i) of this section.
(b) Definitions.—For purposes of this section:
(1) Required primary health services.—
(A) In general.—The term “required primary health services” means—
(i) basic health services which, for purposes of this section, shall consist of—
(I) health services related to family medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, obstetrics, or gynecology that are furnished by physicians and where appropriate, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and nurse midwives;
(II) diagnostic laboratory and radiologic services;
(III) preventive health services, including—
(aa) prenatal and perinatal services;
(bb) appropriate cancer screening;
(cc) well-child services;
(dd) immunizations against vaccine-preventable diseases;
(ee) screenings for elevated blood lead levels, communicable diseases, and cholesterol;
(ff) pediatric eye, ear, and dental screenings to determine the need for vision and hearing correction and dental care;
(gg) voluntary family planning services; and
(hh) preventive dental services;
(ii) referrals to providers of medical services (including specialty referral when medically indicated) and other health-related services (including substance abuse and mental health services);
(iii) patient case management services (including counseling, referral, and follow-up services) and other services designed to assist health center patients in establishing eligibility for and gaining access to Federal, State, and local programs that provide or financially support the provision of medical, social, housing, educational, or other related services;
(iv) services that enable individuals to use the services of the health center (including outreach and transportation services and, if a substantial number of the individuals in the population served by a center are of limited English-speaking ability, the services of appropriate personnel fluent in the language spoken by a predominant number of such individuals); and
(v) education of patients and the general population served by the health center regarding the availability and proper use of health services.
(B) Exception.— With respect to a health center that receives a grant only under subsection (g) of this section, the Secretary, upon a showing of good cause, shall—
(i) waive the requirement that the center provide all required primary health services under this paragraph; and
(ii) approve, as appropriate, the provision of certain required primary health services only during certain periods of the year.
(2) Additional health services.— The term “additional health services” means services that are not included as required primary health services and that are appropriate to meet the health needs of the population served by the health center involved. Such term may include—
(A) behavioral and mental health and substance abuse services;
(B) recuperative care services;
(C) environmental health services, including—
(i) the detection and alleviation of unhealthful conditions associated with—
(I) water supply;
(II) chemical and pesticide exposures;
(III) air quality; or
(IV) exposure to lead;
(ii) sewage;
(iii) solid waste disposal;
(iv) rodent and parasitic infestation;
(v) field sanitation;
(vi) housing; and
(vii) other environmental factors related to health; and
(D) in the case of health centers receiving grants under subsection (g) of this section, special occupation-related health services for migratory and seasonal agricultural workers, including—
(i) screening for and control of infectious diseases, including parasitic diseases; and
(ii) injury prevention programs, including prevention of exposure to unsafe levels of agricultural chemicals including pesticides.
(3) Medically underserved populations.—
(A) In general.— The term “medically underserved population” means the population of an urban or rural area designated by the Secretary as an area with a shortage of personal health services or a population group designated by the Secretary as having a shortage of such services.
(B) Criteria.— In carrying out subparagraph (A), the Secretary shall prescribe criteria for determining the specific shortages of personal health services of an area or population group. Such criteria shall—
(i) take into account comments received by the Secretary from the chief executive officer of a State and local officials in a State; and
(ii) include factors indicative of the health status of a population group or residents of an area, the ability of the residents of an area or of a population group to pay for health services and their accessibility to them, and the availability of health professionals to residents of an area or to a population group.
(C) Limitation.— The Secretary may not designate a medically underserved population in a State or terminate the designation of such a population unless, prior to such designation or termination, the Secretary provides reasonable notice and opportunity for comment and consults with—
(i) the chief executive officer of such State;
(ii) local officials in such State; and
(iii) the organization, if any, which represents a majority of health centers in such State.
(D) Permissible designation.— The Secretary may designate a medically underserved population that does not meet the criteria established under subparagraph (B) if the chief executive officer of the State in which such population is located and local officials of such State recommend the designation of such population based on unusual local conditions which are a barrier to access to or the availability of personal health services.
(c) Planning Grants.—
(1) In general.—
(A) Centers.— The Secretary may make grants to public and nonprofit private entities for projects to plan and develop health centers which will serve medically underserved populations. A project for which a grant may be made under this subsection may include the cost of the acquisition and lease of buildings and equipment (including the costs of amortizing the principal of, and paying the interest on, loans) and shall include—
(i) an assessment of the need that the population proposed to be served by the health center for which the project is undertaken has for required primary health services and additional health services;
(ii) the design of a health center program for such population based on such assessment;
(iii) efforts to secure, within the proposed catchment area of such center, financial and professional assistance and support for the project;
(iv) initiation and encouragement of continuing community involvement in the development and operation of the project; and
(v) proposed linkages between the center and other appropriate provider entities, such as health departments, local hospitals, and rural health clinics, to provide better coordinated, higher quality, and more cost-effective health care services.
(B) Managed care network and plans.— The Secretary may make grants to health centers that receive assistance under this section to enable the centers to plan and develop a managed care network or plan. Such a grant may only be made for such a center if—
(i) the center has received grants under subsection (e)(1)(A) of this section for at least 2 consecutive years preceding the year of the grant under this subparagraph or has otherwise demonstrated, as required by the Secretary, that such center has been providing primary care services for at least the 2 consecutive years immediately preceding such year; and
(ii) the center provides assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that the provision of such services on a prepaid basis, or under another managed care arrangement, will not result in the diminution of the level or quality of health services provided to the medically underserved population served prior to the grant under this subparagraph.
(C) Practice management networks.— The Secretary may make grants to health centers that receive assistance under this section to enable the centers to plan and develop practice management networks that will enable the centers to—
(i) reduce costs associated with the provision of health care services;
(ii) improve access to, and availability of, health care services provided to individuals served by the centers;
(iii) enhance the quality and coordination of health care services; or
(iv) improve the health status of communities.
(D) Use of funds.— The activities for which a grant may be made under subparagraph (B) or (C) may include the purchase or lease of equipment, which may include data and information systems (including paying for the costs of amortizing the principal of, and paying the interest on, loans for equipment), the provision of training and technical assistance related to the provision of health care services on a prepaid basis or under another managed care arrangement, and other activities that promote the development of practice management or managed care networks and plans.
(2) Limitation.— Not more than two grants may be made under this subsection for the same project, except that upon a showing of good cause, the Secretary may make additional grant awards.
(3) Recognition of high poverty.—
(A) In general.— In making grants under this subsection, the Secretary may recognize the unique needs of high poverty areas.
(B) High poverty area defined.— For purposes of subparagraph (A), the term “high poverty area” means a catchment area which is established in a manner that is consistent with the factors in subsection (k)(3)(J), and the poverty rate of which is greater than the national average poverty rate as determined by the Bureau of the Census.
(d) Loan Guarantee Program.—
(1) Establishment.—
(A) In general.— The Secretary shall establish a program under which the Secretary may, in accordance with this subsection and to the extent that appropriations are provided in advance for such program, guarantee up to 90 percent of the principal and interest on loans made by non-Federal lenders to health centers, funded under this section, for the costs of developing and operating managed care networks or plans described in subsection (c)(1)(B) of this section, or practice management networks described in subsection (c)(1)(C) of this section.
(B) Use of funds.— Loan funds guaranteed under this subsection may be used—
(i) to establish reserves for the furnishing of services on a pre-paid basis;
(ii) for costs incurred by the center or centers, otherwise permitted under this section, as the Secretary determines are necessary to enable a center or centers to develop, operate, and own the network or plan; or
(iii) to refinance an existing loan (as of the date of refinancing) to the center or centers, if the Secretary determines—
(I) that such refinancing will be beneficial to the health center and the Federal Government; or
(II) that the center (or centers) can demonstrate an ability to repay the refinanced loan equal to or greater than the ability of the center (or centers) to repay the original loan on the date the original loan was made.
(C) Publication of guidance.— Prior to considering an application submitted under this subsection, the Secretary shall publish guidelines to provide guidance on the implementation of this section. The Secretary shall make such guidelines available to the universe of parties affected under this subsection, distribute such guidelines to such parties upon the request of such parties, and provide a copy of such guidelines to the appropriate committees of Congress.
(D) Provision directly to networks or plans.— At the request of health centers receiving assistance under this section, loan guarantees provided under this paragraph may be made directly to networks or plans that are at least majority controlled and, as applicable, at least majority owned by those health centers.
(E) Federal credit reform.— The requirements of the Federal Credit Reform Act of 1990 (2 U.S.C. 661 et seq.)[236] shall apply with respect to loans refinanced under subparagraph (B)(iii).
(2) Protection of financial interests.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary may not approve a loan guarantee for a project under this subsection unless the Secretary determines that—
(i) the terms, conditions, security (if any), and schedule and amount of repayments with respect to the loan are sufficient to protect the financial interests of the United States and are otherwise reasonable, including a determination that the rate of interest does not exceed such percent per annum on the principal obligation outstanding as the Secretary determines to be reasonable, taking into account the range of interest rates prevailing in the private market for similar loans and the risks assumed by the United States, except that the Secretary may not require as security any center asset that is, or may be, needed by the center or centers involved to provide health services; determination that the rate of interest does not exceed such percent per annum on the principal obligation outstanding as the Secretary determines to be reasonable, taking into account the range of interest rates prevailing in the private market for similar loans and the risks assumed by the United States,
(ii) the loan would not be available on reasonable terms and conditions without the guarantee under this subsection; and
(iii) amounts appropriated for the program under this subsection are sufficient to provide loan guarantees under this subsection.
(B) Recovery of payments.—
(i) In general.— The United States shall be entitled to recover from the applicant for a loan guarantee under this subsection the amount of any payment made pursuant to such guarantee, unless the Secretary for good cause waives such right of recovery (subject to appropriations remaining available to permit such a waiver) and, upon making any such payment, the United States shall be subrogated to all of the rights of the recipient of the payments with respect to which the guarantee was made. Amounts recovered under this clause shall be credited as reimbursements to the financing account of the program.
(ii) Modification of terms and conditions.— To the extent permitted by clause (iii) and subject to the requirements of section 504(e) of the Credit Reform Act of 1990 (2 U.S.C. 661c(e)), any terms and conditions applicable to a loan guarantee under this subsection (including terms and conditions imposed under clause (iv)) may be modified or waived by the Secretary to the extent the Secretary determines it to be consistent with the financial interest of the United States.
(iii) Incontestability.— Any loan guarantee made by the Secretary under this subsection shall be incontestable—
(I) in the hands of an applicant on whose behalf such guarantee is made unless the applicant engaged in fraud or misrepresentation in securing such guarantee; and
(II) as to any person (or successor in interest) who makes or contracts to make a loan to such applicant in reliance thereon unless such person (or successor in interest) engaged in fraud or misrepresentation in making or contracting to make such loan.
(iv) Further terms and conditions.— Guarantees of loans under this subsection shall be subject to such further terms and conditions as the Secretary determines to be necessary to assure that the purposes of this section will be achieved.
(3) Loan origination fees.—
(A) In general.— The Secretary shall collect a loan origination fee with respect to loans to be guaranteed under this subsection, except as provided in subparagraph (C).
(B) Amounts.— The amount of a loan origination fee collected by the Secretary under subparagraph (A) shall be equal to the estimated long term cost of the loan guarantees involved to the Federal Government (excluding administrative costs), calculated on a net present value basis, after taking into account any appropriations that may be made for the purpose of offsetting such costs, and in accordance with the criteria used to award loan guarantees under this subsection.
(C) Waiver.— The Secretary may waive the loan origination fee for a health center applicant who demonstrates to the Secretary that the applicant will be unable to meet the conditions of the loan if the applicant incurs the additional cost of the fee.
(4) Defaults.—
(A) In general.—Subject to the requirements of the Credit Reform Act of 1990 (2 U.S.C. 661 et seq.)[237], the Secretary may take such action as may be necessary to prevent a default on a loan guaranteed under this subsection, including the waiver of regulatory conditions, deferral of loan payments, renegotiation of loans, and the expenditure of funds for technical and consultative assistance, for the temporary payment of the interest and principal on such a loan, and for other purposes. Any such expenditure made under the preceding sentence on behalf of a health center or centers shall be made under such terms and conditions as the Secretary shall prescribe, including the implementation of such organizational, operational, and financial reforms as the Secretary determines are appropriate and the disclosure of such financial or other information as the Secretary may require to determine the extent of the implementation of such reforms.
(B) Foreclosure.—The Secretary may take such action, consistent with State law respecting foreclosure procedures and, with respect to reserves required for furnishing services on a prepaid basis, subject to the consent of the affected States, as the Secretary determines appropriate to protect the interest of the United States in the event of a default on a loan guaranteed under this subsection, except that the Secretary may only foreclose on assets offered as security (if any) in accordance with paragraph (2)(A)(i).
(5) Limitation.—Not more than one loan guarantee may be made under this subsection for the same network or plan, except that upon a showing of good cause the Secretary may make additional loan guarantees.
(6) Authorization of appropriations.—There are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this subsection such sums as may be necessary.
(e) Operating Grants.—
(1) Authority.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary may make grants for the costs of the operation of public and nonprofit private health centers that provide health services to medically underserved populations.
(B) Entities that fail to meet certain requirements.—The Secretary may make grants, for a period of not to exceed 2 years, for the costs of the operation of public and nonprofit private entities which provide health services to medically underserved populations but with respect to which the Secretary is unable to make each of the determinations required by subsection (k)(3) of this section.
(C) Operation of networks and plans.—The Secretary may make grants to health centers that receive assistance under this section, or at the request of the health centers, directly to a network or plan (as described in subparagraphs (B) and (C) of subsection (c)(1) of this section) that is at least majority controlled and, as applicable, at least majority owned by such health centers receiving assistance under this section, for the costs associated with the operation of such network or plan, including the purchase or lease of equipment (including the costs of amortizing the principal of, and paying the interest on, loans for equipment).
(2) Use of funds.—The costs for which a grant may be made under subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (1) may include the costs of acquiring and leasing buildings and equipment (including the costs of amortizing the principal of, and paying interest on, loans), and the costs of providing training related to the provision of required primary health services and additional health services and to the management of health center programs.
(3) Construction.—The Secretary may award grants which may be used to pay the costs associated with expanding and modernizing existing buildings or constructing new buildings (including the costs of amortizing the principal of, and paying the interest on, loans) for projects approved prior to October 1, 1996.
(4) Limitation.—Not more than two grants may be made under subparagraph (B) of paragraph (1) for the same entity.
(5) Amount.—
(A) In general.—The amount of any grant made in any fiscal year under subparagraphs (A) and (B) of paragraph (1) to a health center shall be determined by the Secretary, but may not exceed the amount by which the costs of operation of the center in such fiscal year exceed the total of —
(i) State, local, and other operational funding provided to the center; and
(ii) the fees, premiums, and third-party reimbursements, which the center may reasonably be expected to receive for its operations in such fiscal year.
(B) Networks and plans.—The total amount of grant funds made available for any fiscal year under paragraph (1)(C) and subparagraphs (B) and (C) of subsection (c)(1) of this section to a health center or to a network or plan shall be determined by the Secretary, but may not exceed 2 percent of the total amount appropriated under this section for such fiscal year.
(C) Payments.—Payments under grants under subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (1) shall be made in advance or by way of reimbursement and in such installments as the Secretary finds necessary and adjustments may be made for overpayments or underpayments.
(D) Use of nongrant funds.—Nongrant funds described in clauses (i) and (ii) of subparagraph (A), including any such funds in excess of those originally expected, shall be used as permitted under this section, and may be used for such other purposes as are not specifically prohibited under this section if such use furthers the objectives of the project.
(f) Infant Mortality Grants.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may make grants to health centers for the purpose of assisting such centers in—
(A) providing comprehensive health care and support services for the reduction of —
(i) the incidence of infant mortality; and
(ii) morbidity among children who are less than 3 years of age; and
(B) developing and coordinating service and referral arrangements between health centers and other entities for the health management of pregnant women and children described in subparagraph (A).
(2) Priority.—In making grants under this subsection the Secretary shall give priority to health centers providing services to any medically underserved population among which there is a substantial incidence of infant mortality or among which there is a significant increase in the incidence of infant mortality.
(3) Requirements.—The Secretary may make a grant under this subsection only if the health center involved agrees that—
(A) the center will coordinate the provision of services under the grant to each of the recipients of the services;
(B) such services will be continuous for each such recipient;
(C) the center will provide follow-up services for individuals who are referred by the center for services described in paragraph (1);
(D) the grant will be expended to supplement, and not supplant, the expenditures of the center for primary health services (including prenatal care) with respect to the purpose described in this subsection; and
(E) the center will coordinate the provision of services with other maternal and child health providers operating in the catchment area.
(g) Migratory and Seasonal Agricultural workers.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may award grants for the purposes described in subsections (c), (e), and (f) of this section for the planning and delivery of services to a special medically underserved population comprised of—
(A) migratory agricultural workers, seasonal agricultural workers, and members of the families of such migratory and seasonal agricultural workers who are within a designated catchment area; and
(B) individuals who have previously been migratory agricultural workers but who no longer meet the requirements of subparagraph (A) of paragraph (3) because of age or disability and members of the families of such individuals who are within such catchment area.
(2) Environmental concerns.—The Secretary may enter into grants or contracts under this subsection with public and private entities to—
(A) assist the States in the implementation and enforcement of acceptable environmental health standards, including enforcement of standards for sanitation in migratory agricultural worker and seasonal agricultural worker labor camps, and applicable Federal and State pesticide control standards; and
(B) conduct projects and studies to assist the several States and entities which have received grants or contracts under this section in the assessment of problems related to camp and field sanitation, exposure to unsafe levels of agricultural chemicals including pesticides, and other environmental health hazards to which migratory agricultural workers and seasonal agricultural workers, and members of their families, are exposed.
(3) Definitions.—For purposes of this subsection:
(A) Migratory agricultural worker.—The term “migratory agricultural worker” means an individual whose principal employment is in agriculture, who has been so employed within the last 24 months, and who establishes for the purposes of such employment a temporary abode.
(B) Seasonal agricultural worker.—The term “seasonal agricultural worker” means an individual whose principal employment is in agriculture on a seasonal basis and who is not a migratory agricultural worker.
(C) Agriculture.—The term “agriculture” means farming in all its branches, including—
(i) cultivation and tillage of the soil;
(ii) the production, cultivation, growing, and harvesting of any commodity grown on, in, or as an adjunct to or part of a commodity grown in or on, the land; and
(iii) any practice (including preparation and processing for market and delivery to storage or to market or to carriers for transportation to market) performed by a farmer or on a farm incident to or in conjunction with an activity described in clause (ii).
(h) Homeless Population.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may award grants for the purposes described in subsections (c), (e), and (f) of this section for the planning and delivery of services to a special medically underserved population comprised of homeless individuals, including grants for innovative programs that provide outreach and comprehensive primary health services to homeless children and youth and children and youth at risk of homelessness.
(2) Required services.—In addition to required primary health services (as defined in subsection (b)(1) of this section), an entity that receives a grant under this subsection shall be required to provide substance abuse services as a condition of such grant.
(3) Supplement not supplant requirement.—A grant awarded under this subsection shall be expended to supplement, and not supplant, the expenditures of the health center and the value of in kind contributions for the delivery of services to the population described in paragraph (1).
(4) Temporary continued provision of services to certain former homeless individuals.—If any grantee under this subsection has provided services described in this section under the grant to a homeless individual, such grantee may, notwithstanding that the individual is no longer homeless as a result of becoming a resident in permanent housing, expend the grant to continue to provide such services to the individual for not more than 12 months.
(5) Definitions.—For purposes of this section:
(A) Homeless individual.—The term “homeless individual” means an individual who lacks housing (without regard to whether the individual is a member of a family), including an individual whose primary residence during the night is a supervised public or private facility that provides temporary living accommodations and an individual who is a resident in transitional housing.
(B) Substance abuse.—The term “substance abuse” has the same meaning given such term in section 290cc-34(4) of this title.
(C) Substance abuse services.—The term “substance abuse services” includes detoxification, risk reduction, outpatient treatment, residential treatment, and rehabilitation for substance abuse provided in settings other than hospitals.
(i) Residents of Public Housing.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may award grants for the purposes described in subsections (c), (e), and (f) of this section for the planning and delivery of services to a special medically underserved population comprised of residents of public housing (such term, for purposes of this subsection, shall have the same meaning given such term in section 1437a(b)(1) of this title) and individuals living in areas immediately accessible to such public housing.
(2) Supplement not supplant.—A grant awarded under this subsection shall be expended to supplement, and not supplant, the expenditures of the health center and the value of in kind contributions for the delivery of services to the population described in paragraph (1).
(3) Consultation with residents.—The Secretary may not make a grant under paragraph (1) unless, with respect to the residents of the public housing involved, the applicant for the grant—
(A) has consulted with the residents in the preparation of the application for the grant; and
(B) agrees to provide for ongoing consultation with the residents regarding the planning and administration of the program carried out with the grant.
(j) Access Grants.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may award grants to eligible health centers with a substantial number of clients with limited English speaking proficiency to provide translation, interpretation, and other such services for such clients with limited English speaking proficiency.
(2) Eligible health center.—In this subsection, the term “eligible health center” means an entity that—
(A) is a health center as defined under subsection (a) of this section;
(B) provides health care services for clients for whom English is a second language; and
(C) has exceptional needs with respect to linguistic access or faces exceptional challenges with respect to linguistic access.
(3) Grant amount.—The amount of a grant awarded to a center under this subsection shall be determined by the Administrator. Such determination of such amount shall be based on the number of clients for whom English is a second language that is served by such center, and larger grant amounts shall be awarded to centers serving larger numbers of such clients.
(4) Use of funds.—An eligible health center that receives a grant under this subsection may use funds received through such grant to—
(A) provide translation, interpretation, and other such services for clients for whom English is a second language, including hiring professional translation and interpretation services; and
(B) compensate bilingual or multilingual staff for language assistance services provided by the staff for such clients.
(5) Application.—An eligible health center desiring a grant under this subsection shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may reasonably require, including—
(A) an estimate of the number of clients that the center serves for whom English is a second language;
(B) the ratio of the number of clients for whom English is a second language to the total number of clients served by the center;
(C) a description of any language assistance services that the center proposes to provide to aid clients for whom English is a second language; and
(D) a description of the exceptional needs of such center with respect to linguistic access or a description of the exceptional challenges faced by such center with respect to linguistic access.
(6) Authorization of appropriation.—There are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this subsection, in addition to any funds authorized to be appropriated or appropriated for health centers under any other subsection of this section, such sums as may be necessary for each of fiscal years 2002 through 2006.
(k) Applications.—
(1) Submission.—No grant may be made under this section unless an application therefore is submitted to, and approved by, the Secretary. Such an application shall be submitted in such form and manner and shall contain such information as the Secretary shall prescribe.
(2) Description of need.—An application for a grant under subparagraph (A) or (B) of subsection (e)(1) of this section for a health center shall include—
(A) a description of the need for health services in the catchment area of the center;
(B) a demonstration by the applicant that the area or the population group to be served by the applicant has a shortage of personal health services; and
(C) a demonstration that the center will be located so that it will provide services to the greatest number of individuals residing in the catchment area or included in such population group.
Such a demonstration shall be made on the basis of the criteria prescribed by the Secretary under subsection (b)(3) of this section or on any other criteria which the Secretary may prescribe to determine if the area or population group to be served by the applicant has a shortage of personal health services. In considering an application for a grant under subparagraph (A) or (B) of subsection (e)(1) of this section, the Secretary may require as a condition to the approval of such application an assurance that the applicant will provide any health service defined under paragraphs (1) and (2) of subsection (b) of this section that the Secretary finds is needed to meet specific health needs of the area to be served by the applicant. Such a finding shall be made in writing and a copy shall be provided to the applicant.
(3) Requirements.—Except as provided in subsection (e)(1)(B) of this section, the Secretary may not approve an application for a grant under subparagraph (A) or (B) of subsection (e)(1) of this section unless the Secretary determines that the entity for which the application is submitted is a health center (within the meaning of subsection (a) of this section) and that—
(A) the required primary health services of the center will be available and accessible in the catchment area of the center promptly, as appropriate, and in a manner which assures continuity;
(B) the center has made and will continue to make every reasonable effort to establish and maintain collaborative relationships with other health care providers in the catchment area of the center;
(C) the center will have an ongoing quality improvement system that includes clinical services and management, and that maintains the confidentiality of patient records;
(D) the center will demonstrate its financial responsibility by the use of such accounting procedures and other requirements as may be prescribed by the Secretary;
(E) the center—
(i)(I) has or will have a contractual or other arrangement with the agency of the State, in which it provides services, which administers or supervises the administration of a State plan approved under title XIX of the Social Security Act [42 U.S.C. 1396 et seq.] for the payment of all or a part of the center’s costs in providing health services to persons who are eligible for medical assistance under such a State plan; and
(II) has or will have a contractual or other arrangement with the State agency administering the program under title XXI of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1397aa et seq.) with respect to individuals who are State children’s health insurance program beneficiaries; or
(ii) has made or will make every reasonable effort to enter into arrangements described in subclauses (I) and (II) of clause (i);
(F) the center has made or will make and will continue to make every reasonable effort to collect appropriate reimbursement for its costs in providing health services to persons who are entitled to insurance benefits under title XVIII of the Social Security Act [42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.], to medical assistance under a State plan approved under title XIX of such Act [42 U.S.C. 1396 et seq.], or to assistance for medical expenses under any other public assistance program or private health insurance program;
(G) the center—
(i) has prepared a schedule of fees or payments for the provision of its services consistent with locally prevailing rates or charges and designed to cover its reasonable costs of operation and has prepared a corresponding schedule of discounts to be applied to the payment of such fees or payments, which discounts are adjusted on the basis of the patient’s ability to pay;
(ii) has made and will continue to make every reasonable effort—
(I) to secure from patients payment for services in accordance with such schedules; and
(II) to collect reimbursement for health services to persons described in subparagraph (F) on the basis of the full amount of fees and payments for such services without application of any discount;
(iii)(I) will assure that no patient will be denied health care services due to an individual’s inability to pay for such services; and
(II) will assure that any fees or payments required by the center for such services will be reduced or waived to enable the center to fulfill the assurance described in subclause (I); and
(iv) has submitted to the Secretary such reports as the Secretary may require to determine compliance with this subparagraph;
(H) the center has established a governing board which except in the case of an entity operated by an Indian tribe or tribal or Indian organization under the Indian Self-Determination Act[238] [25 U.S.C. 450f et seq.] or an urban Indian organization under the Indian Health Care Improvement Act[239] (25 U.S.C. 1651 et seq.)—
(i) is composed of individuals, a majority of whom are being served by the center and who, as a group, represent the individuals being served by the center;
(ii) meets at least once a month, selects the services to be provided by the center, schedules the hours during which such services will be provided, approves the center’s annual budget, approves the selection of a director for the center, and, except in the case of a governing board of a public center (as defined in the second sentence of this paragraph), establishes general policies for the center; and
(iii) in the case of an application for a second or subsequent grant for a public center, has approved the application or if the governing body has not approved the application, the failure of the governing body to approve the application was unreasonable; except that, upon a showing of good cause the Secretary shall waive, for the length of the project period, all or part of the requirements of this subparagraph in the case of a health center that receives a grant pursuant to subsection (g), (h), (i), or (p) of this section;
(I) the center has developed—
(i) an overall plan and budget that meets the requirements of the Secretary; and
(ii) an effective procedure for compiling and reporting to the Secretary such statistics and other information as the Secretary may require relating to—
(I) the costs of its operations;
(II) the patterns of use of its services;
(III) the availability, accessibility, and acceptability of its services; and
(IV) such other matters relating to operations of the applicant as the Secretary may require;
(J) the center will review periodically its catchment area to—
(i) ensure that the size of such area is such that the services to be provided through the center (including any satellite) are available and accessible to the residents of the area promptly and as appropriate;
(ii) ensure that the boundaries of such area conform, to the extent practicable, to relevant boundaries of political subdivisions, school districts, and Federal and State health and social service programs; and
(iii) ensure that the boundaries of such area eliminate, to the extent possible, barriers to access to the services of the center, including barriers resulting from the area’s physical characteristics, its residential patterns, its economic and social grouping, and available transportation;
(K) in the case of a center which serves a population including a substantial proportion of individuals of limited English-speaking ability, the center has—
(i) developed a plan and made arrangements responsive to the needs of such population for providing services to the extent practicable in the language and cultural context most appropriate to such individuals; and
(ii) identified an individual on its staff who is fluent in both that language and in English and whose responsibilities shall include providing guidance to such individuals and to appropriate staff members with respect to cultural sensitivities and bridging linguistic and cultural differences;
(L) the center, has developed an ongoing referral relationship with one or more hospitals; and
(M) the center encourages persons receiving or seeking health services from the center to participate in any public or private (including employer-offered) health programs or plans for which the persons are eligible, so long as the center, in complying with this subparagraph, does not violate the requirements of subparagraph (G)(iii)(I).
For purposes of subparagraph (H), the term “public center” means a health center funded (or to be funded) through a grant under this section to a public agency.
(4) Approval of new or expanded service applications.—The Secretary shall approve applications for grants under subparagraph (A) or (B) of subsection (e)(1) of this section for health centers which—
(A) have not received a previous grant under such subsection; or
(B) have applied for such a grant to expand their services; in such a manner that the ratio of the medically underserved populations in rural areas which may be expected to use the services provided by such centers to the medically underserved populations in urban areas which may be expected to use the services provided by such centers is not less than two to three or greater than three to two.
(l) Technical Assistance.—The Secretary shall establish a program through which the Secretary shall provide (either through the Department of Health and Human Services or by grant or contract) technical and other assistance to eligible entities to assist such entities to meet the requirements of subsection (k)(3) of this section. Services provided through the program may include necessary technical and nonfinancial assistance, including fiscal and program management assistance, training in fiscal and program management, operational and administrative support, and the provision of information to the entities of the variety of resources available under this subchapter and how those resources can be best used to meet the health needs of the communities served by the entities.
(m) Memorandum of Agreement.—In carrying out this section, the Secretary may enter into a memorandum of agreement with a State. Such memorandum may include, where appropriate, provisions permitting such State to—
(1) analyze the need for primary health services for medically underserved populations within such State;
(2) assist in the planning and development of new health centers;
(3) review and comment upon annual program plans and budgets of health centers, including comments upon allocations of health care resources in the State;
(4) assist health centers in the development of clinical practices and fiscal and administrative systems through a technical assistance plan which is responsive to the requests of health centers; and
(5) share information and data relevant to the operation of new and existing health centers.
(n) Records.—
(1) In general.—Each entity which receives a grant under subsection (e) of this section shall establish and maintain such records as the Secretary shall require.
(2) Availability.—Each entity which is required to establish and maintain records under this subsection shall make such books, documents, papers, and records available to the Secretary or the Comptroller General of the United States, or any of their duly authorized representatives, for examination, copying or mechanical reproduction on or off the premises of such entity upon a reasonable request therefore. The Secretary and the Comptroller General of the United States, or any of their duly authorized representatives, shall have the authority to conduct such examination, copying, and reproduction.
(o) Delegation of Authority.—The Secretary may delegate the authority to administer the programs authorized by this section to any office, except that the authority to enter into, modify, or issue approvals with respect to grants or contracts may be delegated only within the central office of the Health Resources and Services Administration.
(p) Special Consideration.—In making grants under this section, the Secretary shall give special consideration to the unique needs of sparsely populated rural areas, including giving priority in the awarding of grants for new health centers under subsections (c) and (e) of this section, and the granting of waivers as appropriate and permitted under subsections (b)(1)(B)(i) and (k)(3)(G) of this section.
(q) Audits.—
(1) In general.—Each entity which receives a grant under this section shall provide for an independent annual financial audit of any books, accounts, financial records, files, and other papers and property which relate to the disposition or use of the funds received under such grant and such other funds received by or allocated to the project for which such grant was made. For purposes of assuring accurate, current, and complete disclosure of the disposition or use of the funds received, each such audit shall be conducted in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Each audit shall evaluate—(A) the entity’s implementation of the guidelines established by the Secretary respecting cost accounting, (B) the processes used by the entity to meet the financial and program reporting requirements of the Secretary, and (C) the billing and collection procedures of the entity and the relation of the procedures to its fee schedule and schedule of discounts and to the availability of health insurance and public programs to pay for the health services it provides. A report of each such audit shall be filed with the Secretary at such time and in such manner as the Secretary may require.
(2) Records.—Each entity which receives a grant under this section shall establish and maintain such records as the Secretary shall by regulation require to facilitate the audit required by paragraph (1). The Secretary may specify by regulation the form and manner in which such records shall be established and maintained.
(3) Availability of records.—Each entity which is required to establish and maintain records or to provide for and[240] audit under this subsection shall make such books, documents, papers, and records available to the Secretary or the Comptroller General of the United States, or any of their duly authorized representatives, for examination, copying or mechanical reproduction on or off the premises of such entity upon a reasonable request therefore. The Secretary and the Comptroller General of the United States, or any of their duly authorized representatives, shall have the authority to conduct such examination, copying, and reproduction.
(4) Waiver.—The Secretary may, under appropriate circumstances, waive the application of all or part of the requirements of this subsection with respect to an entity.
(r) Authorization of Appropriations.—
(1) In general.—For the purpose of carrying out this section, in addition to the amounts authorized to be appropriated under subsection (d) of this section, there are authorized to be appropriated—
(A) $2,065,000,000 for fiscal year 2008;
(B) $2,313,000,000 for fiscal year 2009
(C) $2,602,000,000 for fiscal year 2010;
(D) $2,940,000,000 for fiscal year 2011; and
(E) $3,337,000,000 for fiscal year 2012.
(2) Special provisions.—
(A) Public centers.—The Secretary may not expend in any fiscal year, for grants under this section to public centers (as defined in the second sentence of subsection (k)(3) of this section) the governing boards of which (as described in subsection (k)(3)(H) of this section) do not establish general policies for such centers, an amount which exceeds 5 percent of the amounts appropriated under this section for that fiscal year. For purposes of applying the preceding sentence, the term “public centers” shall not include health centers that receive grants pursuant to subsection (h) or (i) of this section.
(B) Distribution of grants.—For fiscal year 2002 and each of the following fiscal years, the Secretary, in awarding grants under this section, shall ensure that the proportion of the amount made available under each of subsections (g), (h), and (i) of this section, relative to the total amount appropriated to carry out this section for that fiscal year, is equal to the proportion of the amount made available under that subsection for fiscal year 2001, relative to the total amount appropriated to carry out this section for fiscal year 2001.
(3) Funding report.—The Secretary shall annually prepare and submit to the appropriate committees of Congress a report concerning the distribution of funds under this section that are provided to meet the health care needs of medically underserved populations, including the homeless, residents of public housing, and migratory and seasonal agricultural workers, and the appropriateness of the delivery systems involved in responding to the needs of the particular populations. Such report shall include an assessment of the relative health care access needs of the targeted populations and the rationale for any substantial changes in the distribution of funds.
HEALTH PROFESSIONAL SHORTAGE AREAS
Sec. 332. [42 U.S.C. 254e]
(a)(1) For purposes of this subpart the term “health professional shortage area” means (A) an area in an urban or rural area (which need not conform to the geographic boundaries of a political subdivision and which is a rational area for the delivery of health services) which the Secretary determines has a health manpower shortage and which is not reasonably accessible to an adequately served area, (B) a population group which the Secretary determines has such a shortage, or (C) a public or nonprofit private medical facility or other public facility which the Secretary determines has such a shortage. All Federally qualified health centers and rural health clinics, as defined in section 1861(aa) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(aa)), that meet the requirements of section 254g of this title shall be automatically designated as having such a shortage. Not earlier than 6 years after such date of designation, and every 6 years thereafter, each such center or clinic shall demonstrate that the center or clinic meets the applicable requirements of the Federal regulations, regarding the definition of a health professional shortage area for purposes of this section. The Secretary shall not remove an area from the areas determined to be health professional shortage areas under subparagraph (A) of the preceding sentence until the Secretary has afforded interested persons and groups in such area an opportunity to provide data and information in support of the designation as a health professional shortage area or a population group described in subparagraph (B) of such sentence or a facility described in subparagraph (C) of such sentence, and has made a determination on the basis of the data and information submitted by such persons and groups and other data and information available to the Secretary.
BREACH OF SCHOLARSHIP CONTRACT OR LOAN REPAYMENT CONTRACT
Sec. 338E. [42 U.S.C. 254o] (a)(1) An individual who has entered into a written contract with the Secretary under section 338A and who—
(A) fails to maintain an acceptable level of academic standing in the educational institution in which he is enrolled (such level determined by the educational institution under regulations of the Secretary); or
(B) is dismissed from such educational institution for disciplinary reasons; or
(C) voluntarily terminates the training in such an educational institution for which he is provided a scholarship under such contract, before the completion of such training,
in lieu of any service obligation arising under such contract, shall be liable to the United States for the amount which has been paid to him, or on his behalf, under the contract.
(2) An individual who has entered into a written contract with the Secretary under section 338B and who—
(A) in the case of an individual who is enrolled in the final year of a course of study, fails to maintain an acceptable level of academic standing in the educational institution in which such individual is enrolled (such level determined by the educational institution under regulations of the Secretary) or voluntarily terminates such enrollment or is dismissed from such educational institution before completion of such course of study; or
(B) in the case of an individual who is enrolled in a graduate training program, fails to complete such training program and does not receive a waiver from the Secretary under section 338B(b)(1)(B)(ii),
in lieu of any service obligation arising under such contract shall be liable to the United States for the amount that has been paid on behalf of the individual under the contract.
(b)(1) (A) Except as provided in paragraph (2), if an individual breaches his written contract by failing (for any reason not specified in subsection (a) or section 338F(d)) to begin such individual’s service obligation under section 338A in accordance with section 338C or 338D to complete such service obligation under section 338A, or to complete a required residency as specified in section 338B, the United States shall be entitled to recover from the individual an amount determined in accordance with the formula
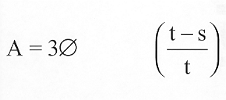
(B)(i) Any amount of damages that the United States is entitled to recover under this subsection or under subsection (c) shall, within the 1-year period beginning on the date of the breach of the written contract (or such longer period beginning on such date as specified by the Secretary), be paid to the United States. Amounts not paid within such period shall be subject to collection through deductions in Medicare payments pursuant to section 1892 of the Social Security Act.
(ii) If damages described in clause (i) are delinquent for 3 months, the Secretary shall, for the purpose of recovering such damages—
(I) utilize collection agencies contracted with by the Administrator of the General Services Administration; or
(II) enter into contracts for the recovery of such damages with collection agencies selected by the Secretary.
(iii) Each contract for recovering damages pursuant to this subsection shall provide that the contractor will, not less than once each 6 months, submit to the Secretary a status report on the success of the contractor in collecting such damages. Section 3718 of title 31, United States Code, shall apply to any such contract to the extent not inconsistent with this subsection.
(iv) To the extent not otherwise prohibited by law, the Secretary shall disclose to all appropriate credit reporting agencies information relating to damages of more than $100 that are entitled to be recovered by the United States under this subsection and that are delinquent by more than 60 days or such longer period as is determined by the Secretary.
(2) If an individual is released under section 753 from a service obligation under section 225 (as in effect on September 30, 1977) and if the individual does not meet the service obligation incurred under section 753, subsection (f) of such section 225 shall apply to such individual in lieu of paragraph (1) of this subsection.
(3) The Secretary may terminate a contract with an individual under section 338A if, not later than 30 days before the end of the school year to which the contract pertains, the individual—
(A) submits a written request for such termination; and
(B) repays all amounts paid to, or on behalf of, the individual under section 338A(g).
(c)(1) If (for any reason not specified in subsection (a) or section 338G(d)) an individual breaches the written contract of the individual under section 338B by failing either to begin such individual’s service obligation in accordance with section 338C or 338D or to complete such service obligation, the United States shall be entitled to recover from the individual an amount equal to the sum of—
(A) the total of the amounts paid by the United States under section 338B(g) on behalf of the individual for any period of obligated service not served;
(B) an amount equal to the product of the number of months of obligated service that were not completed by the individual, multiplied by $7,500; and
(C) the interest on the amounts described in subparagraphs (A) and (B), at the maximum legal prevailing rate, as determined by the Treasurer of the United States, from the date of the breach;
except that the amount the United States is entitled to recover under this paragraph shall not be less than $31,000.
(2) The Secretary may terminate a contract with an individual under section 338B if, not later than 45 days before the end of the fiscal year in which the contract was entered into, the individual—
(A) submits a written request for such termination; and
(B) repays all amounts paid on behalf of the individual under section 338B(g).
(3) Damages that the United States is entitled to recover shall be paid in accordance with subsection (b)(1)(B).
(d)(1) Any obligation of an individual under the Scholarship Program (or a contract thereunder) or the Loan Repayment Program (or a contract thereunder) for service or payment of damages shall be canceled upon the death of the individual.
(2) The Secretary shall by regulation provide for the partial or total waiver or suspension of any obligation of service or payment by an individual under the Scholarship Program (or a contract thereunder) or the Loan Repayment Program (or a contract thereunder) whenever compliance by the individual is impossible or would involve extreme hardship to the individual and if enforcement of such obligation with respect to any individual would be unconscionable.
(3)(A) Any obligation of an individual under the Scholarship Program (or a contract thereunder) or the Loan Repayment Program (or a contract thereunder) for payment of damages may be released by a discharge in bankruptcy under title 11 of the United States Code only if such discharge is granted after the expiration of the 7-year period beginning on the first date that payment of such damages is required, and only if the bankruptcy court finds that nondischarge of the obligation would be unconscionable.
(B)(i) Subparagraph (A) shall apply to any financial obligation of an individual under the provision of law specified in clause (ii) to the same extent and in the same manner as such subparagraph applies to any obligation of an individual under the Scholarship or Loan Repayment Program (or contract thereunder) for payment of damages.
(ii) The provision of law referred to in clause (i) is subsection (f) of section 225 of this Act, as in effect prior to the repeal of such section by section 408(b)(1) of Public Law 94-484.
(e) Notwithstanding any other provision of Federal or State law, there shall be no limitation on the period within which suit may be filed, a judgment may be enforced, or an action relating to an offset or garnishment, or other action, may be initiated or taken by the Secretary, the Attorney General, or the head of another Federal agency, as the case may be, for the repayment of the amount due from an individual under this section.
* * * * * * *
HOME HEALTH SERVICES
Sec. 339. [42 U.S.C. 255]
(a)(1) For the purpose of encouraging the establishment and initial operation of home health programs to provide home health services in areas in which such services are inadequate or not readily accessible, the Secretary may, in accordance with the provisions of this section, make grants to public and nonprofit private entities and loans to proprietary entities to meet the initial costs of establishing and operating such home health programs. Such grants and loans may include funds to provide training for paraprofessionals (including homemaker home health aides) to provide home health services.
(2) In making grants and loans under this subsection, the Secretary shall—
(A) consider the relative needs of the several States for home health services;
(B) give preference to areas in which a high percentage of the population proposed to be served is composed of individuals who are elderly, medically indigent, or disabled; and
(C) give special consideration to areas with inadequate means of transportation to obtain necessary health services.
(3)(A) No loan may be made to a proprietary entity under this section unless the application of such entity for such loan contains assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that—
(i) at the time the application is made the entity is fiscally sound;
(ii) the entity is unable to secure a loan for the project for which the application is submitted from non-Federal lenders at the rate of interest prevailing in the area in which the entity is located; and
(iii) during the period of the loan, such entity will remain fiscally sound.
(B) Loans under this section shall be made at an interest rate comparable to the rate of interest prevailing on the date the loan is made with respect to the marketable obligations of the United States of comparable maturities, adjusted to provide for administrative costs.
(4) Applications for grants and loans under this subsection shall be in such form and contain such information as the Secretary shall prescribe.
(5) There are authorized to be appropriated for grants and loans under this subsection $5,000,000 for each of the fiscal years ending on September 30, 1983, September 30, 1984, September 30, 1985, September 30, 1986, and September 30, 1987.
(b)(1) The Secretary may make grants to and enter into contracts with public and private entities to assist them in developing appropriate training programs for paraprofessionals (including homemaker home health aides) to provide home health services.
(2) Any program established with a grant or contract under this subsection to train homemaker home health aides shall—
(A) extend for at least forty hours, and consist of classroom instruction and at least twenty hours (in the aggregate) of supervised clinical instruction directed toward preparing students to deliver home health services;
(B) be carried out under appropriate professional supervision and be designed to train students to maintain or enhance the personal care of an individual in his home in a manner which promotes the functional independence of the individual; and
(C) include training in—
(i) personal care services designed to assist an individual in the activities of daily living such as bathing, exercising, personal grooming, and getting in and out of bed; and
(ii) household care services such as maintaining a safe living environment, light housekeeping, and assisting in providing good nutrition (by the purchasing and preparation of food).
(3) In making grants and entering into contracts under this subsection, special consideration shall be given to entities which establish or will establish programs to provide training for persons fifty years of age and older who wish to become paraprofessionals (including homemaker home health aides) to provide home health services.
(4) Applications for grants and contracts under this subsection shall be in such form and contain such information as the Secretary shall prescribe.
(5) There are authorized to be appropriated for grants and contracts under this subsection $2,000,000 for each of the fiscal years ending September 30, 1983, September 30, 1984, September 30, 1985, September 30, 1986, and September 30, 1987.
(c) The Secretary shall report to the Committee on Labor and Human Resources of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives on or before January 1, 1984, with respect to—
(1) the impact of grants made and contracts entered into under subsections (a) and (b) (as such subsections were in effect prior to October 1, 1981);
(2) the need to continue grants and loans under subsections (a) and (b) (as such subsections are in effect on the day after the date of enactment of the Orphan Drug Act[241]); and
(3) the extent to which standards have been applied to the training of personnel who provide home health services.
(d) For purposes of this section, the term “home health services” has the meaning prescribed for the term by section 1861(m) of the Social Security Act.
Subpart VII—Drug Pricing Agreements
LIMITATION ON PRICES OF DRUGS PURCHASED BY COVERED ENTITIES
Sec. 340B. [42 U. S. C. 256b]
(a) Requirements for Agreement With Secretary.—
(1) In General.—The Secretary shall enter into an agreement with each manufacturer of covered drugs under which the amount required to be paid (taking into account any rebate or discount, as provided by the Secretary) to the manufacturer for covered drugs (other than drugs described in paragraph (3)) purchased by a covered entity on or after the first day of the first month that begins after the date of the enactment of this section, does not exceed an amount equal to the average manufacturer price for the drug under title XIX of the Social Security Act in the preceding calendar quarter, reduced by the rebate percentage described in paragraph (2).
(2) Rebate percentage defined.—
(A) In general.—For a covered outpatient drug purchased in a calendar quarter, the “rebate percentage” is the amount (expressed as a percentage) equal to—
(i) the average total rebate required under section 1927(c) of the Social Security Act with respect to the drug (for a unit of the dosage form and strength involved) during the preceding calendar quarter; divided by
(ii) the average manufacturer price for such a unit of the drug during such quarter.
(B) Over the counter drugs.—
(i) In general.—For purposes of subparagraph (A), in the case of over the counter drugs, the “rebate percentage” shall be determined as if the rebate required under section 1927(c) of the Social Security Act is based on the applicable percentage provided under section 1927(c)(3) of such Act.
(ii) Definition.—The term “over the counter drug” means a drug that may be sold without a prescription and which is prescribed by a physician (or other persons authorized to prescribe such drug under State law).
(3) Drugs provided under state medicaid plans.—Drugs described in this paragraph are drugs purchased by the entity for which payment is made by the State under the State plan for medical assistance under title XIX of the Social Security Act.
(4) Covered entity defined.—In this section, the term “covered entity” means an entity that meets the requirements described in paragraph (5) and is one of the following:
(A) A Federally-qualified health center (as defined in section 1905(l)(2)(B) of the Social Security Act).
(B) An entity receiving a grant under section 340A.
(C) A family planning project receiving a grant or contract under section 1001.
(D) An entity receiving a grant under subpart II of part C of title XXVI (relating to categorical grants for outpatient early intervention services for HIV disease).
(E) A State-operated AIDS drug purchasing assistance program receiving financial assistance under title XXVI.
(F) A black lung clinic receiving funds under section 427(a) of the Black Lung Benefits Act.
(G) A comprehensive hemophilia diagnostic treatment center receiving a grant under section 501(a)(2) of the Social Security Act.
(H) A Native Hawaiian Health Center receiving funds under the Native Hawaiian Health Care Act of 1988.
(I) An urban Indian organization receiving funds under title V of the Indian Health Care Improvement Act.
(J) Any entity receiving assistance under title XXVI (other than a State or unit of local government or an entity described in subparagraph (D)), but only if the entity is certified by the Secretary pursuant to paragraph (7).
(K) An entity receiving funds under section 318 (relating to treatment of sexually transmitted diseases) or section 317(j)(2) (relating to treatment of tuberculosis) through a State or unit of local government, but only if the entity is certified by the Secretary pursuant to paragraph (7).
(L) A subsection (d) hospital (as defined in section 1886(d)(1)(B) of the Social Security Act) that—
(i) is owned or operated by a unit of State or local government, is a public or private non-profit corporation which is formally granted governmental powers by a unit of State or local government, or is a private non-profit hospital which has a contract with a State or local government to provide health care services to low income individuals who are not entitled to benefits under title XVIII of the Social Security Act or eligible for assistance under the State plan under this title;
(ii) for the most recent cost of reporting period that ended before the calendar quarter involved, had a disproportionate share adjustment percentage (as determined under section 1886(d)(5)(F) of the Social Security Act) greater than 11.75 percent or was described in section 1886(d)(5)(F)(i)(II) of such Act; and
(iii) does not obtain covered outpatient drugs through a group purchasing organization or other group purchasing arrangement.
(5) Requirements for covered entities.—
(A) Prohibiting duplicate discounts or rebates.—
(i) In general.—A covered entity shall not request payment under title XIX of the Social Security Act for medical assistance described in section 1905(a)(12) of such Act with respect to a drug that is subject to an agreement under this section if the drug is subject to the payment of a rebate to the State under section 1927 of such Act.
(ii) Establishment of mechanism.—The Secretary shall establish a mechanism to ensure that covered entities comply with clause (i). If the Secretary does not establish a mechanism within 12 months under the previous sentence, the requirements of section 1927(a)(5)(C) of the Social Security Act shall apply.
(B) Prohibiting resale of drugs.—With respect to any covered outpatient drug that is subject to an agreement under this subsection, a covered entity shall not resell or otherwise transfer the drug to a person who is not a patient of the entity.
(C) Auditing.—A covered entity shall permit the Secretary and the manufacturer of a covered outpatient drug that is subject to an agreement under this subsection with the entity (acting in accordance with procedures established by the Secretary relating to the number, duration, and scope of audits) to audit at the Secretary’s or the manufacturer’s expense the records of the entity that directly pertain to the entity’s compliance with the requirements described in subparagraphs (A) or (B) with respect to drugs of the manufacturer.
(D) Additional sanction for noncompliance.—If the Secretary finds, after notice and hearing, that a covered entity is in violation of a requirement described in subparagraphs (A) or (B), the covered entity shall be liable to the manufacturer of the covered outpatient drug that is the subject of the violation in an amount equal to the reduction in the price of the drug (as described in subparagraph (A)) provided under the agreement between the entity and the manufacturer under this paragraph.
(6) Treatment of distinct units of hospitals.—In the case of a covered entity that is a distinct part of a hospital, the hospital shall not be considered a covered entity under this paragraph unless the hospital is otherwise a covered entity under this subsection.
(7) Certification of certain covered entities.—
(A) Development of process.—Not later than 60 days after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Secretary shall develop and implement a process for the certification of entities described in subparagraphs (J) and (K) of paragraph (4).
(B) Inclusion of purchase information.—The process developed under subparagraph (A) shall include a requirement that an entity applying for certification under this paragraph submit information to the Secretary concerning the amount such entity expended for covered outpatient drugs in the preceding year so as to assist the Secretary in evaluating the validity of the entity’s subsequent purchases of covered outpatient drugs at discounted prices.
(C) Criteria.—The Secretary shall make available to all manufacturers of covered outpatient drugs a description of the criteria for certification under this paragraph.
(D) List of purchasers and dispensers.—The certification process developed by the Secretary under subparagraph (A) shall include procedures under which each State shall, not later than 30 days after the submission of the descriptions under subparagraph (C), prepare and submit a report to the Secretary that contains a list of entities described in subparagraphs (J) and (K) of paragraph (4) that are located in the State.
(E) Recertification.—The Secretary shall require the recertification of entities certified pursuant to this paragraph on a not more frequent than annual basis, and shall require that such entities submit information to the Secretary to permit the Secretary to evaluate the validity of subsequent purchases by such entities in the same manner as that required under subparagraph (B).
(8) Development of prime vendor program.—The Secretary shall establish a prime vendor program under which covered entities may enter into contracts with prime vendors for the distribution of covered outpatient drugs. If a covered entity obtains drugs directly from a manufacturer, the manufacturer shall be responsible for the costs of distribution.
(9) Notice to manufacturers.—The Secretary shall notify manufacturers of covered outpatient drugs and single State agencies under section 1902(a)(5) of the Social Security Act of the identities of covered entities under this paragraph, and of entities that no longer meet the requirements of paragraph (5) or that are no longer certified pursuant to paragraph (7).
(10) No prohibition on larger discount.—Nothing in this subsection shall prohibit a manufacturer from charging a price for a drug that is lower than the maximum price that may be charged under paragraph (1).
(b) Other Definitions.—In this section, the terms “average manufacturer price”, “covered outpatient drug”, and “manufacturer” have the meaning given such terms in section 1927(k) of the Social Security Act.
(c) Compliance with Requirements.—A manufacturer is deemed to meet the requirements of subsection (a) if the manufacturer establishes to the satisfaction of the Secretary that the manufacturer would comply (and has offered to comply) with the provisions of this section (as in effect immediately after the enactment of the Veterans Health Care Act of 1992), as applied by the Secretary, and would have entered into an agreement under this section (as such section was in effect at such time), but for a legislative change in this section (or the application of this section) after the date of the enactment of such Act.
* * * * * * *
CERTIFICATION OF LABORATORIES
Sec. 353. [42 U.S.C. 263a]
(a) Definition.—As used in this section, the term “laboratory” or “clinical laboratory” means a facility for the biological, microbiological, serological, chemical, immuno-hematological, hematological, biophysical, cytological, pathological, or other examination of materials derived from the human body for the purpose of providing information for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of any disease or impairment of, or the assessment of the health of, human beings.
(b) Certificate Requirement.—No person may solicit or accept materials derived from the human body for laboratory examination or other procedure unless there is in effect for the laboratory a certificate issued by the Secretary under this section applicable to the category of examinations or procedures which includes such examination or procedure.
(c) Issuance and Renewal of Certificates.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may issue or renew a certificate for a laboratory only if the laboratory meets the requirements of subsection (d).
(2) Term.—A certificate issued under this section shall be valid for a period of 2 years or such shorter period as the Secretary may establish.
(d) Requirements for Certificates.—
(1) In general.—A laboratory may be issued a certificate or have its certificate renewed if—
(A) the laboratory submits (or if the laboratory is accredited under subsection (e), the accreditation body which accredited the laboratory submits), an application—
(i) in such form and manner as the Secretary shall prescribe,
(ii) that describes the characteristics of the laboratory examinations and other procedures performed by the laboratory including—
(I) the number and types of laboratory examinations and other procedures performed,
(II) the methodologies for laboratory examinations and other procedures employed, and
(III) the qualifications (educational background, training, and experience) of the personnel directing and supervising the laboratory and performing the laboratory examinations and other procedures, and
(iii) that contains such other information as the Secretary may require to determine compliance with this section, and
the laboratory agrees to provide to the Secretary (or if the laboratory is accredited, to the accreditation body which accredited it) a description of any change in the information submitted under clause (ii) not later than 6 months after the change was put into effect,
(B) the laboratory provides the Secretary—
(i) with satisfactory assurances that the laboratory will be operated in accordance with standards issued by the Secretary under subsection (f), or
(ii) with proof of accreditation under subsection (e),
(C) the laboratory agrees to permit inspections by the Secretary under subsection (g),
(D) the laboratory agrees to make records available and submit reports to the Secretary as the Secretary may reasonably require, and
(E) the laboratory agrees to treat proficiency testing samples in the same manner as it treats materials derived from the human body referred to it for laboratory examinations or other procedures in the ordinary course of business.
(2) Requirements for certificates of waiver.—
(A) In general.—A laboratory which only performs laboratory examinations and procedures described in paragraph (3) shall be issued a certificate of waiver or have its certificate of waiver renewed if—
(i) the laboratory submits an application—
(I) in such form and manner as the Secretary shall prescribe,
(II) that describes the characteristics of the laboratory examinations and other procedures performed by the laboratory, including the number and types of laboratory examinations and other procedures performed, the methodologies for laboratory examinations and other procedures employed, and the qualifications (educational background, training, and experience) of the personnel directing and supervising the laboratory and performing the laboratory examinations and other procedures, and
(III) that contains such other information as the Secretary may reasonably require to determine compliance with this section, and
(ii) the laboratory agrees to make records available and submit reports to the Secretary as the Secretary may require.
(B) Changes.—If a laboratory makes changes in the examinations and other procedures performed by it only with respect to examinations and procedures which are described in paragraph (3), the laboratory shall report such changes to the Secretary not later than 6 months after the change has been put into effect. If a laboratory proposes to make changes in the examinations and procedures performed by it such that the laboratory will perform an examination or procedure not described in paragraph (3), the laboratory shall report such change to the Secretary before the change takes effect.
(C) Effect.—Subsections (f) and (g) shall not apply to a laboratory to which has been issued a certificate of waiver.
(3) Examinations and procedures.—The examinations and procedures identified in paragraph (2) are laboratory examinations and procedures that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for home use or that, as determined by the Secretary, are simple laboratory examinations and procedures that have an insignificant risk of an erroneous result, including those that
(A) employ methodologies that are so simple and accurate as to render the likelihood of erroneous results by the user negligible, or
(C) the Secretary has determined pose no unreasonable risk of harm to the patient if performed incorrectly.
(4) Definition.—As used in this section, the term “certificate” includes a certificate of waiver issued under paragraph (2).
(e) Accreditation.—
(1) In general.—A laboratory may be accredited for purposes of obtaining a certificate if the laboratory—
(A) meets the standards of an approved accreditation body, and
(B) authorizes the accreditation body to submit to the Secretary (or such State agency as the Secretary may designate) such records or other information as the Secretary may require.
(2) Approval of accreditation bodies.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary may approve a private nonprofit organization to be an accreditation body for the accreditation of laboratories if—
(i) using inspectors qualified to evaluate the methodologies used by the laboratories in performing laboratory examinations and other procedures, the accreditation body agrees to inspect a laboratory for purposes of accreditation with such frequency as determined by Secretary,
(ii) the standards applied by the body in determining whether or not to accredit a laboratory are equal to or more stringent than the standards issued by the Secretary under subsection (f),
(iii) there is adequate provision for assuring that the standards of the accreditation body continue to be met by the laboratory,
(iv) in the case of any laboratory accredited by the body which has had its accreditation denied, suspended, withdrawn, or revoked or which has had any other action taken against it by the accrediting body, the accrediting body agrees to submit to the Secretary the name of such laboratory within 30 days of the action taken,
(v) the accreditation body agrees to notify the Secretary at least 30 days before it changes its standards, and
(vi) if the accreditation body has its approval withdrawn by the Secretary, the body agrees to notify each laboratory accredited by the body of the withdrawal within 10 days of the withdrawal.
(B) Criteria and procedures.—The Secretary shall promulgate criteria and procedures for approving an accreditation body and for withdrawing such approval if the Secretary determines that the accreditation body does not meet the requirements of subparagraph (A).
(C) Effect of withdrawal of approval.—If the Secretary withdraws the approval of an accreditation body under subparagraph (B), the certificate of any laboratory accredited by the body shall continue in effect for 60 days after the laboratory receives notification of the withdrawal of the approval, except that the Secretary may extend such period for a laboratory if it determines that the laboratory submitted an application for accreditation or a certificate in a timely manner after receipt of the notification of the withdrawal of approval. If an accreditation body withdraws or revokes the accreditation of a laboratory, the certificate of the laboratory shall continue in effect—
(i) for 45 days after the laboratory receives notice of the withdrawal or revocation of the accreditation, or
(ii) until the effective date of any action taken by the Secretary under subsection (i).
(D) Evaluations.—The Secretary shall evaluate annually the performance of each approved accreditation body by—
(i) inspecting under subsection (g) a sufficient number of the laboratories accredited by such body to allow a reasonable estimate of the performance of such body, and
(ii) such other means as the Secretary determines appropriate.
(f) Standards.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary shall issue standards to assure consistent performance by laboratories issued a certificate under this section of valid and reliable laboratory examinations and other procedures. Such standards shall require each laboratory issued a certificate under this section—
(A) to maintain a quality assurance and quality control program adequate and appropriate for the validity and reliability of the laboratory examinations and other procedures of the laboratory and to meet requirements relating to the proper collection, transportation, and storage of specimens and the reporting of results,
(B) to maintain records, equipment, and facilities necessary for the proper and effective operation of the laboratory,
(C) in performing and carrying out its laboratory examinations and other procedures, to use only personnel meeting such qualifications as the Secretary may establish for the direction, supervision, and performance of examinations and procedures within the laboratory, which qualifications shall take into consideration competency, training, experience, job performance, and education and which qualifications shall, as appropriate, be different on the basis of the type of examinations and procedures being performed by the laboratory and the risks and consequences of erroneous results associated with such examinations and procedures,
(D) to qualify under a proficiency testing program meeting the standards established by the Secretary under paragraph (3), and
(E) to meet such other requirements as the Secretary determines necessary to assure consistent performance by such laboratories of accurate and reliable laboratory examinations and procedures.
(2) Considerations.—In developing the standards to be issued under paragraph (1), the Secretary shall, within the flexibility provided under subparagraphs (A) through (E) of paragraph (1), take into consideration—
(A) the examinations and procedures performed and the methodologies employed,
(B) the degree of independent judgment involved,
(C) the amount of interpretation involved,
(D) the difficulty of the calculations involved,
(E) the calibration and quality control requirements of the instruments used,
(F) the type of training required to operate the instruments used in the methodology, and
(G) such other factors as the Secretary considers relevant.
(3) Proficiency testing program.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary shall establish standards for the proficiency testing programs for laboratories issued a certificate under this section which are conducted by the Secretary, conducted by an organization approved under subparagraph (C), or conducted by an approved accrediting body. The standards shall require that a laboratory issued a certificate under this section be tested for each examination and procedure conducted within a category of examinations or procedures for which it has received a certificate, except for examinations and procedures for which the Secretary has determined that a proficiency test cannot reasonably be developed. The testing shall be conducted on a quarterly basis, except where the Secretary determines for technical and scientific reasons that a particular examination or procedure may be tested less frequently (but not less often than twice per year).
(B) Criteria.—The standards established under subparagraph (A) shall include uniform criteria for acceptable performance under a proficiency testing program, based on the available technology and the clinical relevance of the laboratory examination or other procedure subject to such program. The criteria shall be established for all examinations and procedures and shall be uniform for each examination and procedure. The standards shall also include a system for grading proficiency testing performance to determine whether a laboratory has performed acceptably for a particular quarter and acceptably for a particular examination or procedure or category of examination or procedure over a period of successive quarters.
(C) Approved proficiency testing programs.—For the purpose of administering proficiency testing programs which meet the standards established under subparagraph (A), the Secretary shall approve a proficiency testing program offered by a private nonprofit organization or a State if the program meets the standards established under subparagraph (A) and the organization or State provides technical assistance to laboratories seeking to qualify under the program. The Secretary shall evaluate each program approved under this subparagraph annually to determine if the program continues to meet the standards established under subparagraph (A) and shall withdraw the approval of any program that no longer meets such standards.
(D) On-site testing.—The Secretary shall perform, or shall direct a program approved under subparagraph (C) to perform, onsite proficiency testing to assure compliance with the requirements of subsection (d)(5). The Secretary shall perform, on an onsite or other basis, proficiency testing to evaluate the performance of a proficiency testing program approved under subparagraph (C) and to assure quality performance by a laboratory.
(E) Training, technical assistance, and enhanced proficiency testing.—The Secretary may, in lieu of or in addition to actions authorized under subsection (h), (i), or (j), require any laboratory which fails to perform acceptably on an individual examination and procedure or a category of examination and procedures—
(i) to undertake training and to obtain the necessary technical assistance to meet the requirements of the proficency [242] testing program,
(ii) to enroll in a program of enhanced proficiency testing, or
(iii) to undertake any combination of the training, technical assistance, or testing described in clauses (i) and (ii).
(F) Testing results.—The Secretary shall establish a system to make the results of the proficiency testing programs subject to the standards established by the Secretary under subparagraph (A) available, on a reasonable basis, upon request of any person. The Secretary shall include with results made available under this subparagraph such explanatory information as may be appropriate to assist in the interpretation of such results.
(4) National standards for quality assurance in cytology services.—
(A) Establishment.—The Secretary shall establish national standards for quality assurance in cytology services designed to assure consistent performance by laboratories of valid and reliable cytological services.
(B) Standards.—The standards established under subparagraph (A) shall include—
(i) the maximum number of cytology slides that any individual may screen in a 24-hour period,
(ii) requirements that a clinical laboratory maintain a record of (I) the number of cytology slides screened during each 24-hour period by each individual who examines cytology slides for the laboratory, and (II) the number of hours devoted during each 24-hour period to screening cytology slides by such individual,
(iii) criteria for requiring rescreening of cytological preparations, such as (I) random rescreening of cytology specimens determined to be in the benign category, (II) focused rescreening of such preparations in high risk groups, and (III) for each abnormal cytological result, rescreening of all prior cytological specimens for the patient, if available,
(iv) periodic confirmation and evaluation of the proficiency of individuals involved in screening or interpreting cytological preparations, including announced and unannounced on-site proficiency testing of such individuals, with such testing to take place, to the extent practicable, under normal working conditions,
(v) procedures for detecting inadequately prepared slides, for assuring that no cytological diagnosis is rendered on such slides, and for notifying referring physicians of such slides,
(vi) requirements that all cytological screening be done on the premises of a laboratory that is certified under this section,
(vii) requirements for the retention of cytology slides by laboratories for such periods of time as the Secretary considers appropriate, and
(viii) standards requiring periodic inspection of cytology services by persons capable of evaluating the quality of cytology services.
(g) Inspections.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary may, on an announced or unannounced basis, enter and inspect, during regular hours of operation, laboratories which have been issued a certificate under this section. In conducting such inspections the Secretary shall have access to all facilities, equipment, materials, records, and information that the Secretary determines have a bearing on whether the laboratory is being operated in accordance with this section. As part of such an inspection the Secretary may copy any such material or require to it[243] be submitted to the Secretary. An inspection under this paragraph may be made only upon presenting identification to the owner, operator, or agent in charge of the laboratory being inspected.
(2) Compliance with requirements and standards.—The Secretary shall conduct inspections of laboratories under paragraph (1) to determine their compliance with the requirements of subsection (d) and the standards issued under subsection (f). Inspections of laboratories not accredited under subsection (e) shall be conducted on a biennial basis or with such other frequency as the Secretary determines to be necessary to assure compliance with such requirements and standards. Inspections of laboratories accredited under subsection (e) shall be conducted on such basis as the Secretary determines is necessary to assure compliance with such requirements and standards.
(h) Intermediate Sanctions.—
(1) In general.—If the Secretary determines that a laboratory which has been issued a certificate under this section no longer substantially meets the requirements for the issuance of a certificate, the Secretary may impose intermediate sanctions in lieu of the actions authorized by subsection (i).
(2) Types of sanctions.—The intermediate sanctions which may be imposed under paragraph (1) shall consist of—
(A) directed plans of correction,
(B) civil money penalties in an amount not to exceed $10,000 for each violation listed in subsection (i)(1) or for each day of substantial noncompliance with the requirements of this section,
(C) payment for the costs of onsite monitoring, or
(D) any combination of the actions described in subparagraphs (A), (B), and (C).
(3) Procedures.—The Secretary shall develop and implement procedures with respect to when and how each of the intermediate sanctions is to be imposed under paragraph (1). Such procedures shall provide for notice to the laboratory and a reasonable opportunity to respond to the proposed sanction and appropriate procedures for appealing determinations relating to the imposition of intermediate sanctions[244]
(i) Suspension, Revocation, and Limitation.—
(1) In general.—Except as provided in paragraph (2), the certificate of a laboratory issued under this section may be suspended, revoked, or limited if the Secretary finds, after reasonable notice and opportunity for hearing to the owner or operator of the laboratory, that such owner or operator or any employee of the laboratory—
(A) has been guilty of misrepresentation in obtaining the certificate,
(B) has performed or represented the laboratory as entitled to perform a laboratory examination or other procedure which is not within a category of laboratory examinations or other procedures authorized in the certificate,
(C) has failed to comply with the requirements of subsection (d) or the standards prescribed by the Secretary under subsection (f),
(D) has failed to comply with reasonable requests of the Secretary for—
(i) any information or materials, or
(ii) work on materials,
that the Secretary concludes is necessary to determine the laboratory’s continued eligibility for its certificate or continued compliance with the Secretary’s standards under subsection (f),
(E) has refused a reasonable request of the Secretary, or any Federal officer or employee duly designated by the Secretary, for permission to inspect the laboratory and its operations and pertinent records during the hours the laboratory is in operation,
(F) has violated or aided and abetted in the violation of any provisions of this section or of any regulation promulgated thereunder, or
(G) has not complied with an intermediate sanction imposed under subsection (h).
(2) Action before a hearing.—If the Secretary determines that—
(A) the failure of a laboratory to comply with the standards of the Secretary under subsection (f) presents an imminent and serious risk to human health, or
(B) a laboratory has engaged in an action described in subparagraph (D) or (E) of paragraph (1),
the Secretary may suspend or limit the certificate of the laboratory before holding a hearing under paragraph (1) regarding such failure or refusal. The opportunity for a hearing shall be provided no later than 60 days from the effective date of the suspension or limitation. A suspension or limitation under this paragraph shall stay in effect until the decision of the Secretary made after the hearing under paragraph (1).
(3) Ineligibility to own or operate laboratories after revocation.—No person who has owned or operated a laboratory which has had its certificate revoked may, within 2 years of the revocation of the certificate, own or operate a laboratory for which a certificate has been issued under this section. The certificate of a laboratory which has been excluded from participation under the medicare program under title XVIII of the Social Security Act because of actions relating to the quality of the laboratory shall be suspended for the period the laboratory is so excluded.
(4) Improper referrals.—Any laboratory that the Secretary determines intentionally refers its proficiency testing samples to another laboratory for analysis shall have its certificate revoked for at least one year and shall be subject to appropriate fines and penalties as provided for in subsection (h).
(j) Injunctions.—Whenever the Secretary has reason to believe that continuation of any activity by a laboratory would constitute a significant hazard to the public health the Secretary may bring suit in the district court of the United States for the district in which such laboratory is situated to enjoin continuation of such activity. Upon proper showing, a temporary injunction or restraining order against continuation of such activity pending issuance of a final order under this subsection shall be granted without bond by such court.
(k) Judicial Review.—
(1) Petition.—Any laboratory which has had an intermediate sanction imposed under subsection (h) or has had its certificate suspended, revoked, or limited under subsection (i) may, at any time within 60 days after the date the action of the Secretary under subsection (i) or (h) becomes final, file a petition with the United States court of appeals for the circuit wherein the laboratory has its principal place of business for judicial review of such action. As soon as practicable after receipt of the petition, the clerk of the court shall transmit a copy of the petition to the Secretary or other officer designated by the Secretary for that purpose. As soon as practicable after receipt of the copy, the Secretary shall file in the court the record on which the action of the Secretary is based, as provided in section 2112 of title 28, United State Code.
(2) Additional evidence.—If the petitioner applies to the court for leave to adduce additional evidence, and shows to the satisfaction of the court that such additional evidence is material and that there were reasonable grounds for the failure to adduce such evidence in the proceeding before the Secretary, the court may order such additional evidence (and evidence in rebuttal of such additional evidence) to be taken before the Secretary, and to be adduced upon the hearing in such manner and upon such terms and conditions as the court may deem proper. The Secretary may modify the findings of the Secretary as to the facts, or make new findings, by reason of the additional evidence so taken, and the Secretary shall file such modified or new findings, and the recommendations of the Secretary, if any, for the modification or setting aside of his original action, with the return of such additional evidence.
(3) Judgment of court.—Upon the filing of the petition referred to in paragraph (1), the court shall have jurisdiction to affirm the action, or to set it aside in whole or in part, temporarily or permanently. The findings of the Secretary as to the facts, if supported by substantial evidence, shall be conclusive.
(4) Finality of judgment.—The judgment of the court affirming or setting aside, in whole or in part, any such action of the Secretary shall be final, subject to review by the Supreme Court of the United States upon certiorari or certification as provided in section 1254 of title 28, United States Code.
(l) Sanctions.—Any person who intentionally violates any requirement of this section or any regulation promulgated thereunder shall be imprisoned for not more than one year or fined under title 18, United States Code or both, except that if the conviction is for a second or subsequent violation of such a requirement such person shall be imprisoned for not more than 3 years or fined in accordance with title 18, United States Code or both.
(m) Fees.—
(1) Certificate fees.—The Secretary shall require payment of fees for the issuance and renewal of certificates, except that the Secretary shall only require a nominal fee for the issuance and renewal of certificates of waiver.
(2) Additional fees.—The Secretary shall require the payment of fees for inspections of laboratories which are not accredited and for the cost of performing proficiency testing on laboratories which do not participate in proficiency testing programs approved under subsection (f)(3)(C).
(3) Criteria.—
(A) Fees under paragraph (1).—Fees imposed under paragraph (1) shall be sufficient to cover the general costs of administering this section, including evaluating and monitoring proficiency testing programs approved under subsection (f) and accrediting bodies and implementing and monitoring compliance with the requirements of this section.
(B) Fees under paragraph (2).—Fees imposed under paragraph (2) shall be sufficient to cover the cost of the Secretary in carrying out the inspections and proficiency testing described in paragraph (2).
(C) Fees imposed under paragraphs (1) and (2).—Fees imposed under paragraphs (1) and (2) shall vary by group or classification of laboratory, based on such considerations as the Secretary determines are relevant, which may include the dollar volume and scope of the testing being performed by the laboratories.
(n) Information.—On April 1, 1990 and annually thereafter, the Secretary shall compile and make available to physicians and the general public information, based on the previous calendar year, which the Secretary determines is useful in evaluating the performance of a laboratory, including—
(1) a list of laboratories which have been convicted under Federal or State laws relating to fraud and abuse, false billings, or kickbacks,
(2) a list of laboratories—
(A) which have had their certificates revoked, suspended, or limited under subsection (i), or
(B) which have been the subject of a sanction under subsection (l),
together with a statement of the reasons for the revocation, suspension, limitation, or sanction,
(3) a list of laboratories subject to intermediate sanctions under subsection (h) together with a statement of the reasons for the sanctions,
(4) a list of laboratories whose accreditation has been withdrawn or revoked together with a statement of the reasons for the withdrawal or revocation,
(5) a list of laboratories against which the Secretary has taken action under subsection (j) together with a statement of the reasons for such action, and
(6) a list of laboratories which have been excluded from participation under title XVIII or XIX of the Social Security Act.
The information to be compiled under paragraphs (1) through (6) shall be information for the calendar year preceding the date the information is to be made available to the public and shall be accompanied by such explanatory information as may be appropriate to assist in the interpretation of the information compiled under such paragraphs.
(o) Delegation.—In carrying out this section, the Secretary may, pursuant to agreement, use the services or facilities of any Federal or State or local public agency or nonprofit private organization, and may pay therefor in advance or by way of reimbursement, and in such installments, as the Secretary may determine.
(p) State Laws.—
(1) Except as provided in paragraph (2), nothing in this section shall be construed as affecting the power of any State to enact and enforce laws relating to the matters covered by this section to the extent that such laws are not inconsistent with this section or with the regulations issued under this section.
(2) If a State enacts laws relating to matters covered by this section which provide for requirements equal to or more stringent than the requirements of this section or than the regulations issued under this section, the Secretary may exempt clinical laboratories in that State from compliance with this section.
(q) Consultations.—In carrying out this section, the Secretary shall consult with appropriate private organizations and public agencies.
* * * * * * *
CERTIFICATION OF MAMMOGRAPHY FACILITIES
Sec. 354. [42 U.S.C. 263b]
(a) Definitions.—
As used in this section:
(1) Accreditation body
The term “accreditation body” means a body that has been approved by the Secretary under subsection (e)(1)(A) of this section to accredit mammography facilities.
(2) Certificate
The term “certificate” means the certificate described in subsection (b)(1) of this section.
(3) Facility
(A) In general
The term “facility” means a hospital, outpatient department, clinic, radiology practice, or mobile unit, an office of a physician, or other facility as determined by the Secretary, that conducts breast cancer screening or diagnosis through mammography activities. Such term does not include a facility of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
(B) Activities
For the purposes of this section, the activities of a facility include the operation of equipment to produce the mammogram, the processing of the film, the initial interpretation of the mammogram and the viewing conditions for that interpretation. Where procedures such as the film processing, or the interpretation of the mammogram are performed in a location different from where the mammogram is performed, the facility performing the mammogram shall be responsible for meeting the quality standards described in subsection (f) of this section.
(4) Inspection
The term “inspection” means an onsite evaluation of the facility by the Secretary, or State or local agency on behalf of the Secretary.
(5) Mammogram
The term “mammogram” means a radiographic image produced through mammography.
(6) Mammography
The term “mammography” means radiography of the breast.
(7) Survey
The term “survey” means an onsite physics consultation and evaluation performed by a medical physicist as described in subsection (f)(1)(E) of this section.
(8) Review physician
The term “review physician” means a physician as prescribed by the Secretary under subsection (f)(1)(D) of this section who meets such additional requirements as may be established by an accreditation body under subsection (e) of this section and approved by the Secretary to review clinical images under subsection (e)(1)(B)(i) of this section on behalf of the accreditation body.
(b) Certificate Requirement.—
(1) Certificate
No facility may conduct an examination or procedure described in paragraph (2) involving mammography after October 1, 1994, unless the facility obtains—
(A) a certificate—
(i) that is issued, and, if applicable, renewed, by the Secretary in accordance with subsection (c)(1) of this section;
(ii) that is applicable to the examination or procedure to be conducted; and
(iii) that is displayed prominently in such facility; or
(B) a provisional certificate—
(i) that is issued by the Secretary in accordance with subsection (c)(2) of this section;
(ii) that is applicable to the examination or procedure to be conducted; and
(iii) that is displayed prominently in such facility.
The reference to a certificate in this section includes a provisional certificate.
(2) Examination or procedure
A facility shall obtain a certificate in order to—
(A) operate radiological equipment that is used to image the breast;
(B) provide for the interpretation of a mammogram produced by such equipment at the facility or under arrangements with a qualified individual at a facility different from where the mammography examination is performed; and
(C) provide for the processing of film produced by such equipment at the facility or under arrangements with a qualified individual at a facility different from where the mammography examination is performed.
(c) Issuance and Renewal of Certificates.—
(1) In general
The Secretary may issue or renew a certificate for a facility if the person or agent described in subsection (d)(1)(A) of this section meets the applicable requirements of subsection (d)(1) of this section with respect to the facility. The Secretary may issue or renew a certificate under this paragraph for not more than 3 years.
(2) Provisional certificate
The Secretary may issue a provisional certificate for an entity to enable the entity to qualify as a facility. The applicant for a provisional certificate shall meet the requirements of subsection (d)(1) of this section, except providing information required by clauses (iii) and (iv) of subsection (d)(1)(A) of this section. A provisional certificate may be in effect no longer than 6 months from the date it is issued, except that it may be extended once for a period of not more than 90 days if the owner, lessor, or agent of the facility demonstrates to the Secretary that without such extension access to mammography in the geographic area served by the facility would be significantly reduced and if the owner, lessor, or agent of the facility will describe in a report to the Secretary steps that will be taken to qualify the facility for certification under subsection (b)(1) of this section.
(d) Application for Certificate.—
(1) Submission
The Secretary may issue or renew a certificate for a facility if—
(A) the person who owns or leases the facility or an authorized agent of the person, submits to the Secretary, in such form and manner as the Secretary shall prescribe, an application that contains at a minimum—
(i) a description of the manufacturer, model, and type of each x-ray machine, image receptor, and processor operated in the performance of mammography by the facility;
(ii) a description of the procedures currently used to provide mammography at the facility, including—
(I) the types of procedures performed and the number of such procedures performed in the prior 12 months;
(II) the methodologies for mammography; and
(III) the names and qualifications (educational background, training, and experience) of the personnel performing mammography and the physicians reading and interpreting the results from the procedures;
(iii) proof of on-site survey by a qualified medical physicist as described in subsection (f)(1)(E) of this section; and
(iv) proof of accreditation in such manner as the Secretary shall prescribe; and
(B) the person or agent submits to the Secretary—
(i) a satisfactory assurance that the facility will be operated in accordance with standards established by the Secretary under subsection (f) of this section to assure the safety and accuracy of mammography;
(ii) a satisfactory assurance that the facility will—
(I) permit inspections under subsection (g) of this section;
(II) make such records and information available, and submit such reports, to the Secretary as the Secretary may require; and
(III) update the information submitted under subparagraph (A) or assurances submitted under this subparagraph on a timely basis as required by the Secretary; and
(iii) such other information as the Secretary may require.
An applicant shall not be required to provide in an application under subparagraph (A) any information which the applicant has supplied to the accreditation body which accredited the applicant, except as required by the Secretary.
(2) Appeal
If the Secretary denies an application for the certification of a facility submitted under paragraph (1)(A), the Secretary shall provide the owner or lessor of the facility or the agent of the owner or lessor who submitted such application—
(A) a statement of the grounds on which the denial is based, and
(B) an opportunity for an appeal in accordance with the procedures set forth in regulations of the Secretary published at part 498 of title 42 Code of Federal Regulations.
(3) Effect of denial
If the application for the certification of a facility is denied, the facility may not operate unless the denial of the application is overturned at the conclusion of the administrative appeals process provided in the regulations referred to in paragraph (2)(B).
(e) Accreditation.—
(1) Approval of accreditation bodies
(A) In general
The Secretary may approve a private nonprofit organization or State agency to accredit facilities for purposes of subsection (d)(1)(A)(iv) of this section if the accreditation body meets the standards for accreditation established by the Secretary as described in subparagraph (B) and provides the assurances required by subparagraph (C).
(B) Standards
The Secretary shall establish standards for accreditation bodies, including—
(i) standards that require an accreditation body to perform—
(I) a review of clinical images from each facility accredited by such body not less often than every 3 years which review will be made by qualified practicing physicians; and
(II) a review of a random sample of clinical images from such facilities in each 3-year period beginning October 1, 1994, which review will be made by qualified review physicians;
(ii) standards that prohibit individuals conducting the reviews described in clause (i) from maintaining any relationship to the facility undergoing review which would constitute a conflict of interest;
(iii) standards that limit the imposition of fees for accreditation to reasonable amounts;
(iv) standards that require as a condition of accreditation that each facility undergo a survey at least annually by a medical physicist as described in subsection (f)(1)(E) of this section to ensure that the facility meets the standards described in subparagraphs (A) and (B) of subsection (f)(1) of this section;
(v) standards that require monitoring and evaluation of such survey, as prescribed by the Secretary;
(vi) standards that are equal to standards established under subsection (f) of this section which are relevant to accreditation as determined by the Secretary; and
(vii) such additional standards as the Secretary may require.
(C) Assurances
The accrediting body shall provide the Secretary satisfactory assurances that the body will—
(i) comply with the standards as described in subparagraph (B);
(ii) comply with the requirements described in paragraph (4);
(iii) submit to the Secretary the name of any facility for which the accreditation body denies, suspends, or revokes accreditation;
(iv) notify the Secretary in a timely manner before the accreditation body changes the standards of the body;
(v) notify each facility accredited by the accreditation body if the Secretary withdraws approval of the accreditation body under paragraph (2) in a timely manner; and
(vi) provide such other additional information as the Secretary may require.
(D) Regulations
Not later than 9 months after October 27, 1992, the Secretary shall promulgate regulations under which the Secretary may approve an accreditation body.
(2) Withdrawal of approval
(A) In general
The Secretary shall promulgate regulations under which the Secretary may withdraw the approval of an accreditation body if the Secretary determines that the accreditation body does not meet the standards under subparagraph (B) of paragraph (1), the requirements of clauses (i) through (vi) of subparagraph (C) of paragraph (1), or the requirements of paragraph (4).
(B) Effect of withdrawal
If the Secretary withdraws the approval of an accreditation body under subparagraph (A), the certificate of any facility accredited by the body shall continue in effect until the expiration of a reasonable period, as determined by the Secretary, for such facility to obtain another accreditation.
(3) Accreditation
To be accredited by an approved accreditation body a facility shall meet—
(A) the standards described in paragraph (1)(B) which the Secretary determines are applicable to the facility, and
(B) such other standards which the accreditation body may require.
(4) Compliance
To ensure that facilities accredited by an accreditation body will continue to meet the standards of the accreditation body, the accreditation body shall—
(A) make onsite visits on an annual basis of a sufficient number of the facilities accredited by the body to allow a reasonable estimate of the performance of the body; and
(B) take such additional measures as the Secretary determines to be appropriate.
Visits made under subparagraph (A) shall be made after providing such notice as the Secretary may require.
(5) Revocation of accreditation
If an accreditation body revokes the accreditation of a facility, the certificate of the facility shall continue in effect until such time as may be determined by the Secretary.
(6) Evaluation and report
(A) Evaluation
The Secretary shall evaluate annually the performance of each approved accreditation body by—
(i) inspecting under subsection (g)(2) of this section a sufficient number of the facilities accredited by the body to allow a reasonable estimate of the performance of the body; and
(ii) such additional means as the Secretary determines to be appropriate.
(B) Report
The Secretary shall annually prepare and submit to the Committee on Labor and Human Resources of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report that describes the results of the evaluation conducted in accordance with subparagraph (A).
(f) Quality standards
(1) In general
The standards referred to in subsection (d)(1)(B)(i) of this section are standards established by the Secretary which include—
(A) standards that require establishment and maintenance of a quality assurance and quality control program at each facility that is adequate and appropriate to ensure the reliability, clarity, and accuracy of interpretation of mammograms and standards for appropriate radiation dose;
(B) standards that require use of radiological equipment specifically designed for mammography, including radiologic standards and standards for other equipment and materials used in conjunction with such equipment;
(C) a requirement that personnel who perform mammography—
(i)(I) be licensed by a State to perform radiological procedures; or
(II) be certified as qualified to perform radiological procedures by an organization described in paragraph (2)(A); and
(ii) during the 2-year period beginning October 1, 1994, meet training standards for personnel who perform mammography or meet experience requirements which shall at a minimum include 1 year of experience in the performance of mammography; and
(iii) upon the expiration of such 2-year period meet minimum training standards for personnel who perform mammograms;
(D) a requirement that mammograms be interpreted by a physician who is certified as qualified to interpret radiological procedures, including mammography—
(i)(I) by a board described in paragraph (2)(B); or
(II) by a program that complies with the standards described in paragraph (2)(C); and
(ii) who meets training and continuing medical education requirements as established by the Secretary;
(E) a requirement that individuals who survey mammography facilities be medical physicists—
(i) licensed or approved by a State to perform such surveys, reviews, or inspections for mammography facilities;
(ii) certified in diagnostic radiological physics or certified as qualified to perform such surveys by a board as described in paragraph (2)(D); or
(iii) in the first 5 years after October 27, 1992, who meet other criteria established by the Secretary which are comparable to the criteria described in clause (i) or (ii);
(F) a requirement that a medical physicist who is qualified in mammography as described in subparagraph (E) survey mammography equipment and oversee quality assurance practices at each facility;
(G) a requirement that—
(i) a facility that performs any mammogram maintain the mammogram in the permanent medical records of the patient—
(I) except as provided in subclause (II), maintain the mammogram in the permanent medical records of the patient for a period of not less than 5 years, or not less than 10 years if no subsequent mammograms of such patient are performed at the facility, or longer if mandated by State law; and
(II) upon the request of or on behalf of the patient, transfer the mammogram to a medical institution, to a physician of the patient, or to the patient directly; and
whichever is longer; and
(ii)(I) a facility must assure the preparation of a written report of the results of any mammography examination signed by the interpreting physician;
(II) such written report shall be provided to the patient’s physicians (if any);
(III) if such a physician is not available or if there is no such physician, the written report shall be sent directly to the patient; and
(IV) whether or not such a physician is available or there is no such physician, a summary of the written report shall be sent directly to the patient in terms easily understood by a lay person; and
(H) standards relating to special techniques for mammography of patients with breast implants.
Subparagraph (G) shall not be construed to limit a patient’s access to the patient’s medical records.
(2) Certification of personnel
The Secretary shall by regulation—
(A) specify organizations eligible to certify individuals to perform radiological procedures as required by paragraph (1)(C);
(B) specify boards eligible to certify physicians to interpret radiological procedures, including mammography, as required by paragraph (1)(D);
(C) establish standards for a program to certify physicians described in paragraph (1)(D); and
(D) specify boards eligible to certify medical physicists who are qualified to survey mammography equipment and to oversee quality assurance practices at mammography facilities.
(g) Inspections
(1) Annual inspections
(A) In general
The Secretary may enter and inspect facilities to determine compliance with the certification requirements under subsection (b) of this section and the standards established under subsection (f) of this section. The Secretary shall, if feasible, delegate to a State or local agency the authority to make such inspections.
(B) Identification
The Secretary, or State agency acting on behalf of the Secretary, may conduct inspections only on presenting identification to the owner, operator, or agent in charge of the facility to be inspected.
(C) Scope of inspection
In conducting inspections, the Secretary or State or local agency acting on behalf of the Secretary—
(i) shall have access to all equipment, materials, records, and information that the Secretary or State or local agency considers necessary to determine whether the facility is being operated in accordance with this section; and
(ii) may copy, or require the facility to submit to the Secretary or the State or local agency, any of the materials, records, or information.
(D) Qualifications of inspectors
Qualified individuals, as determined by the Secretary, shall conduct all inspections. The Secretary may request that a State agency acting on behalf of the Secretary designate a qualified officer or employee to conduct the inspections, or designate a qualified Federal officer or employee to conduct inspections. The Secretary shall establish minimum qualifications and appropriate training for inspectors and criteria for certification of inspectors in order to inspect facilities for compliance with subsection (f) of this section.
(E) Frequency
The Secretary or State agency acting on behalf of the Secretary shall conduct inspections under this paragraph of each facility not less often than annually subject to paragraph (6).
(F) Records and annual reports
The Secretary or a State or local agency acting on behalf of the Secretary which is responsible for inspecting mammography facilities shall maintain records of annual inspections required under this paragraph for a period as prescribed by the Secretary. Such a State or local agency shall annually prepare and submit to the Secretary a report concerning the inspections carried out under this paragraph. Such reports shall include a description of the facilities inspected and the results of such inspections.
(2) Inspection of accredited facilities
The Secretary shall inspect annually a sufficient number of the facilities accredited by an accreditation body to provide the Secretary with a reasonable estimate of the performance of such body.
(3) Inspection of facilities inspected by State or local agencies
The Secretary shall inspect annually facilities inspected by State agencies acting on behalf of the Secretary to assure a reasonable performance by such State or local agencies.
(4) Timing
The Secretary, or State or local agency, may conduct inspections under paragraphs (1), (2), and (3), during regular business hours or at a mutually agreeable time and after providing such notice as the Secretary may prescribe, except that the Secretary may waive such requirements if the continued performance of mammography at such facility threatens the public health.
(5) Limited reinspection
Nothing in this section limits the authority of the Secretary to conduct limited reinspections of facilities found not to be in compliance with this section.
6) Demonstration program
(A) In general
The Secretary may establish a demonstration program under which inspections under paragraph (1) of selected facilities are conducted less frequently by the Secretary (or as applicable, by State or local agencies acting on behalf of the Secretary) than the interval specified in subparagraph (E) of such paragraph.
(B) Requirements
Any demonstration program under subparagraph (A) shall be carried out in accordance with the following:
(i) The program may not be implemented before April 1, 2001. Preparations for the program may be carried out prior to such date.
(ii) In carrying out the program, the Secretary may not select a facility for inclusion in the program unless the facility is substantially free of incidents of noncompliance with the standards under subsection (f) of this section. The Secretary may at any time provide that a facility will no longer be included in the program.
(iii) The number of facilities selected for inclusion in the program shall be sufficient to provide a statistically significant sample, subject to compliance with clause (ii).
(iv) Facilities that are selected for inclusion in the program shall be inspected at such intervals as the Secretary determines will reasonably ensure that the facilities are maintaining compliance with such standards.
(h) Sanctions
(1) In general
In order to promote voluntary compliance with this section, the Secretary may, in lieu of taking the actions authorized by subsection (i) of this section, impose one or more of the following sanctions;
(A) Directed plans of correction which afford a facility an opportunity to correct violations in a timely manner.
(B) Payment for the cost of onsite monitoring.
(2) Patient Information
If the Secretary determines that the quality of mammography performed by a facility (whether or not certified pursuant to subsection (c) of this section) was so inconsistent with the quality standards established pursuant to subsection (f) of this section as to present a significant risk to individual or public health, the Secretary may require such facility to notify patients who received mammograms at such facility, and their referring physicians, of the deficiencies presenting such risk, the potential harm resulting, appropriate remedial measures, and such other relevant information as the Secretary may require.
(3) Civil money penalties
The Secretary may assess civil money penalties in an amount not to exceed $10,000 for—
(A) failure to obtain a certificate as required by subsection (b) of this section,
(B) each failure by a facility to substantially comply with, or each day on which a facility fails to substantially comply with, the standards established under subsection (f) of this section or the requirements described in subclauses (I) through (III) of subsection (d)(1)(B)(ii) of this section, and
(C) each failure to notify a patient of risk as required by the Secretary pursuant to paragraph (2), and
(D) each violation, or for each aiding and abetting in a violation of, any provision of, or regulation promulgated under, this section by an owner, operator, or any employee of a facility required to have a certificate.
(4) Procedures
The Secretary shall develop and implement procedures with respect to when and how each of the sanctions is to be imposed under paragraphs (1) through (4). Such procedures shall provide for notice to the owner or operator of the facility and a reasonable opportunity for the owner or operator to respond to the proposed sanctions and appropriate procedures for appealing determinations relating to the imposition of sanctions.
(i) Suspension and revocation
(1) In general
The certificate of a facility issued under subsection (c) of this section may be suspended or revoked if the Secretary finds, after providing, except as provided in paragraph (2), reasonable notice and an opportunity for a hearing to the owner or operator of the facility, that the owner, operator, or any employee of the facility—
(A) has been guilty of misrepresentation in obtaining the certificate;
(B) has failed to comply with the requirements of subsection (d)(1)(B)(ii)(III) of this section or the standards established by the Secretary under subsection (f) of this section;
(C) has failed to comply with reasonable requests of the Secretary (or of an accreditation body approved pursuant to subsection (e) of this section) for any record, information, report, or material that the Secretary (or such accreditation body or State carrying out certification program requirements pursuant to subsection (q) of this section) concludes is necessary to determine the continued eligibility of the facility for a certificate or continued compliance with the standards established under subsection (f) of this section;
(D) has refused a reasonable request of the Secretary, any Federal officer or employee duly designated by the Secretary, or any State or local officer or employee duly designated by the State or local agency, for permission to inspect the facility or the operations and pertinent records of the facility in accordance with subsection (g) of this section;
(E) has violated or aided and abetted in the violation of any provision of, or regulation promulgated under, this section; or
(F) has failed to comply with a sanction imposed under subsection (h) of this section.
(2) Action before a hearing
(A) In general
The Secretary may suspend the certificate of the facility before holding a hearing required by paragraph (1) if the Secretary has reason to believe that the circumstance of the case will support one or more of the findings described in paragraph (1) and determines that—
(i) the failure or violation was intentional; or
(ii) the failure or violation presents a serious risk to human health.
(B) Hearing
If the Secretary suspends a certificate under subparagraph (A), the Secretary shall provide an opportunity for a hearing to the owner or operator of the facility not later than 60 days from the effective date of the suspension. The suspension shall remain in effect until the decision of the Secretary made after the hearing.
(3) Ineligibility to own or operate facilities after revocation
If the Secretary revokes the certificate of a facility on the basis of an act described in paragraph (1), no person who owned or operated the facility at the time of the act may, within 2 years of the revocation of the certificate, own or operate a facility that requires a certificate under this section.
(j) Injunctions
If the Secretary determines that—
(1) continuation of any activity related to the provision of mammography by a facility would constitute a serious risk to human health, the Secretary may bring suit in the district court of the United States for the district in which the facility is situated to enjoin continuation of the activity; and
(2) a facility is operating without a certificate as required by subsection (b) of this section, the Secretary may bring suit in the district court of the United States for the district in which the facility is situated to enjoin the operation of the facility.
Upon a proper showing, the district court shall grant a temporary injunction or restraining order against continuation of the activity or against operation of a facility, as the case may be, without requiring the Secretary to post a bond, pending issuance of a final order under this subsection.
(k) Judicial review
(1) Petition
If the Secretary imposes a sanction on a facility under subsection (h) of this section or suspends or revokes the certificate of a facility under subsection (i) of this section, the owner or operator of the facility may, not later than 60 days after the date the action of the Secretary becomes final, file a petition with the United States court of appeals for the circuit in which the facility is situated for judicial review of the action. As soon as practicable after receipt of the petition, the clerk of the court shall transmit a copy of the petition to the Secretary or other officer designated by the Secretary. As soon as practicable after receipt of the copy, the Secretary shall file in the court the record on which the action of the Secretary is based, as provided in section 2112 of title 28.
(2) Additional evidence
If the petitioner applies to the court for leave to adduce additional evidence, and shows to the satisfaction of the court that the additional evidence is material and that there were reasonable grounds for the failure to adduce such evidence in the proceeding before the Secretary, the court may order the additional evidence (and evidence in rebuttal of the additional evidence) to be taken before the Secretary, and to be adduced upon the hearing in such manner and upon such terms and conditions as the court may determine to be proper. The Secretary may modify the findings of the Secretary as to the facts, or make new findings, by reason of the additional evidence so taken, and the Secretary shall file the modified or new findings, and the recommendations of the Secretary, if any, for the modification or setting aside of the original action of the Secretary with the return of the additional evidence.
(3) Judgment of court
Upon the filing of the petition referred to in paragraph (1), the court shall have jurisdiction to affirm the action, or to set the action aside in whole or in part, temporarily or permanently. The findings of the Secretary as to the facts, if supported by substantial evidence, shall be conclusive.
(4) Finality of judgment
The judgment of the court affirming or setting aside, in whole or in part, any action of the Secretary shall be final, subject to review by the Supreme Court of the United States upon certiorari or certification, as provided in section 1254 of title 28.
(l) Information
(1) In general
Not later than October 1, 1996, and annually thereafter, the Secretary shall compile and make available to physicians and the general public information that the Secretary determines is useful in evaluating the performance of facilities, including a list of facilities—
(A) that have been convicted under Federal or State laws relating to fraud and abuse, false billings, or kickbacks;
(B) that have been subject to sanctions under subsection (h) of this section, together with a statement of the reasons for the sanctions;
(C) that have had certificates revoked or suspended under subsection (i) of this section, together with a statement of the reasons for the revocation or suspension;
(D) against which the Secretary has taken action under subsection (j) of this section, together with a statement of the reasons for the action;
(E) whose accreditation has been revoked, together with a statement of the reasons of the revocation;
(F) against which a State has taken adverse action; and
(G) that meets such other measures of performance as the Secretary may develop.
(2) Date
The information to be compiled under paragraph (1) shall be information for the calendar year preceding the date the information is to be made available to the public.
(3) Explanatory information
The information to be compiled under paragraph (1) shall be accompanied by such explanatory information as may be appropriate to assist in the interpretation of the information compiled under such paragraph.
(m) State laws
Nothing in this section shall be construed to limit the authority of any State to enact and enforce laws relating to the matters covered by this section that are at least as stringent as this section or the regulations issued under this section.
(n) National Advisory Committee
(1) Establishment
In carrying out this section, the Secretary shall establish an advisory committee to be known as the National Mammography Quality Assurance Advisory Committee (hereafter in this subsection referred to as the “Advisory Committee”).
(2) Composition
The Advisory Committee shall be composed of not fewer than 13, nor more than 19 individuals, who are not officers or employees of the Federal Government. The Secretary shall make appointments to the Advisory Committee from among—
(A) physicians,
(B) practitioners, and
(C) other health professionals,
whose clinical practice, research specialization, or professional expertise include a significant focus on mammography. The Secretary shall appoint at least 4 individuals from among national breast cancer or consumer health organizations with expertise in mammography and at least 2 practicing physicians who provide mammography services.
(3) Functions and duties
The Advisory Committee shall—
(A) advise the Secretary on appropriate quality standards and regulations for mammography facilities;
(B) advise the Secretary on appropriate standards and regulations for accreditation bodies;
(C) advise the Secretary in the development of regulations with respect to sanctions;
(D) assist in developing procedures for monitoring compliance with standards under subsection (f) of this section;
(E) make recommendations and assist in the establishment of a mechanism to investigate consumer complaints;
(F) report on new developments concerning breast imaging that should be considered in the oversight of mammography facilities;
(G) determine whether there exists a shortage of mammography facilities in rural and health professional shortage areas and determine the effects of personnel or other requirements of subsection (f) of this section on access to the services of such facilities in such areas;
(H) determine whether there will exist a sufficient number of medical physicists after October 1, 1999, to assure compliance with the requirements of subsection (f)(1)(E) of this section;
(I) determine the costs and benefits of compliance with the requirements of this section (including the requirements of regulations promulgated under this section); and
(J) perform other activities that the Secretary may require.
The Advisory Committee shall report the findings made under subparagraphs (G) and (I) to the Secretary and the Congress no later than October 1, 1993.
(4) Meetings
The Advisory Committee shall meet not less than quarterly for the first 3 years of the program and thereafter, at least biannually.
(5) Chairperson
The Secretary shall appoint a chairperson of the Advisory Committee.
(o) Consultations
In carrying out this section, the Secretary shall consult with appropriate Federal agencies within the Department of Health and Human Services for the purposes of developing standards, regulations, evaluations, and procedures for compliance and oversight.
(p) Breast cancer screening surveillance research grants
(1) Research
(A) Grants
The Secretary shall award grants to such entities as the Secretary may determine to be appropriate to establish surveillance systems in selected geographic areas to provide data to evaluate the functioning and effectiveness of breast cancer screening programs in the United States, including assessments of participation rates in screening mammography, diagnostic procedures, incidence of breast cancer, mode of detection (mammography screening or other methods), outcome and follow up information, and such related epidemiologic analyses that may improve early cancer detection and contribute to reduction in breast cancer mortality. Grants may be awarded for further research on breast cancer surveillance systems upon the Secretary’s review of the evaluation of the program.
(B) Use of funds
Grants awarded under subparagraph (A) may be used—
(i) to study—
(I) methods to link mammography and clinical breast examination records with population-based cancer registry data;
(II) methods to provide diagnostic outcome data, or facilitate the communication of diagnostic outcome data, to radiology facilities for purposes of evaluating patterns of mammography interpretation; and
(III) mechanisms for limiting access and maintaining confidentiality of all stored data; and
(ii) to conduct pilot testing of the methods and mechanisms described in subclauses (I), (II), and (III) of clause (i) on a limited basis.
(C) Grant application
To be eligible to receive funds under this paragraph, an entity shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may require.
(D) Report
A recipient of a grant under this paragraph shall submit a report to the Secretary containing the results of the study and testing conducted under clauses (i) and (ii) of subparagraph (B), along with recommendations for methods of establishing a breast cancer screening surveillance system.
(2) Establishment
The Secretary shall establish a breast cancer screening surveillance system based on the recommendations contained in the report described in paragraph (1)(D).
(3) Standards and procedures
The Secretary shall establish standards and procedures for the operation of the breast cancer screening surveillance system, including procedures to maintain confidentiality of patient records.
(4) Information
The Secretary shall recruit facilities to provide to the breast cancer screening surveillance system relevant data that could help in the research of the causes, characteristics, and prevalence of, and potential treatments for, breast cancer and benign breast conditions, if the information may be disclosed under section 552 of title 5.
(q) State program
(1) In general
The Secretary may, upon application, authorize a State—
(A) to carry out, subject to paragraph (2), the certification program requirements under subsections (b), (c), (d), (g)(1), (h), (i), and (j) of this section (including the requirements under regulations promulgated pursuant to such subsections), and
(B) to implement the standards established by the Secretary under subsection (f) of this section,
with respect to mammography facilities operating within the State.
(2) Approval
The Secretary may approve an application under paragraph (1) if the Secretary determines that—
(A) the State has enacted laws and issued regulations relating to mammography facilities which are the requirements of this section (including the requirements under regulations promulgated pursuant to such subsections), and
(B) the State has provided satisfactory assurances that the State—
(i) has the legal authority and qualified personnel necessary to enforce the requirements of and the regulations promulgated pursuant to this section (including the requirements under regulations promulgated pursuant to such subsections),
(ii) will devote adequate funds to the administration and enforcement of such requirements, and
(iii) will provide the Secretary with such information and reports as the Secretary may require.
(3) Authority of Secretary
In a State with an approved application—
(A) the Secretary shall carry out the Secretary’s functions under subsections (e) and (f) of this section;
(B) the Secretary may take action under subsections (h), (i), and (j) of this section; and
(C) the Secretary shall conduct oversight functions under subsections (g)(2) and (g)(3) of this section.
(4) Withdrawal of approval
(A) In general
The Secretary may, after providing notice and opportunity for corrective action, withdraw the approval of a State’s authority under paragraph (1) if the Secretary determines that the State does not meet the requirements of such paragraph. The Secretary shall promulgate regulations for the implementation of this subparagraph.
(B) Effect of withdrawal
If the Secretary withdraws the approval of a State under subparagraph (A), the certificate of any facility accredited by the State shall continue in effect until the expiration of a reasonable period, as determined by the Secretary, for such facility to obtain certification by the Secretary.
(r) Funding
(1) Fees
(A) In general
The Secretary shall, in accordance with this paragraph assess and collect fees from persons described in subsection (d)(1)(A) of this section (other than persons who are governmental entities, as determined by the Secretary) to cover the costs of inspections conducted under subsection (g)(1) of this section by the Secretary or a State acting under a delegation under subparagraph (A) of such subsection. Fees may be assessed and collected under this paragraph only in such manner as would result in an aggregate amount of fees collected during any fiscal year which equals the aggregate amount of costs for such fiscal year for inspections of facilities of such persons under subsection (g)(1) of this section. A person’s liability for fees shall be reasonably based on the proportion of the inspection costs which relate to such person.
(B) Deposit and appropriations
(i) Deposit and availability
Fees collected under subparagraph (A) shall be deposited as an offsetting collection to the appropriations for the Department of Health and Human Services as provided in appropriation Acts and shall remain available without fiscal year limitation.
(ii) Appropriations
Fees collected under subparagraph (A) shall be collected and available only to the extent provided in advance in appropriation Acts.
(2) Authorization of appropriations
There are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this section—
(A) to award research grants under subsection (p) of this section, such sums as may be necessary for each of the fiscal years 1993 through 2002; and
(B) for the Secretary to carry out other activities which are not supported by fees authorized and collected under paragraph (1), such sums as may be necessary for fiscal years 1993 through 2002.
* * * * * * *
PART H—ORGAN TRANSPLANTS
ORGAN PROCUREMENT ORGANIZATIONS
Sec. 371. [42 U.S.C. 273]
(a)(1) The Secretary may make grants for the planning of qualified organ procurement organizations described in subsection (b).
(2) The Secretary may make grants for the establishment, initial operation, consolidation, and expansion of qualified organ procurement organizations described in subsection (b).
(3) The Secretary may make grants to, and enter into contracts with, qualified organ procurement organizations described in subsection (b) and other nonprofit private entities for the purpose of carrying out special projects designed to increase the number of organ donors.
(b)(1) A qualified organ procurement organization for which grants may be made under subsection (a) is an organization which, as determined by the Secretary, will carry out the functions described in paragraph (2) and—
(A) is a nonprofit entity,
(B) has accounting and other fiscal procedures (as specified by the Secretary) necessary to assure the fiscal stability of the organization,
(C) has an agreement with the Secretary to be reimbursed under title XVIII of the Social Security Act for the procurement of kidneys,
(D) notwithstanding any other provision of law, has met the other requirements of this section and has been certified or recertified by the Secretary within the previous 4-year period as meeting the performance standards to be a qualified organ procurement organization through a process that either—
(i) granted certification or recertification within such 4-year period with such certification or recertification in effect as of January 1, 2000, and remaining in effect through the earlier of—
(I) January 1, 2002; or
(II) the completion of recertification under the requirements of clause (ii);
(ii) is defined through regulations that are promulgated by the Secretary by not later than January 1, 2002, that—
(I) require recertifications of qualified organ procurement organizations not more frequently than once every 4 years;
(II) rely on outcome and process performance measures that are based on empirical evidence, obtained through reasonable efforts, of organ donor potential and other related factors in each service area of qualified organ procurement organizations;
(III) use multiple outcome measures as part of the certification process; and
(IV) provide for a qualified organ procurement organization to appeal a decertification to the Secretary on substantive and procedural grounds;[245]
(E) has procedures to obtain payment for non-renal organs provided to transplant centers,
(F) has a defined service area that is of sufficient size to assure maximum effectiveness in the procurement and equitable distribution of organs, and that either includes an entire metropolitan statistical area (as specified by the Director of the Office of Management and Budget) or does not include any part of the area,
(G) has a director and such other staff, including the organ donation coordinators and organ procurement specialists necessary to effectively obtain organs from donors in its service area, and
(H) has a board of directors or an advisory board which—
(i) is composed of—
(I) members who represent hospital administrators, intensive care or emergency room personnel, tissue banks, and voluntary health associations in its service area,
(II) members who represent the public residing in such area,
(III) a physician with knowledge, experience, or skill in the field of histocompatibility or an individual with a doctorate degree in a biological science with knowledge, experience, or skill in the field of histocompatibility,
(IV) a physician with knowledge or skill in the field of neurology, and
(V) from each transplant center in its service area which has arrangements described in paragraph (2)(G) with the organization, a member who is a surgeon who has practicing privileges in such center and who performs organ transplant surgery,
(ii) has the authority to recommend policies for the procurement of organs and the other functions described in paragraph (2), and
(iii) has no authority over any other activity of the organization.
(2)(A) Not later than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this paragraph, the Secretary shall publish in the Federal Register a notice of proposed rulemaking to establish criteria for determining whether an entity meets the requirement established in paragraph (1)(E).
(B) Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this paragraph, the Secretary shall publish in the Federal Register a final rule to establish the criteria described in subparagraph (A).
(c) Pancreata procured by an organ procurement organization and used for islet cell transplantation or research shall be counted for purposes of certification or recertification under subsection (b).
ORGAN PROCUREMENT AND TRANSPLANTATION NETWORK
Sec. 372. [42 U.S.C. 274]
(a) The Secretary shall by contract provide for the establishment and operation of an Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network which meets the requirements of subsection (b). The amount provided under such contract in any fiscal year may not exceed $2,000,000. Funds for such contracts shall be made available from funds available to the Public Health Service from appropriations for fiscal years beginning after fiscal year 1984.
(b)(1) The Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network shall carry out the functions described in paragraph (2) and shall—
(A) be a private nonprofit entity that has an expertise in organ procurement and transplantation, and
(B) have a board of directors—
(i) that includes representatives of organ procurement organizations (including organizations that have received grants under section 371), transplant centers, voluntary health associations, and the general public; and
(ii) that shall establish an executive committee and other committees, whose chairpersons shall be selected to ensure continuity of leadership for the board.
(2) The Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network shall—
(A) establish in one location or through regional centers—
(i) a national list of individuals who need organs, and
(ii) a national system, through the use of computers and in accordance with established medical criteria, to match organs and individuals included in the list, especially individuals whose immune system makes it difficult for them to receive organs,
(B) establish membership criteria and medical criteria for allocating organs and provide to members of the public an opportunity to comment with respect to such criteria,
(C) maintain a twenty-four-hour telephone service to facilitate matching organs with individuals included in the list,
(D) assist organ procurement organizations in the nationwide distribution of organs equitably among transplant patients,
(E) adopt and use standards of quality for the acquisition and transportation of donated organs, including standards for preventing the acquisition of organs that are infected with the etiologic agent for acquired immune deficiency syndrome,
(F) prepare and distribute, on a regionalized basis (and, to the extent practicable, among regions or on a national basis), samples of blood sera from individuals who are included on the list and whose immune system makes it difficult for them to receive organs, in order to facilitate matching the compatibility of such individuals with organ donors,
(G) coordinate, as appropriate, the transportation of organs from organ procurement organizations to transplant centers,
(H) provide information to physicians and other health professionals regarding organ donation,
(I) collect, analyze, and publish data concerning organ donation and transplants,
(J) carry out studies and demonstration projects for the purpose of improving procedures for organ procurement and allocation, and
(K) work actively to increase the supply of donated organs.
(L) submit to the Secretary an annual report containing information on the comparative costs and patient outcomes at each transplant center affiliated with the organ procurement and transplantation network.
(M) recognize the differences in health and in organ transplantation issues between children and adults throughout the system and adopt criteria, polices, and procedures that address the unique health care needs of children,
(N) carry out studies and demonstration projects for the purpose of improving procedures for organ donation procurement and allocation, including but not limited to projects to examine and attempt to increase transplantation among populations with special needs, including children and individuals who are members of racial or ethnic minority groups, and among populations with limited access to transportation, and
(O) provide that for purposes of this paragraph, the term “children” refers to individuals who are under the age of 18.
(c) The Secretary shall establish procedures for—
(1) receiving from interested persons critical comments relating to the manner in which the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network is carrying out the duties of the Network under subsection (b); and
(2) the consideration by the Secretary of such critical comments.
* * * * * * *
PART S—HEALTH CARE QUALITY PROGRAMS
Subpart I—National Strategy for Quality Improvement in Health Care
Sec. 399HH. [42 U.S.C. 280j] NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR QUALITY IMPROVEMENT IN HEALTH CARE.
(a) Establishment of National Strategy and Priorities.—
(1) National strategy.—The Secretary, through a transparent collaborative process, shall establish a national strategy to improve the delivery of health care services, patient health outcomes, and population health.
(2) Identification of priorities.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary shall identify national priorities for improvement in developing the strategy under paragraph (1).
(B) Requirements.—The Secretary shall ensure that priorities identified under subparagraph (A) will—
(i) have the greatest potential for improving the health outcomes, efficiency, and patient-centeredness of health care for all populations, including children and vulnerable populations;
(ii) identify areas in the delivery of health care services that have the potential for rapid improvement in the quality and efficiency of patient care;
(iii) address gaps in quality, efficiency, comparative effectiveness information, and health outcomes measures and data aggregation techniques;
(iv) improve Federal payment policy to emphasize quality and efficiency;
(v) enhance the use of health care data to improve quality, efficiency, transparency, and outcomes;
(vi) address the health care provided to patients with high-cost chronic diseases;
(vii) improve research and dissemination of strategies and best practices to improve patient safety and reduce medical errors, preventable admissions and readmissions, and health care-associated infections;
(viii) reduce health disparities across health disparity populations (as defined in section 485E) and geographic areas; and
(ix) address other areas as determined appropriate by the Secretary.
(C) Considerations.—In identifying priorities under subparagraph (A), the Secretary shall take into consideration the recommendations submitted by the entity with a contract under section 1890(a) of the Social Security Act and other stakeholders.
(D) Coordination with state agencies.—The Secretary shall collaborate, coordinate, and consult with State agencies responsible for administering the Medicaid program under title XIX of the Social Security Act and the Children’s Health Insurance Program under title XXI of such Act with respect to developing and disseminating strategies, goals, models, and timetables that are consistent with the national priorities identified under subparagraph (A).
(b) Strategic Plan.—
(1) In general.—The national strategy shall include a comprehensive strategic plan to achieve the priorities described in subsection (a).
(2) Requirements.—The strategic plan shall include provisions for addressing, at a minimum, the following:
(A) Coordination among agencies within the Department, which shall include steps to minimize duplication of efforts and utilization of common quality measures, where available. Such common quality measures shall be measures identified by the Secretary under section 1139A or 1139B of the Social Security Act or endorsed under section 1890 of such Act.
(B) Agency-specific strategic plans to achieve national priorities.
(C) Establishment of annual benchmarks for each relevant agency to achieve national priorities.
(D) A process for regular reporting by the agencies to the Secretary on the implementation of the strategic plan.
(E) Strategies to align public and private payers with regard to quality and patient safety efforts.
(F) Incorporating quality improvement and measurement in the strategic plan for health information technology required by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (Public Law 111–5).
(c) Periodic Update of National Strategy.—The Secretary shall update the national strategy not less than annually. Any such update shall include a review of short- and long-term goals.
(d) Submission and Availability of National Strategy and Updates.—
(1) Deadline for initial submission of national strategy.—Not later than January 1, 2011, the Secretary shall submit to the relevant committees of Congress the national strategy described in subsection (a).
(2) Updates.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary shall submit to the relevant committees of Congress an annual update to the strategy described in paragraph (1).
(B) Information submitted.—Each update submitted under subparagraph (A) shall include—
(i) a review of the short- and long-term goals of the national strategy and any gaps in such strategy;
(ii) an analysis of the progress, or lack of progress, in meeting such goals and any barriers to such progress;
(iii) the information reported under section 1139A of the Social Security Act, consistent with the reporting requirements of such section; and
(iv) the information reported under section 1139A of the Social Security Act, consistent with the reporting requirements of such section; and
(C) Satisfaction of other reporting requirements.—Compliance with the requirements of clauses (iii) and (iv) of subparagraph (B) shall satisfy the reporting requirements under sections 1139A(a)(6) and 1139B(b)(4), respectively, of the Social Security Act.
(e) Health Care Quality Internet Website.—Not later than January 1, 2011, the Secretary shall create an Internet website to make public information regarding—
(1) the national priorities for health care quality improvement established under subsection (a)(2);
(2) the agency-specific strategic plans for health care quality described in subsection (b)(2)(B); and
(3) other information, as the Secretary determines to be appropriate.
STATE PLANS
Sec. 604. [42 U.S.C. 291d]
(a) Any State desiring to participate in this part may submit a State plan. Such plan must—
(1) designate a single State agency as the sole agency for the administration of the plan, or designate such agency as the sole agency for supervising the administration of the plan;
(2) contain satisfactory evidence that the State agency designated in accordance with paragraph (1) will have authority to carry out such plan in conformity with this part;
(3) provide for the designation of a State advisory council which shall include (A) representatives of nongovernmental organizations or groups, and of public agencies, concerned with the operation, construction, or utilization of hospital or other facilities for diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of illness or disease, or for provision of rehabilitation services, and representatives particularly concerned with education or training of health professions personnel, and (B) an equal number of representatives of consumers familiar with the need for the services provided by such facilities, to consult with the State agency in carrying out the plan, and provide, if such council does not include any representatives of nongovernmental organizations or groups, or State agencies, concerned with rehabilitation, for consultation with organizations, groups, and State agencies so concerned;
(4) set forth, in accordance with criteria established in regulations prescribed under section 603 and on the basis of a statewide inventory of existing facilities, a survey of need, and (except to the extent provided by or pursuant to such regulations) community, area, or regional plans—
(A) the number of general hospital beds and long-term care beds, and the number and types of hospital facilities and facilities for long-term care, needed to provide adequate facilities for inpatient care of people residing in the State, and a plan for the distribution of such beds and facilities in service areas throughout the State;
(B) the public health centers needed to provide adequate public health services for people residing in the State, and a plan for the distribution of such centers throughout the State;
(C) the outpatient facilities needed to provide adequate diagnostic or treatment services to ambulatory patients residing in the State, and a plan for distribution of such facilities throughout the State;
(D) the rehabilitation facilities needed to assure adequate rehabilitation services for disabled persons residing in the State, and a plan for distribution of such facilities throughout the State; and
(E) effective January 1, 1966, the extent to which existing facilities referred to in section 601(a) or (b) in the State are in need of modernization;
(5) set forth a construction and modernization program conforming to the provisions set forth pursuant to paragraph (4) and regulations prescribed under section 603 and providing for construction or modernization of the hospital or long-term care facilities, public health centers, outpatient facilities, and rehabilitation facilities which are needed, as determined under the provisions so set forth pursuant to paragraph (4);
(6) set forth, with respect to each of such types of medical facilities, the relative need, determined in accordance with regulations prescribed under section 603, for projects for facilities of that type, and provide for the construction or modernization, insofar as financial resources available therefor and for maintenance and operation make possible, in the order of such relative need;
(7) provide minimum standards (to be fixed in the discretion of the State) for the maintenance and operation of facilities providing inpatient care which receive aid under this part and, effective July 1, 1966, provide for enforcement of such standards with respect to projects approved by the Surgeon General under this part after June 30, 1964;
(8) [246] provide such methods of administration of the State plan, including methods relating to the establishment and maintenance of personnel standards on a merit basis (except that the Surgeon General shall exercise no authority with respect to the selection, tenure of office, or compensation of any individual employed in accordance with such methods), as are found by the Surgeon General to be necessary for the proper and efficient operation of the plan;
(9) provide for affording to every applicant for a construction or modernization project an opportunity for a hearing before the State agency;
(10) provide that the State agency will make such reports, in such form and containing such information, as the Surgeon General may from time to time reasonably require, and will keep such records and afford such access thereto as the Surgeon General may find necessary to assure the correctness and verification of such reports;
(11) provide that the Comptroller General of the United States or his duly authorized representatives shall have access for the purpose of audit and examination to the records specified in paragraph (10);
(12) provide that the State agency will from time to time, but not less often than annually, review its State plan and submit to the Surgeon General any modifications thereof which it considers necessary; and
(13) Effective[247] July 1, 1971, provide that before any project for construction or modernization of any general hospital is approved by the State agency there will be reasonable assurance of adequate provision for extended care services (as determined in accordance with regulations) to patients of such hospital when such services are medically appropriate for them, with such services being provided in facilities which (A) are structurally part of, physically connected with, or in immediate proximity to, such hospital, and (B) either (i) are under the supervision of the professional staff of such hospital or (ii) have organized medical staffs and have in effect transfer agreements with such hospital; except that the Secretary may, at the request of the State agency, waive compliance with clause (A) or (B), or both such clauses, as the case may be, in the case of any project if the State agency has determined that compliance with such clause or clauses in such case would be inadvisable.
* * * * * * *
SUBCHAPTER VII—AGENCY FOR HEALTHCARE RESEARCH AND QUALITY
PART B—HEALTH CARE IMPROVEMENT RESEARCH
INFORMATION ON QUALITY AND COST OF CARE
Sec. 913. [42 U.S.C. 299b-2]
(a) In General.—The Director shall—
(1) conduct a survey to collect data on a nationally representative sample of the population on the cost, use and, for fiscal year 2001 and subsequent fiscal years, quality of health care, including the types of health care services Americans use, their access to health care services, frequency of use, how much is paid for the services used, the source of those payments, the types and costs of private health insurance, access, satisfaction, and quality of care for the general population including rural residents and also for populations identified in section 299(c) of this title; and
(2) develop databases and tools that provide information to States on the quality, access, and use of health care services provided to their residents.
(b) Quality and Outcomes Information.—
(1) In general.—Beginning in fiscal year 2001, the Director shall ensure that the survey conducted under subsection (a)(1) of this section will—
(A) identify determinants of health outcomes and functional status, including the health care needs of populations identified in section 299(c) of this title, provide data to study the relationships between health care quality, outcomes, access, use, and cost, measure changes over time, and monitor the overall national impact of Federal and State policy changes on health care;
(B) provide information on the quality of care and patient outcomes for frequently occurring clinical conditions for a nationally representative sample of the population including rural residents; and
(C) provide reliable national estimates for children and persons with special health care needs through the use of supplements or periodic expansions of the survey.
In expanding the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, as in existence on December 6, 1999, in fiscal year 2001 to collect information on the quality of care, the Director shall take into account any outcomes measurements generally collected by private sector accreditation organizations.
(2) Annual report.—Beginning in fiscal year 2003, the Secretary, acting through the Director, shall submit to Congress an annual report on national trends in the quality of health care provided to the American people.
INFORMATION SYSTEMS FOR HEALTH CARE IMPROVEMENT
Sec. 914. [42 U.S.C. 299b-3]
(a) In General.—In order to foster a range of innovative approaches to the management and communication of health information, the Agency shall conduct and support research, evaluations, and initiatives to advance—
(1) the use of information systems for the study of health care quality and outcomes, including the generation of both individual provider and plan-level comparative performance data;
(2) training for health care practitioners and researchers in the use of information systems;
(3) the creation of effective linkages between various sources of health information, including the development of information networks;
(4) the delivery and coordination of evidence-based health care services, including the use of real-time health care decision-support programs;
(5) the utility and comparability of health information data and medical vocabularies by addressing issues related to the content, structure, definitions and coding of such information and data in consultation with appropriate Federal, State and private entities;
(6) the use of computer-based health records in all settings for the development of personal health records for individual health assessment and maintenance, and for monitoring public health and outcomes of care within populations; and
(7) the protection of individually identifiable information in health services research and health care quality improvement.
* * * * * * *
PART D—HEALTH CARE QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
Subpart I—Quality Measure Development
Sec. 931. [42 USC 299b-31] QUALITY MEASURE DEVELOPMENT.
(a) Quality Measure.—In this subpart, the term “quality measure” means a standard for measuring the performance and improvement of population health or of health plans, providers of services, and other clinicians in the delivery of health care services.
(b) Identification of Quality Measures.—
(1) Identification.—The Secretary, in consultation with the Director of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, shall identify, not less often than triennially, gaps where no quality measures exist and existing quality measures that need improvement, updating, or expansion, consistent with the national strategy under section 399HH, to the extent available, for use in Federal health programs. In identifying such gaps and existing quality measures that need improvement, the Secretary shall take into consideration—
(A) the gaps identified by the entity with a contract under section 1890(a) of the Social Security Act and other stakeholders;
(B) quality measures identified by the pediatric quality measures program under section 1139A of the Social Security Act; and
(C) quality measures identified through the Medicaid Quality Measurement Program under section 1139B of the Social Security Act.
(2) Publication.—The Secretary shall make available to the public on an Internet website a report on any gaps identified under paragraph (1) and the process used to make such identification.
(c) Grants or Contracts for Quality Measure Development.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary shall award grants, contracts, or intergovernmental agreements to eligible entities for purposes of developing, improving, updating, or expanding quality measures identified under subsection (b).
(2) Prioritization in the development of quality measures.—In awarding grants, contracts, or agreements under this subsection, the Secretary shall give priority to the development of quality measures that allow the assessment of—
(A) health outcomes and functional status of patients;
(B) the management and coordination of health care across episodes of care and care transitions for patients across the continuum of providers, health care settings, and health plans;
(C) the experience, quality, and use of information provided to and used by patients, caregivers, and authorized representatives to inform decisionmaking about treatment options, including the use of shared decisionmaking tools and preference sensitive care (as defined in section 936);
(D) the meaningful use of health information technology;
(E) the safety, effectiveness, patient- centeredness, appropriateness, and timeliness of care;
(F) the efficiency of care;
(G) the equity of health services and health disparities across health disparity populations (as defined in section 485E) and geographic areas;
(H) patient experience and satisfaction;
(I) the use of innovative strategies and methodologies identified under section 933; and
(J) other areas determined appropriate by the Secretary.
(3) Eligible entities.—To be eligible for a grant or contract under this subsection, an entity shall—
(A) have demonstrated expertise and capacity in the development and evaluation of quality measures;
(B) have adopted procedures to include in the quality measure development process—
(i) the views of those providers or payers whose performance will be assessed by the measure; and
(ii) the views of other parties who also will use the quality measures(such as patients, consumers, and health care purchasers);
(C) collaborate with the entity with a contract under section 1890(a) of the Social Security Act and other stakeholders, as practicable, and the Secretary so that quality measures developed by the eligible entity will meet the requirements to be considered for endorsement by the entity with a contract under such section 1890(a);
(D) have transparent policies regarding governance and conflicts of interest; and
(E) submit an application to the Secretary at such time and in such manner, as the Secretary may require.
(4) Use of funds.—An entity that receives a grant, contract, or agreement under this subsection shall use such award to develop quality measures that meet the following requirements:
(A) Such measures support measures required to be reported under the Social Security Act, where applicable, and in support of gaps and existing quality measures that need improvement, as described in subsection (b)(1)(A).
(B) Such measures support measures developed under section 1139A of the Social Security Act and the Medicaid Quality Measurement Program under section 1139B of such Act, where applicable.
(C) To the extent practicable, data on such quality measures is able to be collected using health information technologies.
(D) Each quality measure is free of charge to users of such measure.
(E) Each quality measure is publicly available on an Internet website.
(d) Other Activities by the Secretary.—The Secretary may use amounts available under this section to update and test, where applicable, quality measures endorsed by the entity with a contract under section 1890(a) of the Social Security Act or adopted by the Secretary.
(e) Coordination of Grants.—The Secretary shall ensure that grants or contracts awarded under this section are coordinated with grants and contracts awarded under sections 1139A(5) and 1139B(4)(A) of the Social Security Act.
Subpart II--Health Care Quality Improvement Programs
Sec. 933. [42 USC 299b-33] HEALTH CARE DELIVERY SYSTEM RESEARCH.
(a) Purpose.— The purposes of this section are to—
(1) enable the Director to identify, develop, evaluate, disseminate, and provide training in innovative methodologies and strategies for quality improvement practices in the delivery of health care services that represent best practices (referred to as “best practices”) in health care quality, safety, and value; and
(2) ensure that the Director is accountable forimplementing a model to pursue such research in a collaborative manner with other related Federal agencies.
(b) General Functions of the Center.— The Center for Quality Improvement and Patient Safety of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (referred to in this section as the “Center”), or any other relevant agency or department designated by the Director, shall
(1) carry out its functions using research from a variety of disciplines, which may include epidemiology, health services, sociology, psychology, human factors engineering, biostatistics, health economics, clinical research, and health informatics;
(2) conduct or support activities consistent with the purposes described in subsection (a), and for—
(A) best practices for quality improvement practices in the delivery of health care services; and
(B) that include changes in processes of care and the redesign of systems used by providers that will reliably result in intended health outcomes, improve patient safety, and reduce medical errors (such as skill development for health care providers in team-based health care delivery and rapid cycle process improvement) and facilitate adoption of improved workflow;
(3) identify health care providers, including health care systems, single institutions, and individual providers, that
(A) deliver consistently high-quality, efficient health care services (as determined by the Secretary); and
(B) employ best practices that are adaptable and scalable to diverse health care settings or effective in improving care across diverse settings;
(4) assess research, evidence, and knowledge about what strategies and methodologies are most effective in improving health care delivery;
(5) find ways to translate such information rapidly and effectively into practice, and document the sustainability of those improvements;
(6) create strategies for quality improvement through the development of tools, methodologies, and interventions that can successfully reduce variations in the delivery of health care;
(7) identify, measure, and improve organizational, human, or other causative factors, including those related to the culture and system design of a health care organization, that contribute to the success and sustainability of specific quality improvement and patient safety strategies;
(8) provide for the development of best practices in the delivery of health care services that—
(A) have a high likelihood of success, based on structured review of empirical evidence;
(B) are specified with sufficient detail of the individual processes, steps, training, skills, and knowledge required for implementation and incorporation into workflow of health care practitioners in a variety of settings;
(C) are designed to be readily adapted by health care providers in a variety of settings; and
(D) where applicable, assist health care providers in working with other health care providers across the continuum of care and in engaging patients and their families in improving the care and patient health outcomes;
(9) provide for the funding of the activities of organizations with recognized expertise and excellence in improving the delivery of health care services, including children’s health care, by involving multiple disciplines, managers of health care entities, broad development and training, patients, caregivers and families, and frontline health care workers, including activities for the examination of strategies to share best quality improvement practices and to promote excellence in the delivery of health care services; and
(10) build capacity at the State and community level to lead quality and safety efforts through education, training, and mentoring programs to carry out the activities under paragraphs (1) through (9).
(c) Research Functions of Center.—
(1) In general.—The Center shall support, such as through a contract or other mechanism, research on health care delivery system improvement and the development of tools to facilitate adoption of best practices that improve the quality, safety, and efficiency of health care delivery services. Such support may include establishing a Quality Improvement Network Research Program for the purpose of testing, scaling, and disseminating of interventions to improve quality and efficiency in health care. Recipients of funding under the Program may include national, State, multi-State, or multi-site quality improvement networks.
(2) Research requirements.—The research conducted pursuant to paragraph (1) shall
(A) address the priorities identified by the Secretary in the national strategic plan established under section 399HH;
(B) identify areas in which evidence is insufficient to identify strategies and methodologies, taking into consideration areas of insufficient evidence identified by the entity with a contract under section 1890(a) of the Social Security Act in the report required under section 399JJ;
(C) address concerns identified by health care institutions and providers and communicated through the Center pursuant to subsection (d);
(D) reduce preventable morbidity, mortality, and associated costs of morbidity and mortality by building capacity for patient safety research;
(E) support the discovery of processes for the reliable, safe, efficient, and responsive delivery of health care, taking into account discoveries from clinical research and comparative effectiveness research;
(F) allow communication of research findings and translate evidence into practice recommendations that are adaptable to a variety of settings, and which, as soon as practicable after the establishment of the Center, shall include—
(i) the implementation of a national application of Intensive Care Unit improvement projects relating to the adult (including geriatric), pediatric, and neonatal patient populations;
(ii) practical methods for addressing health care associated infections, including Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant Entercoccus infections and other emerging infections; and
(iii) practical methods for reducing preventable hospital admissions and readmissions;
(G) expand demonstration projects for improving the quality of children’s health care and the use of health information technology, such as through Pediatric Quality Improvement Collaboratives and Learning Networks, consistent with provisions of section 1139A of the Social Security Act for assessing and improving quality, where applicable;
(H) identify and mitigate hazards by—
(i) analyzing events reported to patient safety reporting systems and patient safety organizations; and
(ii) using the results of such analyses to develop scientific methods of response to such events;
(I) include the conduct of systematic reviews of existing practices that improve the quality, safety, and efficiency of health care delivery, as well as new research on improving such practices; and
(J) include the examination of how to measure and evaluate the progress of quality and patient safety activities.
(d) Dissemination of Research Findings.—
(1) Public availability.—The Director shall make the research findings of the Center available to the public through multiple media and appropriate formats to reflect the varying needs of health care providers and consumers and diverse levels of health literacy.
(2) Linkage to health information technology.—The Secretary shall ensure that research findings and results generated by the Center are shared with the Office of the National Coordinator of Health Information Technology and used to inform the activities of the health information technology extension program under section 3012, as well as any relevant standards, certification criteria, or implementation specifications.
(e) Prioritization.—The Director shall identify and regularly update a list of processes or systems on which to focus research and dissemination activities of the Center, taking into account—
(1) the cost to Federal health programs;
(2) consumer assessment of health care experience;
(3) provider assessment of such processes or systems and opportunities to minimize distress and injury to the health care workforce;
(4) the potential impact of such processes or systems on health status and function of patients, including vulnerable populations including children;
(5) the areas of insufficient evidence identified under subsection (c)(2)(B); and
(6) the evolution of meaningful use of health information technology, as defined in section 3000.
(f) Coordination.— The Center shall coordinate its activities with activities conducted by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation established under section 1115A of the Social Security Act.
(g) Funding.— There is authorized to be appropriated to carry out this section $20,000,000 for fiscal years 2010 through 2014.
Sec. 934. [42 USC 299b–34] QUALITY IMPROVEMENT TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND IMPLEMENTATION.
(a) In General.— The Director, through the Center for Quality Improvement and Patient Safety of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (referred to in this section as the ‘Center’), shall award—
(1) technical assistance grants or contracts to eligible entities to provide technical support to institutions that deliver health care and health care providers (including rural and urban providers of services and suppliers with limited infrastructure and financial resources to implement and support quality improvement activities, providers of services and suppliers with poor performance scores, and providers of services and suppliers for which there are disparities in care among subgroups of patients) so that such institutions and providers understand, adapt, and implement the models and practices identified in the research conducted by the Center, including the Quality Improvement Networks Research Program; and
(2) implementation grants or contracts to eligible entities to implement the models and practices described under paragraph (1).
(b) Eligible Entities.—
(1) Technical assistance award.— To be eligible to receive a technical assistance grant or contract under subsection (a)(1), an entity—
(A) may be a health care provider, health care provider association, professional society, health care worker organization, Indian health organization, quality improvement organization, patient safety organization, local quality improvement collaborative, the Joint Commission, academic health center, university, physician-based research network, primary care extension program established under section 399W, a Federal Indian Health Service program or a health program operated by an Indian tribe (as defined in section 4 of the Indian Health Care Improvement Act), or any other entity identified by the Secretary; and
(B) shall have demonstrated expertise in providing information and technical support and assistance to health care providers regarding quality improvement.
(2) Implementation award.—To be eligible to receive an implementation grant or contract under subsection (a)(2), an entity—
(A) may be a hospital or other health care provider or consortium or providers, as determined by the Secretary; and
(B) shall have demonstrated expertise in providing information and technical support and assistance to health care providers regarding quality improvement.
(c) Application.—
(1) Technical assistance award.— To receive a technical assistance grant or contract under subsection (a)(1), an eligible entity shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time, in such manner, and containing—
(A) a plan for a sustainable business model that may include a system of—
(i) charging fees to institutions and providers that receive technical support from the entity; and
(ii) reducing or eliminating such fees for such institutions and providers that serve low-income populations; and
(B) such other information as the Director may require.
(2) Implementation award.—To receive a grant or contract under subsection (a)(2), an eligible entity shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time, in such manner, and containing—
(A) a plan for implementation of a model or practice identified in the research conducted by the Center including—
(i) financial cost, staffing requirements, and timeline for implementation; and
(ii) pre- and projected post-implementation quality measure performance data in targeted improvement areas identified by the Secretary; and
(B) such other information as the Director may require.
(d) Matching Funds.— The Director may not award a grant or contract under this section to an entity unless the entity agrees that it will make available (directly or through contributions from other public or private entities) non-Federal contributions toward the activities to be carried out under the grant or contract in an amount equal to $1 for each $5 of Federal funds provided under the grant or contract. Such non-Federal matching funds may be provided directly or through donations from public or private entities and may be in cash or in-kind, fairly evaluated, including plant, equipment, or services.
(e) Evaluation.—
(1) In general.—The Director shall evaluate the performance of each entity that receives a grant or contract under this section. The evaluation of an entity shall include a study of—
(A) the success of such entity in achieving the implementation, by the health care institutions and providers assisted by such entity, of the models and practices identified in the research conducted by the Center under section 933;
(B) the perception of the health care institutions and providers assisted by such entity regarding the value of the entity; and
(C) where practicable, better patient health outcomes and lower cost resulting from the assistance provided by such entity.
(2) Effect of Evaluation.—Based on the outcome of the evaluation of the entity under paragraph (1), the Director shall determine whether to renew a grant or contract with such entity under this section.
(f) Coordination.— The entities that receive a grant or contract under this section shall coordinate with health information technology regional extension centers under section 3012(c) and the primary care extension program established under section 399W regarding the dissemination of quality improvement, system delivery reform, and best practices information.
Sec. 935. [42 USC 299b-35] GRANTS OR CONTRACTS TO IMPLEMENT MEDICATION MANAGEMENT SERVICES IN TREATMENT OF CHRONIC DISEASES.
(a) In General.— The Secretary, acting through the Patient Safety Research Center established in section 933 (referred to in this section as the “Center”), shall establish a program to provide grants or contracts to eligible entities to implement medication management (referred to in this section as “MTM”) services provided by licensed pharmacists, as a collaborative, multidisciplinary, interprofessional approach to the treatment of chronic diseases for targeted individuals, to improve the quality of care and reduce overall cost in the treatment of such diseases. The Secretary shall commence the program under this section not later than May 1, 2010.
(b) Eligible Entities.— To be eligible to receive a grant or contract under subsection (a), an entity shall—
(1) provide a setting appropriate for MTM services, as recommended by the experts described in subsection (e);
(2) submit to the Secretary a plan for achieving long-term financial sustainability;
(3) where applicable, submit a plan for coordinating MTM services through local community health teams established in section 3502 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act or in collaboration with primary care extension programs established in section 399W;
(4) submit a plan for meeting the requirements under subsection (c); and
(5) submit to the Secretary such other information as the Secretary may require.
(c) MTM Services to Targeted Individuals.— The MTM services provided with the assistance of a grant or contract awarded under subsection (a) shall, as allowed by State law including applicable collaborative pharmacy practice agreements, include—
(1) performing or obtaining necessary assessments of the health and functional status of each patient receiving such MTM services;
(2) formulating a medication treatment plan according to therapeutic goals agreed upon by the prescriber and the patient or caregiver or authorized representative of the patient;
(3) selecting, initiating, modifying, recommending changes to, or administering medication therapy;
(4) monitoring, which may include access to, ordering, or performing laboratory assessments, and evaluating the response of the patient to therapy, including safety and effectiveness;
(5) performing an initial comprehensive medication review to identify, resolve, and prevent medication-related problems, including adverse drug events, quarterly targeted medication reviews for ongoing monitoring, and additional followup interventions on a schedule developed collaboratively with the prescriber;
(6) documenting the care delivered and communicating essential information about such care, including a summary of the medication review, and the recommendations of the pharmacist to other appropriate health care providers of the patient in a timely fashion;
(7) providing education and training designed to enhance the understanding and appropriate use of the medications by the patient, caregiver, and other authorized representative;
(8) providing information, support services, and resources and strategies designed to enhance patient adherence with therapeutic regimens;
(9) coordinating and integrating MTM services within the broader health care management services provided to the patient; and
(10) such other patient care services allowed under pharmacist scopes of practice in use in other Federal programs that have implemented MTM services.
(d) Targeted Individuals.— MTM services provided by licensed pharmacists under a grant or contract awarded under subsection (a) shall be offered to targeted individuals who—
(1) take 4 or more prescribed medications (including over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements);
(2) take any “high risk” medications;
(3) have 2 or more chronic diseases, as identified by the Secretary; or
(4) have undergone a transition of care, or other factors, as determined by the Secretary, that are likely to create a high risk of medication-related problems.
(e) Consultation With Experts.—In designing and implementing MTM services provided under grants or contracts awarded under subsection (a), the Secretary shall consult with Federal, State, private, public-private, and academic entities, pharmacy and pharmacist organizations, health care organizations, consumer advocates, chronic disease groups, and other stakeholders involved with the research, dissemination, and implementation of pharmacist- delivered MTM services, as the Secretary determines appropriate. The Secretary, in collaboration with this group, shall determine whether it is possible to incorporate rapid cycle process improvement concepts in use in other Federal programs that have implemented MTM services.
(f) Reporting to the Secretary.—An entity that receives a grant or contract under subsection (a) shall submit to the Secretary a report that describes and evaluates, as requested by the Secretary, the activities carried out under subsection (c), including quality measures endorsed by the entity with a contract under section 1890 of the Social Security Act, as determined by the Secretary.
(g) Evaluation and Report.—The Secretary shall submit to the relevant committees of Congress a report which shall—
(1) assess the clinical effectiveness of pharmacist-provided services under the MTM services program, as compared to usual care, including an evaluation of whether enrollees maintained better health with fewer hospitalizations and emergency room visits than similar patients not enrolled in the program;
(2) assess changes in overall health care resource use by targeted individuals;
(3) assess patient and prescriber satisfaction with MTM services;
(4) assess the impact of patient-cost sharing requirements on medication adherence and recommendations for modifications;
(5) identify and evaluate other factors that may impact clinical and economic outcomes, including demographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, and health services use of the patient, as well as characteristics of the regimen, pharmacy benefit, and MTM services provided; and
(6) evaluate the extent to which participating pharmacists who maintain a dispensing role have a conflict of interest in the provision of MTM services, and if such conflict is found, provide recommendations on how such a conflict might be appropriately addressed.
(h) Grants or Contracts To Fund Development of Performance Measures.— The Secretary may, through the quality measure development program under section 931 of the Public Health Service Act, award grants or contracts to eligible entities for the purpose of funding the development of performance measures that assess the use and effectiveness of medication therapy management services.
Sec. 936. [42 USC 299b-36] PROGRAM TO FACILITATE SHARED DECISIONMAKING.
(a) Purpose.— The purpose of this section is to facilitate collaborative processes between patients, caregivers or authorized representatives, and clinicians that engages the patient, caregiver or authorized representative in decisionmaking, provides patients, caregivers or authorized representatives with information about trade-offs among treatment options, and facilitates the incorporation of patient preferences and values into the medical plan.
(b) Definitions.— In this section:
(1) Patient decision aid.— The term “patient decision aid” means an educational tool that helps patients, caregivers or authorized representatives understand and communicate their beliefs and preferences related to their treatment options, and to decide with their health care provider what treatments are best for them based on their treatment options, scientific evidence, circumstances, beliefs, and preferences.
(2) Preference sensitive care.— The term “preference sensitive care” means medical care for which the clinical evidence does not clearly support one treatment option such that the appropriate course of treatment depends on the values of the patient or the preferences of the patient, caregivers or authorized representatives regarding the benefits, harms and scientific evidence for each treatment option, the use of such care should depend on the informed patient choice among clinically appropriate treatment options.
(c) Establishment of Independent Standards for Patient Decision Aids for Preference Sensitive Care.—
(1) Contract with entity to establish standards and certify patient decision aids.—
(A) In general.— For purposes of supporting consensus-based standards for patient decision aids for preference sensitive care and a certification process for patient decision aids for use in the Federal health programs and by other interested parties, the Secretary shall have in effect a contract with the entity with a contract under section 1890 of the Social Security Act. Such contract shall provide that the entity perform the duties described in paragraph (2).
(B) Timing for first contract.— As soon as practicable after the date of the enactment of this section, the Secretary shall enter into the first contract under subparagraph (A).
(C) Period of contract.— A contract under subparagraph (A) shall be for a period of 18 months (except such contract may be renewed after a subsequent bidding process).
(2) Duties.— The following duties are described in this paragraph:
(A) Develop and identify standards for patient decision aids.— The entity shall synthesize evidence and convene a broad range of experts and key stakeholders to develop and identify consensus-based standards to evaluate patient decision aids for preference sensitive care.
(B) Endorse patient decision aids.— The entity shall review patient decision aids and develop a certification process whether patient decision aids meet the standards developed and identified under subparagraph (A). The entity shall give priority to the review and certification of patient decision aids for preference sensitive care.
(d) Program To Develop, Update and Patient Decision Aids To Assist Health Care Providers and Patients.—
(1) In general.— The Secretary, acting through the Director, and in coordination with heads of other relevant agencies, such as the Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Director of the National Institutes of Health, shall establish a program to award grants or contracts—
(A) to develop, update, and produce patient decision aids for preference sensitive care to assist health care providers in educating patients, caregivers, and authorized representatives concerning the relative safety, relative effectiveness (including possible health outcomes and impact on functional status), and relative cost of treatment or, where appropriate, palliative care options;
(B) to test such materials to ensure such materials are balanced and evidence based in aiding health care providers and patients, caregivers, and authorized representatives to make informed decisions about patient care and can be easily incorporated into a broad array of practice settings; and
(C) to educate providers on the use of such materials, including through academic curricula.
(2) Requirements for patient decision aids.— Patient decision aids developed and produced pursuant to a grant or contract under paragraph (1)—
(A) shall be designed to engage patients, caregivers, and authorized representatives in informed decisionmaking with health care providers;
(B) shall present up-to-date clinical evidence about the risks and benefits of treatment options in a form and manner that is age-appropriate and can be adapted for patients, caregivers, and authorized representatives from a variety of cultural and educational backgrounds to reflect the varying needs of consumers and diverse levels of health literacy;
(C) shall, where appropriate, explain why there is a lack of evidence to support one treatment option over another; and
(D) shall address health care decisions across the age span, including those affecting vulnerable populations including children.
(3) Distribution.—The Director shall ensure that patient decision aids produced with grants or contracts under this section are available to the public.
(4) Nonduplication of efforts.—The Director shall ensure that the activities under this section of the Agency and other agencies, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health, are free of unnecessary duplication of effort.
(e) Grants To Support Shared Decisionmaking Implementation.—
(1) In general.—The Secretary shall establish a program to provide for the phased-in development, implementation, and evaluation of shared decisionmaking using patient decision aids to meet the objective of improving the understanding of patients of their medical treatment options.
(2) Shared decisionmaking resource centers.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary shall provide grants for the establishment and support of Shared Decisionmaking Resource Centers (referred to in this subsection as “Centers”) to provide technical assistance to providers and to develop and disseminate best practices and other information to support and accelerate adoption, implementation, and effective use of patient decision aids and shared decisionmaking by providers.
(B) Objectives.—The objective of a Center is to enhance and promote the adoption of patient decision aids and shared decisionmaking through—
(i) providing assistance to eligible providers with the implementation and effective use of, and training on, patient decision aids; and
(ii) the dissemination of best practices and research on the implementation and effective use of patient decision aids.
(3) Shared decisionmaking participation grants.—
(A) In general.—The Secretary shall provide grants to health care providers for the development and implementation of shared decisionmaking techniques and to assess the use of such techniques.
(B) Preference.—In order to facilitate the use of best practices, the Secretary shall provide a preference in making grants under this subsection to health care providers who participate in training by Shared Decisionmaking Resource Centers or comparable training.
(C) Limitation.—Funds under this paragraph shall not be used to purchase or implement use of patient decision aids other than those certified under the process identified in subsection (c).
(4) Guidance.—The Secretary may issue guidance to eligible grantees under this subsection on the use of patient decision aids.
(f) Funding.—For purposes of carrying out this section there are authorized to be appropriated such sums as may be necessary for fiscal year 2010 and each subsequent fiscal year.
DISSEMINATION AND BUILDING CAPACITY FOR RESEARCH
Sec. 937. [42 U.S.C. 299b-37] (a) In General.—
(1) Dissemination.—The Office of Communication and Knowledge Transfer (referred to in this section as the “Office”) at the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (or any other relevant office designated by Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality), in consultation with the National Institutes of Health, shall broadly disseminate the research findings that are published by the Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute established under section 1181(b) of the Social Security Act (referred to in this section as the “Institute”) and other government-funded research relevant to comparative clinical effectiveness research. The Office shall create informational tools that organize and disseminate research findings for physicians, health care providers, patients, payers, and policy makers. The Office shall also develop a publicly available resource database that collects and contains government-funded evidence and research from public, private, not-for profit, and academic sources.
(2) Requirements.—The Office shall provide for the dissemination of the Institute’s research findings and government-funded research relevant to comparative clinical effectiveness research to physicians, health care providers, patients, vendors of health information technology focused on clinical decision support, appropriate professional associations, and Federal and private health plans. Materials, forums, and media used to disseminate the findings, informational tools, and resource databases shall—
(A) include a description of considerations for specific subpopulations, the research methodology, and the limitations of the research, and the names of the entities, agencies, instrumentalities, and individuals who conducted any research which was published by the Institute; and
(B) not be construed as mandates, guidelines, or recommendations for payment, coverage, or treatment.
(b) Incorporation of Research Findings.—The Office, in consultation with relevant medical and clinical associations, shall assist users of health information technology focused on clinical decision support to promote the timely incorporation of research findings disseminated under subsection (a) into clinical practices and to promote the ease of use of such incorporation.
(c) Feedback.—The Office shall establish a process to receive feedback from physicians, health care providers, patients, and vendors of health information technology focused on clinical decision support, appropriate professional associations, and Federal and private health plans about the value of the information disseminated and the assistance provided under this section.
(d) Rule of Construction.—Nothing in this section shall preclude the Institute from making its research findings publicly available as required under section 1181(d)(8) of the Social Security Act.
(e) Training of Researchers.—The Agency for Health Care Research and Quality, in consultation with the National Institutes of Health, shall build capacity for comparative clinical effectiveness research by establishing a grant program that provides for the training of researchers in the methods used to conduct such research, including systematic reviews of existing research and primary research such as clinical trials. At a minimum, such training shall be in methods that meet the methodological standards adopted under section 1181(d)(9) of the Social Security Act.
(f) Building Data for Research.—The Secretary shall provide for the coordination of relevant Federal health programs to build data capacity for comparative clinical effectiveness research, including the development and use of clinical registries and health outcomes research data networks, in order to develop and maintain a comprehensive, interoperable data network to collect, link, and analyze data on outcomes and effectiveness from multiple sources, including electronic health records.
(g) Authority To Contract With the Institute.—Agencies and instrumentalities of the Federal Government may enter into agreements with the Institute, and accept and retain funds, for the conduct and support of research described in this part, provided that the research to be conducted or supported under such agreements is authorized under the governing statutes of such agencies and instrumentalities.
* * * * * * *
Sec. 1301. [42 U.S.C. 300e]
(a) For purposes of this title, the term “health maintenance organization” means a public or private entity which is organized under the laws of any State and which (1) provides basic and supplemental health services to its members in the manner prescribed by subsection (b), and (2) is organized and operated in the manner prescribed by subsection (c).
* * * * * * *
(c) Each health maintenance organization shall—
* * * * * * *
(3)(A) enroll persons who are broadly representative of the various age, social, and income groups within the area it serves, except that in the case of a health maintenance organization which has a medically underserved population located (in whole or in part) in the area it serves, not more than 75 per centum of the members of that organization may be enrolled from the medically underserved population unless the area in which such population resides is also a rural area (as designated by the Secretary), and (B) carry out enrollment of members who are entitled to medical assistance under a State plan approved under title XIX of the Social Security Act in accordance with procedures approved under regulations promulgated by the Secretary;
* * * * * * *
(8) provide, in accordance with regulations of the Secretary (including safeguards concerning the confidentiality of the doctor-patient relationship), an effective procedure for developing, compiling, evaluating, and reporting to the Secretary, statistics and other information (which the Secretary shall publish and disseminate on an annual basis and which the health maintenance organization shall disclose, in a manner acceptable to the Secretary, to its members and the general public) relating to (A) the cost of its operations, (B) the patterns of utilization of its services, (C) the availability, accessibility, and acceptability of its services, (D) to the extent practical, developments in the health status of its members, and (E) such other matters as the Secretary may require.
* * * * * * *
DEFINITIONS
Sec. 1302. [42 U.S.C. 300e-1] For purposes of this title:
* * * * * * *
(7) The term “medically underserved population” means the population of an urban or rural area designated by the Secretary as an area with a shortage of personal health services or a population group designated by the Secretary as having a shortage of such services. Such a designation may be made by the Secretary only after consideration of the comments (if any) of (A) each State health planning and development agency which covers (in whole or in part) such urban or rural area or the area in which such population group resides, and (B) each health systems agency designated for a health service area which covers (in whole or in part) such urban or rural area or the area in which such population group resides.
(8)(A) The term “community rating system” means the systems, described in subparagraphs (B) and (C), of fixing rates of payments for health services. A health maintenance organization may fix its rates of payments under the system described in subparagraph (B) or (C) or under both such systems, but a health maintenance organization may use only one such system for fixing its rates of payments for any one group.
(B) A system of fixing rates of payment for health services may provide that the rates shall be fixed on a per-person or per-family basis and may authorize the rates to vary with the number of persons in a family, but, except as authorized in subparagraph (D), such rates must be equivalent for all individuals and for all families of similar composition.
(C) A system of fixing rates of payment for health services may provide that the rates shall be fixed for individuals and families by groups. Except as authorized in subparagraph (D), such rates must be equivalent for all individuals in the same group and for all families of similar composition in the same group. If a health maintenance organization is to fix rates of payment for individuals and families by groups, it shall—
(i)(I) classify all of the members of the organization into classes based on factors which the health maintenance organization determines predict the differences in the use of health services by the individuals or families in each class and which have not been disapproved by the Secretary,
(II) determine its revenue requirements for providing services to the members of each class established under subclause (I), and
(III) fix the rates of payments for the individuals and families of a group on the basis of a composite of the organization’s revenue requirements determined under subclause (II) for providing services to them as members of the classes established under subclause (I), or
(ii) fix the rates of payments for the individuals and families of a group on the basis of the organization’s revenue requirements for providing services to the group, except that the rates of payments for the individuals and families of a group of less than 100 persons may not be fixed at rates greater than 110 percent of the rate that would be fixed for such individuals and families under subparagraph (B) or clause (i) of this subparagraph.
The Secretary shall review the factors used by each health maintenance organization to establish classes under clause (i). If the Secretary determines that any such factor may not reasonably be used to predict the use of the health services by individuals and families, the Secretary shall disapprove such factor for such purpose.
(D) The following differentials in rates of payments may be established under the systems described in subparagraphs (B) and (C):
(i) Nominal differentials in such rates may be established to reflect differences in marketing costs and the different administrative costs of collecting payments from the following categories of members:
(I) Individual members (including their families).
(II) Small groups of members (as determined under regulations of the Secretary).
(III) Large groups of members (as determined under regulations of the Secretary).
(ii) Nominal differentials in such rates may be established to reflect the compositing of the rates of payment in a systematic manner to accommodate group purchasing practices of the various employers.
(iii) Differentials in such rates may be established for members enrolled in a health maintenance organization pursuant to a contract with a governmental authority under section 1079 or 1086 of title 10, United States Code[248], or under any other governmental program (other than the health benefits program authorized by chapter 89 of title 5, United States Code) or any health benefits program for employees of States, political subdivision of States, and other public entities.
* * * * * * *
EMPLOYEES’ HEALTH BENEFITS PLANS
Sec. 1310. [42 U.S.C. 300e-9]
* * * * * * *
(c) For purposes of this section, the term “qualified health maintenance organization” means (1) a health maintenance organization which has provided assurances satisfactory to the Secretary that it provides basic and supplemental health services to its members in the manner prescribed by section 1301(b) and that it is organized and operated in the manner prescribed by section 1301(c), and (2) an entity which proposes to becomes a health maintenance organization and which the Secretary determines will when it becomes operational provide basic and supplemental health services to its members in the manner prescribed by section 1301(b) and will be organized and operated in the manner prescribed by section 1301(c).
* * * * * * *
CONTINUED REGULATION OF HEALTH MAINTENANCE ORGANIZATIONS
Sec. 1312. [42 U.S.C. 300e-11]
(a) If the Secretary determines that an entity which received a grant, contract, loan, or loan guarantee under this title as a health maintenance organization or which was included in a health benefits plan offered to employees pursuant to section 1310—
(1) fails to provide basic and supplemental services to its members,
(2) fails to provide such services in the manner prescribed by section 1301(b), or
(3) is not organized or operated in the manner prescribed by section 1301(c),
the Secretary may take the action authorized by subsection (b).
(b)(1) If the Secretary makes, with respect to any entity which provided assurances to the Secretary under section 1310(d)(1), a determination described in subsection (a), the Secretary shall notify the entity in writing of the determination. Such notice shall specify the manner in which the entity has not complied with such assurances and direct that the entity initiate (within 30 days of the date the notice is issued by the Secretary or within such longer period as the Secretary determines is reasonable) such action as may be necessary to bring (within such period as the Secretary shall prescribe) the entity into compliance with the assurances. If the entity fails to initiate corrective action within the period prescribed by the notice or fails to comply with the assurances within such period as the Secretary prescribes, then after the Secretary provides the entity a reasonable opportunity for reconsideration of his determination, including, at the entity’s election, a fair hearing (A) the entity shall not be a qualified health maintenance organization for purposes of section 1310 until such date as the Secretary determines that it is in compliance with the assurances, and (B) each employer which has offered membership in the entity in compliance with section 1310, each lawfully recognized collective bargaining representative or other employee representative which represents the employees of each such employer, and the members of such entity shall be notified by the entity that the entity is not a qualified health maintenance organization for purposes of such section. The notice required by clause (B) of the preceding sentence shall contain, in readily understandable language, the reasons for the determination that the entity is not a qualified health maintenance organization. The Secretary shall publish in the Federal Register each determination referred to in this paragraph.
(2) If the Secretary makes, with respect to an entity which has received a grant, contract, loan, or loan guarantee under this title, a determination described in subsection (a), the Secretary may, in addition to any other remedies available to him, bring a civil action in the United States district court for the district in which such entity is located to enforce its compliance with the assurances it furnished respecting the provision of basic and supplemental health services or its organization or operation, as the case may be, which assurances were made in connection with its application under this title for the grant, contract, loan, or loan guarantee.
* * * * * * *
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
Sec. 1318. [42 U.S.C. 300e-17]
(a) Each health maintenance organization shall, in accordance with regulations of the Secretary, report to the Secretary financial information which shall include the following:
(1) Such information as the Secretary may require demonstrating that the health maintenance organization has a fiscally sound operation.
(2) A copy of the report, if any, filed with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services containing the information required to be reported under section 1124 of the Social Security Act by disclosing entities and the information required to be supplied under section 1902(a)(38) of such Act.
(3) A description of transactions, as specified by the Secretary, between the health maintenance organization and a party in interest. Such transactions shall include—
(A) any sale or exchange, or leasing of any property between the health maintenance organization and a party in interest;
(B) any furnishing for consideration of goods, services (including management services), or facilities between the health maintenance organization and a party in interest, but not including salaries paid to employees for services provided in the normal course of their employment and health services provided to members by hospitals and other providers and by staff, medical group (or groups), individual practice association (or associations), or any combination thereof; and
(C) any lending of money or other extension of credit between a health maintenance organization and a party in interest.
The Secretary may require that information reported respecting a health maintenance organization which controls, is controlled by, or is under common control with, another entity be in the form of a consolidated financial statement for the organization and such entity.
(b) For the purposes of this section the term “party in interest” means:
(1) any director, officer, partner, or employee responsible for management or administration of a health maintenance organization, any person who is directly or indirectly the beneficial owner of more than 5 per centum of the equity of the organization, any person who is the beneficial owner of a mortgage, deed of trust, note, or other interest secured by, and valuing more than 5 per centum of the health maintenance organization, and, in the case of a health maintenance organization organized as a nonprofit corporation, an incorporator or member of such corporation under applicable State corporation law;
(2) any entity in which a person described in paragraph (1)—
(A) is an officer or director;
(B) is a partner (if such entity is organized as a partnership);
(C) has directly or indirectly a beneficial interest of more than 5 per centum of the equity; or
(D) has a mortgage, deed of trust, note, on[249] other interest valuing more than 5 per centum of the assets of such entity;
(3) any person directly or indirectly controlling, controlled by, or under common control with a health maintenance organization; and
(4) any spouse, child, or parent of an individual described in paragraph (1).
(c) Each health maintenance organization shall make the information reported pursuant to subsection (a) available to its enrollees upon reasonable request.
* * * * * * *
Sec. 2791. [42 U.S.C. 300gg-91(a)(1)]
(a) Group health plan.—
(1) Definition.—The term “group health plan” means an employee welfare benefit plan (as defined in section 3(1) of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 [29 U.S.C. 1002(1)]) to the extent that the plan provides medical care (as defined in paragraph (2)) and including items and services paid for as medical care) to employees or their dependents (as defined under the terms of the plan) directly or through insurance, reimbursement, or otherwise.
(2) Medical care.—The term “medical” means amounts paid for—
(A) the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease, or amounts paid for the purpose of affecting any structure or function of the body,
(B) amounts paid for transportation primarily for and essential to medical care referred to in subparagraph (A), and
(C) amounts paid for insurance covering medical care referred to in subparagraphs (A) and (B).
* * * * * * *
(b) Definitions relating to health insurance.—
* * * * * * *
(3) Health maintenance organization.—The term “health maintenance organization”—
(A) a Federally qualified health maintenance organization (as defined in section 300e(a) of this title),
(B) an organization recognized under State law as a health maintenance organization, or
(C) a similar organization regulated under State law for solvency in the same manner and to the same extent as such a health maintenance organization.
* * * * * * *
(d) Definitions relating to health insurance.—
* * * * * * *
(15) Family member.—The term “family member” means, with respect to any individual—
(A) a dependent (as such term is used for purposes of section 2701(f)(2)) of such individual; and
(B) any other individual who is a first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, or fourth-degree relative of such individual or of an individual described in subparagraph (A).
(16) Genetic information.—
(A) In general.—The term “genetic information” means, with respect to any individual, information about—
(i) such individual’s genetic tests,
(ii) the genetic tests of family members of such individual, and
(iii) the manifestation of a disease or disorder in family members of such individual.
(B) Inclusion of genetic services and participation in genetic research.—Such term includes, with respect to any individual, any request for, or receipt of, genetic services, or participation in clinical research which includes genetic services, by such individual or any family member of such individual.
(C) Exclusions.—The term “genetic information” shall not include information about the sex or age of any individual.
(17) Genetic test.—
(A) In general.—The term “genetic test” means an analysis of human DNA, RNA, chromosomes, proteins, or metabolites, that detects genotypes, mutations, or chromosomal changes.
(B) Exceptions.—The term “genetic test” does not mean—
(i) an analysis of proteins or metabolites that does not detect genotypes, mutations, or chromosomal changes; or
(ii) an analysis of proteins or metabolites that is directly related to a manifested disease, disorder, or pathological condition that could reasonably be detected by a health care professional with appropriate training and expertise in the field of medicine involved.
(18) Genetic services.—The term “genetic services” means—
(A) a genetic test;
(B) genetic counseling (including obtaining, interpreting, or assessing genetic information; or
(C) genetic education.
(19) Underwriting purposes.—The term “underwriting purposes” means, with respect to any group health plan, or health insurance coverage offered in connection with a group health plan—
(A) rules for, or determination of, eligibility (including enrollment and continued eligibility) for benefits under the plan or coverage;
(B) the computation of premium or contribution amounts under the plan or coverage;
(C) the application of any pre-existing condition exclusion under the plan or coverage; and
(D) other activities related to the creation, renewal, or replacement of a contract of health insurance or health benefits.
* * * * * * *
[Internal References.—SSAct §§501(b), 512(c), 1101(a), 1115A(b)(2)(B), 1121(a) and (c), 1122(b) and (d), 1124(a), 1128B(b), 1138(a) and (b), 1142(a) and (b), 1171, 1180(b), 1181(d) and (g), 1833(m), 1861(s), (v), and (aa), 1874(e) 1876(b), (e), and (i), 1890(b)(5)(A)(iv) and(v) and (b)(7)(A)(ii), 1890A(b)(1)(B), 1892(a) and (b), 1903(g) and (m), 1905(l), 1927(a) and (b), 1928(d), 1937(b)(1)(C)(i) and 2103(b) cite the Public Health Service Act. SSAct Titles V, XVIII, XIX XXI and §1124 headings and §1902(a) have footnotes referring to P.L. 78-410.]
[235] Sec. 208(a)(3) of P.L. 91-648 (42 U.S.C. 4728) transferred to the U.S. Civil Service Commission all functions, powers, and duties of the Secretary under any law applicable to a grant program which requires the establishment and maintenance of personnel standards on a merit basis with respect to the program.
[236] P. L. 93-344, title V, as added by P. L. 101-508, title XIII, §13201(a), Nov. 5, 1990, 104 Stat. 1388-609.
[237] P. L. 93-344, title V, as added by P. L. 101-508, title XIII, §13201(a), Nov. 5, 1990, 104 Stat. 1388-609.
[238] P. L. 93-368.
[239] See P. L. 94-437, Title V (this Volume).
[240] As in original. Probably should be “an”.
[241] January 4, 1983 [P.L. 97-414; 96 Stat. 2049].
[242] As in original; should be “proficiency”.
[243] Probably should be “it to”.
[244] As in original; no closing punctuation.
[245] As in original. The semicolon probably should be a comma.
[246] Sec. 208(a)(3) of P.L. 91-648 (42 U.S.C. 4728) transferred to the U.S. Civil Service Commission all functions, powers, and duties of the Secretary under any law applicable to a grant program which requires the establishment and maintenance of personnel standards on a merit basis with respect to the program.
[247] As in original. Possibly should be “effective”.
[248] See 10 U.S.C.1079 and 1086 (this Volume).
[249] As in original. Possibly should be “or”.